Prompt Engineering
Prompt design is the process of creating a prompt that is tailored to the specific task that the system is being asked to perform.
Prompt engineering is the process of creating a prompt that is designed to improve performance.
Types of Prompt
User Prompts, which are conversational prompts that a user asks, and
System Prompts, which are at the backend and guide the LLM model to provide the desired output.
Prompting Principles
Principle 1: Write clear and specific instructions
Tactic 1: Use delimiters to clearly indicate distinct parts of the input
- Delimiters can be anything like: ,
""",< >,<tag> </tag>,:
Tactic 2: Ask for a structured output
- JSON, HTML
Tactic 3: Ask the model to check whether conditions are satisfied
Tactic 4: "Few-shot" prompting
Example
🔴 The Lazy Prompt (Bad): "Give me a workout."
Result: The AI will give you a generic list. It might be for bodybuilders, or it might need a gym. It's like asking for "Food" at the restaurant.
🟢 The Effective Prompt (Good): "I am a beginner with no equipment (Context). Create a 15-minute home workout plan to improve flexibility (Specificity). Please present it as a simple bulleted list (Format)."
Result: You get exactly what you need: a short, easy plan you can do in your living room right now.
Principle 2: Give the model time to "think"
Tactic 1: Specify the steps required to complete a task
Tactic 2: Instruct the model to work out its own solution before rushing to a conclusion
Others
- Imitating - In the style of x write about y
- At the end of prompts add - make it catchy!
Prompting Techniques
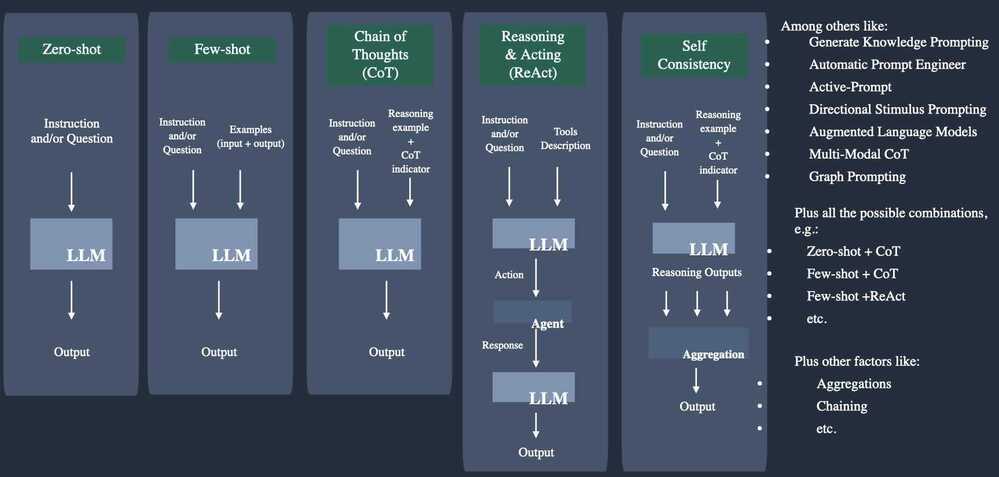
Chain-of-thought
Chain-of-thought (CoT) prompting is a technique that allows large language models (LLMs) to solve a problem as a series of intermediate steps before giving a final answer. Chain-of-thought prompting improves reasoning ability by inducing the model to answer a multi-step problem with steps of reasoning that mimic a train of thought. It allows large language models to overcome difficulties with some reasoning tasks that require logical thinking and multiple steps to solve, such as arithmetic or commonsense reasoning questions.
Least to most prompting
Least-to-most prompting is a prompt engineering technique where complex problems are broken down into smaller, simpler subproblems, and then solved sequentially. This approach is particularly effective in tasks involving symbolic manipulation, compositional generalization, and mathematical reasoning, often exceeding the performance of Chain-of-Thought prompting on more difficult problems.
Here's a breakdown of how it works:
- Problem Decomposition: The initial prompt guides the Large Language Model (LLM) to decompose a complex problem into a series of simpler subproblems.
- Sequential Solving: The LLM then solves each subproblem sequentially, utilizing the solutions to previous subproblems to guide the next step.
- Enhanced Reasoning: By breaking down complex tasks into simpler components, least-to-most prompting allows LLMs to leverage their reasoning capabilities more effectively, leading to improved performance, especially on challenging problems.
Few-Shot Prompting
Teaching the AI your personal writing style by giving it examples to mimic.
The R.C.C.F. Framework
- Role: Giving the AI a specific persona
- Context: Giving the AI background info so it doesn't hallucinate or guess.
- Constraints: Telling the AI what not to do (e.g., "No jargon," "Under 200 words").
- Format: forcing the AI to output exactly how you need it (Table, JSON, CSV, Email draft).
Advanced workflows
1. Prompt Chaining (The "Decomposition" Strategy)
The Concept: The longer the prompt, the "dumber" the model gets because its attention is split. We fix this by breaking one massive request into 3-4 distinct, sequential interactions.
The Skill: You will learn to output the results of Step 1 (e.g., "Extract Facts") and feed them explicitly into Step 2 (e.g., "Draft Strategy based only on those facts"). This dramatically reduces hallucinations.
