Comparison
Architectural Considerations
Why Confluent over AWS MSK?
AWS MSK is essentially Kafka as a managed cluster, but it stops at basic operations. Confluent provides a full data streaming platform on top of Kafka. For example:
- Built-in stream governance with Schema Registry, lineage, and access controls.
- 120+ fully managed connectors for databases and SaaS apps, so customers don’t need to build integrations from scratch.
- ksqlDB for real-time stream processing without needing a separate engine like Flink or Spark.
- Tiered storage and cluster linking for infinite retention and multi-cloud replication, which MSK doesn’t offer natively.
The difference is that MSK is infrastructure, whereas Confluent is an enterprise platform for data in motion. That’s why enterprises that care about scale, governance, and multi-cloud strategies choose Confluent.
A Complete Comparison of Apache Kafka vs Confluent
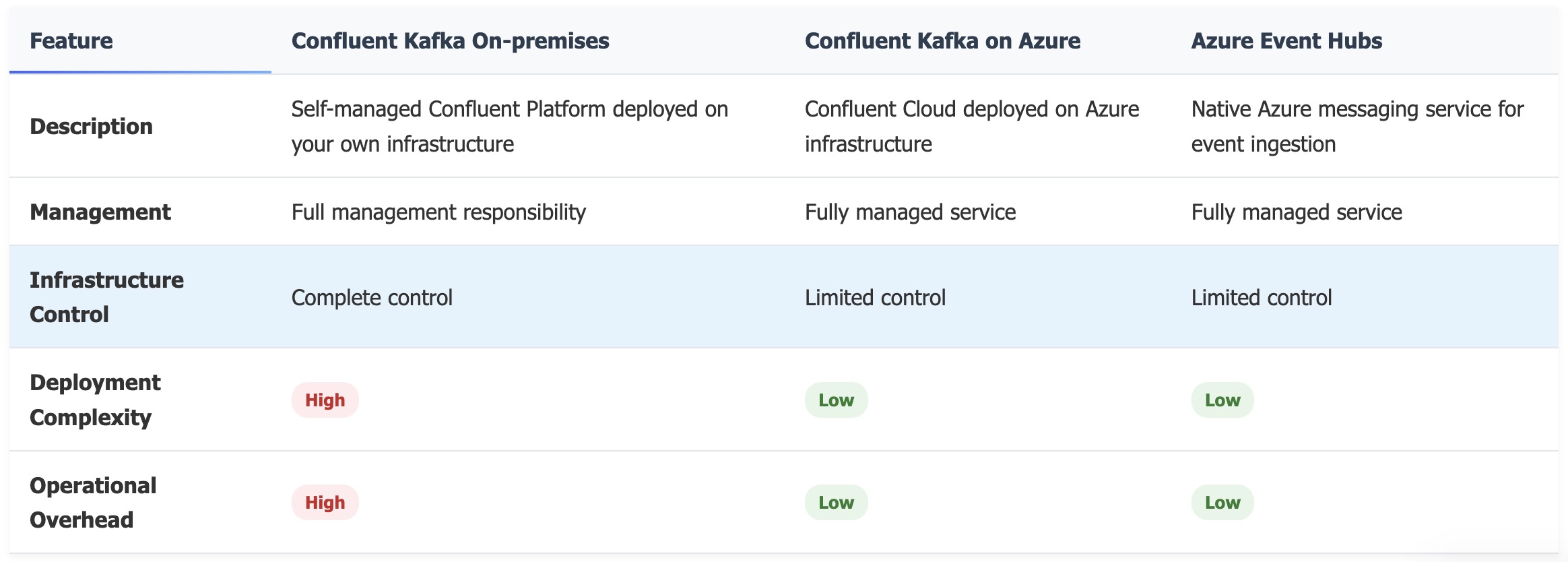
Confluent Kafka On-premises
- Complete control over hardware, network, and security configurations
- Requires dedicated infrastructure team for maintenance
- Supports multi-datacenter deployments
- Fully customizable retention and scaling policies
- Can be deployed in air-gapped environments
- Requires manual updates and maintenance windows
Confluent Kafka on Azure
- Managed by Confluent while running on Azure infrastructure
- Seamless integration with other Azure services
