LLM Tuning
The process of adapting a model to a new domain or set of custom use cases by training the model on new data
Fine Tuning
Large language model (LLM) fine-tuning is the process of taking pre-trained models and further training them on smaller, specific datasets to refine their capabilities and improve performance in a particular task or domain. Fine-tuning is about turning general-purpose models and turning them into specialized models. It bridges the gap between generic pre-trained models and the unique requirements of specific applications, ensuring that the language model aligns closely with human expectations.
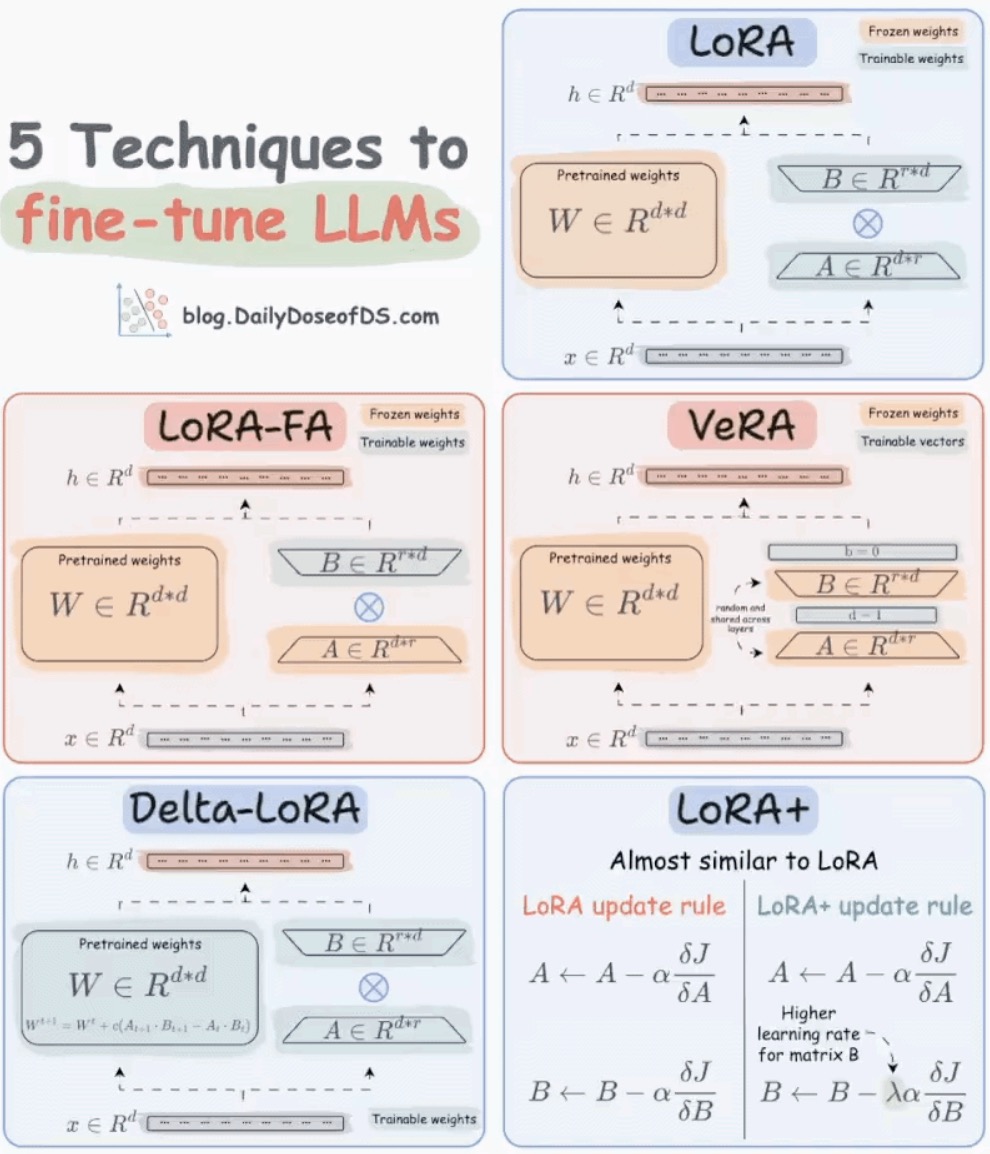
LoRA
- Introduce two low-rank matrices, A and B, to work alongside the weight matrix W.
- Adjust these matrices instead of the behemoth W, making updates manageable.
LoRA-FA (Frozen-A)
- Takes LoRA a step further by freezing matrix A.
- Only matrix B is tweaked, reducing the activation memory needed.
VeRA
- All about efficiency: matrices A and B are fixed and shared across all layers.
- Focuses on tiny, trainable scaling vectors in each layer, making it super memory-friendly.
Delta-LoRA
- A twist on LoRA: adds the difference (delta) between products of matrices A and B across training steps to the main weight matrix W.
- Offers a dynamic yet controlled approach to parameter updates.
LoRA+
- An optimized variant of LoRA where matrix B gets a higher learning rate. This tweak leads to faster and more effective learning.
 trr
trr
Supervised fine-tuning (SFT)
Supervised fine-tuning means updating a pre-trained language model using labeled data to do a specific task. The data used has been checked earlier. This is different from unsupervised methods, where data isn't checked. Usually, the initial training of the language model is unsupervised, but fine-tuning is supervised.
Methods for fine-tuning LLMs
- Instruction fine-tuning
- Full fine-tuning
- Parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT)
Performance Optimization
GitHub - microsoft/BitNet: Official inference framework for 1-bit LLMs
bitnet.cpp is the official inference framework for 1-bit LLMs (e.g., BitNet b1.58). It offers a suite of optimized kernels, that support fast and lossless inference of 1.58-bit models on CPU (with NPU and GPU support coming next).
The first release of bitnet.cpp is to support inference on CPUs. bitnet.cpp achieves speedups of 1.37x to 5.07x on ARM CPUs, with larger models experiencing greater performance gains. Additionally, it reduces energy consumption by 55.4% to 70.0%, further boosting overall efficiency. On x86 CPUs, speedups range from 2.37x to 6.17x with energy reductions between 71.9% to 82.2%. Furthermore, bitnet.cpp can run a 100B BitNet b1.58 model on a single CPU, achieving speeds comparable to human reading (5-7 tokens per second), significantly enhancing the potential for running LLMs on local devices.
BitNet - Inference framework for 1-bit LLMs : r/LocalLLaMA
Bitnet.cpp an opensource LLM platform by Microsoft | by Kldurga | Medium
bitnet.cpp from Microsoft: Run LLMs locally on CPU! (hands-on) - YouTube
[2504.12285] BitNet b1.58 2B4T Technical Report
Others
- Instruct tuning / Instruction Tuning