2. Data Handling with Delimiters (The "Fencing" Technique)
The Concept: When you paste a large email or report into the chat, the AI struggles to separate your instructions from the content it needs to analyze.
The Skill: You will learn to use syntax like triple quotes (""") or hashes (###) to "fence off" your data.
- Example: "Summarize the text found inside the
"""delimiters."
3. The Self-Correction Loop (The "Reviewer" Step)
The Concept: AI models generate text probabilistically; they don't "think" before they speak. However, they are excellent editors of their own work if prompted correctly.
The Skill: You will learn to insert a verification step before finalizing a document.
- Example: "Review your previous answer. Identify any logic gaps or missing data points. Output a corrected version."
4. Dynamic Role Switching (The "Multi-Persona" Workflow)
The Concept: A single chat session can host multiple "experts."
The Skill: You will learn to switch the AI's role mid-conversation to improve the output.
- Workflow: First, ask it to act as a Creative Writer to brainstorm. Then, ask it to act as a Risk Analyst to tear those ideas apart. Finally, ask it to act as a Project Manager to synthesize the remaining ideas.
5. Structured Output (The "Format" Requirement)
The Concept: Text is hard to process. Tables, Markdown, and CSVs are actionable.
The Skill: You will learn to force the AI to output data in specific formats that can be copied directly into Excel, Notion, or code editors, bypassing the need for manual formatting.
Mechanics and Reliability
1. HOW THE ENGINE WORKS: "Prediction, Not Knowledge"
- The Concept: AI is not a database of facts (like Google). It is a Probabilistic Prediction Engine.
- The Analogy: Think of it as "Autocomplete on Steroids." It looks at the words you wrote and predicts the most likely next word based on patterns it learned during training.
- The Consequence: The AI prioritizes Fluency (sounding smooth and human) over Factuality (being correct). It wants to make you happy with a good-sounding answer, even if the facts are wrong.
2. THE GLITCH: "Hallucinations"
- The Definition: When the AI confidently states something that is factually incorrect or completely made up.
- Common Examples: Inventing a URL (link) that leads nowhere, citing a court case that doesn't exist, or getting a math problem wrong.
- Why it Happens: The AI is like an Improv Actor. Its rule is "Yes, and..." It tries to fill in the blank. If you ask for a link, and it doesn't know one, it predicts what a link should look like (e.g.,
www.nytimes.com/fake-article-name) rather than saying "I don't know."
3. THE LIMITATION: "The Context Window" (Memory)
- The Concept: The AI has a limited amount of short-term memory called the "Context Window."
- The Analogy: The Whiteboard.
- Imagine a small whiteboard.
- As you chat, we write on the board.
- Eventually, the board fills up.
- To write new answers at the bottom, the AI must erase the notes at the top.
- The Result: In a very long conversation, the AI will "forget" the instructions or persona you gave it at the very beginning.
4. THE FIX: "Grounding" (Stopping the Lies)
- The Definition: Forcing the AI to stop guessing and answer using only specific data you provide.
- How to do it:
- Copy the text you want it to use (an article, a report, an email).
- Paste it into the chat.
- Add this command: "Answer the question using ONLY the text provided above. Do not use outside knowledge."
- Why it works: You are turning the AI from a "Creative Writer" (who guesses) into a "Data Processor" (who analyzes).
5. THE MAINTENANCE: "Resetting the Memory"
- The Problem: The "Whiteboard" is getting full, and the AI is losing track of the goal.
- The Fix: Ask the AI to summarize itself.
- The Prompt: "Summarize our progress, rules, and goals so far in this chat."
- Why it works: It takes the scattered info from the "erased" top of the board and writes a fresh, concise note at the bottom of the board (in the active memory).
6. THE SAFETY CHECK: "Citations"
- The Rule: Trust, but Verify.
- The Technique: Never accept a summary of a document blindly.
- The Prompt: "Summarize this text and include direct quotes or citations to show where you found the information."
- Why it works: If the AI has to point to the specific sentence where it found the answer, it is much less likely to hallucinate.
Other techniques
- Generated knowledge prompting
- Least-to-most prompting
- Self-consistency decoding
- Complexity-based prompting
- Self-refine
- Tree-of-thought
- Maieutic prompting
- Directional-stimulus prompting
Prompt engineering - Wikipedia
Parameters
Temperature
Controls the randomness of the model's output. A higher temperature makes the output more random, while a lower temperature makes it more deterministic.
Understanding OpenAI's Temperature Parameter | Colt Steele
Temperature (0.0 to 2.0): Think of this like creativity settings.
- Temperature 0.1 = very focused and predictable (good for factual answers),
- Temperature 0.9 = more creative and random (good for brainstorming).
Top P (0.0 to 1.0): Controls word choice diversity.
- Lower = sticks to most likely words,
- Higher = considers more unusual word options.