- Private link support for secure connectivity
- Auto-scaling and self-balancing clusters
- 99.95% uptime SLA
- Automatic updates and maintenance handled by Confluent
Azure Event Hubs
- Native Azure PaaS solution
- Supports Azure Private Link
- Auto-inflate for automatic scaling
- 99.95% availability SLA for standard tier, 99.99% for premium
- Native integration with Azure Monitor and Log Analytics
Comparison Overview
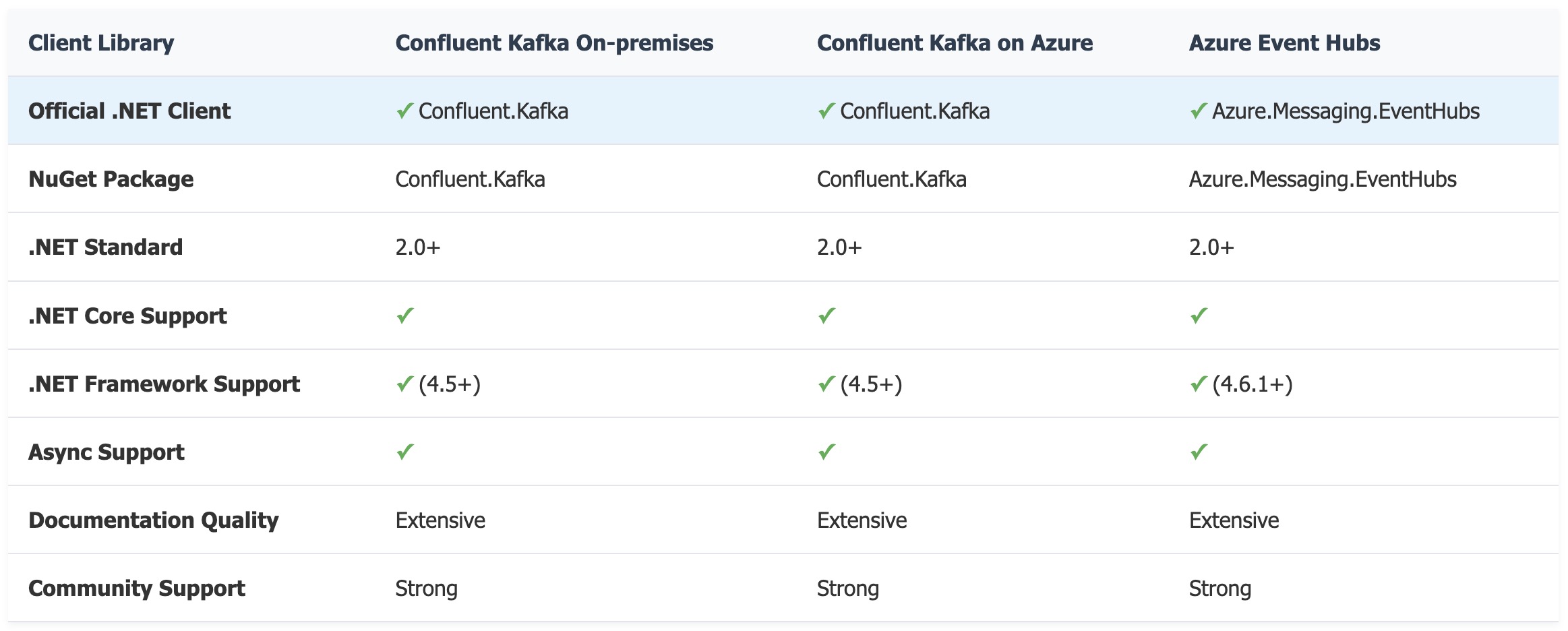
ASP.NET Client Library Support
Pricing Comparison (as of February 2025)
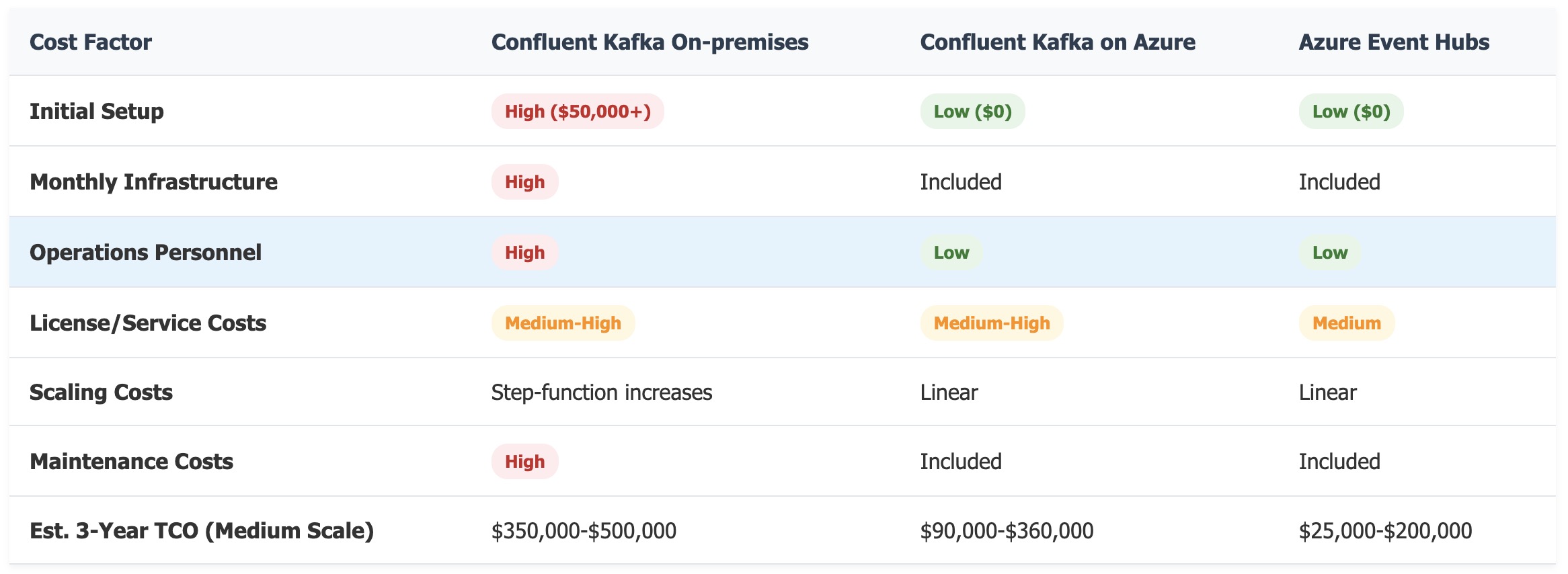
Confluent Kafka On-premises
- License: Per broker, starting at ~$10,000-$15,000 per broker per year for Confluent Enterprise
- Infrastructure: Hardware costs, data center costs, network costs
- Operations: Personnel costs for management and maintenance
- Total Cost Estimate: $100,000+ per year depending on scale (3+ broker cluster with support)
Confluent Kafka on Azure
- Basic: $0.09/hour per CKU (Confluent Kafka Unit)
- Each CKU provides 250 MBps throughput
- 100 GB storage included per CKU
- Standard: $0.12/hour per CKU
- Adds enhanced networking and higher SLAs
- Dedicated: Starting at $15,000/month
- Custom sizing based on requirements
- Additional Storage: $0.10/GB/month
- Connect/ksqlDB: $0.39/CCU/hour (Confluent Compute Unit)
- Schema Registry: $0.08/SR/hour (Schema Registry unit)
- Estimated Monthly Cost: $2,500-$10,000 depending on scale and features