Top K (number): Limits how many word options the AI considers at each step.
| Parameter | Range | Description | Example (Weather) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 0.0 to 2.0 (preferable -0.7) | Controls randomness and creativity | Low (0.1): "Today's weather is very hot with clear skies and high humidity. The temperature is expected to reach 95°F with a UV index of 8. There is a 10% chance of precipitation." High (0.9): "The scorching sun beats down mercilessly today, turning the sidewalks into sizzling griddles that could fry an egg! The sky, a brilliant azure canvas without a single cloud brushstroke, offers no respite from the relentless heat wave that has the whole city moving in slow motion." |
| Top P | 0.0 to 1.0 | Controls diversity by including less common words until reaching a probability threshold | Low (0.3): "Today's weather is very hot and sunny. The temperature will reach 95 degrees with no clouds in sight." High (0.9): "Today's weather is very sweltering with a blinding sun and stifling humidity making the afternoon particularly oppressive for outdoor activities." |
| Top K | number (1- 100) | Directly limits the number of word options considered regardless of probability | For "The weather today is very..." Top K = 2: Can only choose between "hot" (40%) and "cold" (30%), making output more predictable Top K = 5: Can choose from "hot" (40%), "cold" (30%), "nice" (15%), "humid" (10%), or "pleasant" (5%), giving more variety |
The key differences:
- Temperature affects overall randomness and creativity across all word choices
- Top P controls diversity by including less common words until reaching a probability threshold
- Top K directly limits the number of word options considered regardless of probability
These parameters can be combined - for instance, using a moderate Temperature (0.7) with a low Top K (5) would give creative but controlled outputs that don't go too far off track.
Other Topics
- Iterative
- Summarizing
- Inferring
- Transforming
- Expanding
- Chatbot
- Conclusion
ChatGPT Prompt Engineering for Developers - DeepLearning.AI
Summarization
{
"anthropic_version": "bedrock-2023-05-31",
"messages": [
{
"role" : "user",
"content" : "You will be given a conversation between a user and an AI assistant.
When available, in order to have more context, you will also be give summaries you previously generated.
Your goal is to summarize the input conversation.
When you generate summaries you ALWAYS follow the below guidelines:
<guidelines>
- Each summary MUST be formatted in XML format.
- Each summary must contain at least the following topics: 'user goals', 'assistant actions'.
- Each summary, whenever applicable, MUST cover every topic and be place between <topic name='$TOPIC_NAME'></topic>.
- You AlWAYS output all applicable topics within <summary></summary>
- If nothing about a topic is mentioned, DO NOT produce a summary for that topic.
- You summarize in <topic name='user goals'></topic> ONLY what is related to User, e.g., user goals.
- You summarize in <topic name='assistant actions'></topic> ONLY what is related to Assistant, e.g., assistant actions.
- NEVER start with phrases like 'Here's the summary...', provide directly the summary in the format described below.
</guidelines>
The XML format of each summary is as it follows:
<summary>
<topic name='$TOPIC_NAME'>
...
</topic>
...
</summary>
Here is the list of summaries you previously generated.
<previous_summaries>
$past_conversation_summary$
</previous_summaries>
And here is the current conversation session between a user and an AI assistant:
<conversation>
$conversation$
</conversation>
Please summarize the input conversation following above guidelines plus below additional guidelines:
<additional_guidelines>
- ALWAYS strictly follow above XML schema and ALWAYS generate well-formatted XML.
- NEVER forget any detail from the input conversation.
- You also ALWAYS follow below special guidelines for some of the topics.
<special_guidelines>
<user_goals>
- You ALWAYS report in <topic name='user goals'></topic> all details the user provided in formulating their request.
</user_goals>
<assistant_actions>
- You ALWAYS report in <topic name='assistant actions'></topic> all details about action taken by the assistant, e.g., parameters used to invoke actions.
</assistant_actions>
</special_guidelines>
</additional_guidelines>
"
}
]
}
Assistant APIs
The Assistants API allows you to build AI assistants within your own applications. An Assistant has instructions and can leverage models, tools, and knowledge to respond to user queries. The Assistants API currently supports three types of tools: Code Interpreter, Retrieval, and Function calling.
At a high level, a typical integration of the Assistants API has the following flow:
- Create an Assistant in the API by defining its custom instructions and picking a model. If helpful, enable tools like Code Interpreter, Retrieval, and Function calling.
- Create a Thread when a user starts a conversation.
- Add Messages to the Thread as the user ask questions.
- Run the Assistant on the Thread to trigger responses. This automatically calls the relevant tools.
Create AI Assistants with OpenAI's Assistants API
Knowledge based retrieval tool -
platform.openai.com/docs/assistants/overview
Learning
- Large Language Models and Cybersecurity - What You Should Know
- Understanding Large Language Models - by Sebastian Raschka
- The Art of Prompt Design: Use Clear Syntax | by Scott Lundberg | May, 2023 | Towards Data Science
- Prompt Engineering - Google Slides
- Prompt Engineering Tutorial - Master ChatGPT and LLM Responses - YouTube
- Advanced Prompt Engineering for Content Creators - Full Handbook
- Prompt Engineering with Llama 2 - DeepLearning.AI
- GitHub - dair-ai/Prompt-Engineering-Guide: 🐙 Guides, papers, lecture, notebooks and resources for prompt engineering