Azure Event Hubs
- Basic Tier: $0.015 per million operations
- Limited features, no publisher policies
- Standard Tier: $0.03 per throughput unit (TU) per hour
- 1 TU = 1 MB/s ingress, 2 MB/s egress
- Retention: $0.03/GB/day beyond 84GB included
- Premium Tier: Starting at $0.13 per processing unit (PU) per hour
- 1 PU = 1 MB/s ingress, 2 MB/s egress
- Dedicated resources
- Includes extended retention (up to 90 days)
- Event Hubs Dedicated: Starting at $4,000/month
- Custom CUs based on requirements
- Estimated Monthly Cost: $750-$6,000 depending on scale and tier
Total Cost of Ownership Comparison
Ideal Use Cases
Confluent Kafka On-premises
- Stringent data locality requirements
- Air-gapped environments
- Complete infrastructure control needed
- Existing large investment in on-premises infrastructure
- Highly customized deployment requirements
Confluent Kafka on Azure
- Full Kafka ecosystem required (Connect, KSQL, etc.)
- Hybrid cloud architectures with Kafka
- Advanced streaming features needed
- Desire for Kafka-native tools and interfaces
- Need for longer message retention
- Complex stream processing requirements
Azure Event Hubs
- Native Azure integration is a priority
- Simpler event ingestion requirements
- Cost-sensitive implementations
- Azure-centric architectures
- Integration with Azure Functions and Logic Apps
- Quick startup with minimal configuration