Airflow and Kafka Migration
Client - Coto.World | Women-Only Community & Consultation App
Overview
Our project involved migrating from Confluent Kafka to an on-prem Kafka setup on Linode, as well as moving from Airflow SaaS (Astronomer) to an on-prem Airflow setup. This migration was driven by the need to reduce costs, increase control over our infrastructure, and enhance observability and monitoring capabilities.
Tools and Technologies Used
- Linode: Cloud hosting provider for our on-prem Kafka and Airflow setups.
- Kubernetes (K8s): Orchestrated multiple node pools for separate Airflow and Kafka deployments.
- KEDA: Kubernetes-based Event Driven Autoscaling for scaling up Airflow workers.
- Terraform: Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tool to set up all the infrastructure.
- Open Source Airflow: For workflow orchestration.
- Flower: Monitoring tool for Celery workers.
- Redis: Used as the backend for Celery in Airflow.
- Open Source Kafka: Message broker for handling streaming data.
- Kafka UI: For monitoring Kafka clusters.
- Kafka Mirror: For migration of Kafka topics.
- GitHub Actions: For automation of deployment, user creation, and other tasks.
- Datadog: Full end-to-end monitoring, logging, and alerting, integrated with Slack for priority alerts.
- Debezium: Proof of Concept (PoC) for Change Data Capture (CDC) from PostgreSQL to MongoDB using Kafka.
Migration Process
-
Infrastructure Setup - Provisioning with Terraform:
- Used Terraform to automate the setup of Linode infrastructure.
- Defined Kubernetes clusters with separate node pools for Kafka and Airflow.
-
Kubernetes Deployment:
- Deployed Kafka and Airflow on separate Kubernetes node pools.
- Configured KEDA for dynamic scaling of Airflow workers based on task load.
-
Airflow Configuration:
- Set up open source Airflow with Redis as the backend and Flower for worker monitoring.
- Ensured isolation between different DAGs by using separate workers for distinct Airflow tasks.
-
Kafka Configuration:
- Deployed open source Kafka and Kafka UI for monitoring.
- Utilized Kafka Mirror to migrate topics from Confluent Kafka to the on-prem Kafka setup.
-
Automation and Monitoring:
- Implemented GitHub Actions for continuous deployment and infrastructure automation.
- Set up Datadog for comprehensive monitoring and alerting across Linode infrastructure, Airflow, and Kafka.
- Integrated Slack with Datadog for priority alerting and escalation.
-
PoC with Debezium:
- Conducted a PoC to validate the use of Debezium for CDC from PostgreSQL to MongoDB using Kafka.
Outcomes
- Successful Migration: Successfully migrated around 200 DAGs from Astronomer to the open-source Airflow setup.
- Cost Savings: Achieved savings of $10,000 monthly by moving to on-prem Kafka and Airflow.
- High Availability: Ensured high availability (HA) setups for both Kafka and Airflow.
- On-Time Deliveries: Completed the migration within the project timeline.
- Fully Managed Setup: Established a fully managed on-prem setup with automation for easy management.
- Advanced Observability: Implemented state-of-the-art observability, monitoring, and alerting using Datadog, ensuring robust system health and rapid issue resolution.
Conclusion
The migration from Confluent Kafka and Airflow SaaS to on-prem setups on Linode was a significant success, resulting in substantial cost savings, improved infrastructure control, and enhanced monitoring and alerting capabilities. The project showcased the effective use of Kubernetes, Terraform, and various open-source tools to achieve a scalable, reliable, and cost-effective solution.
Architecture Details
Confluent Cloud to Kafka on K8s Migration
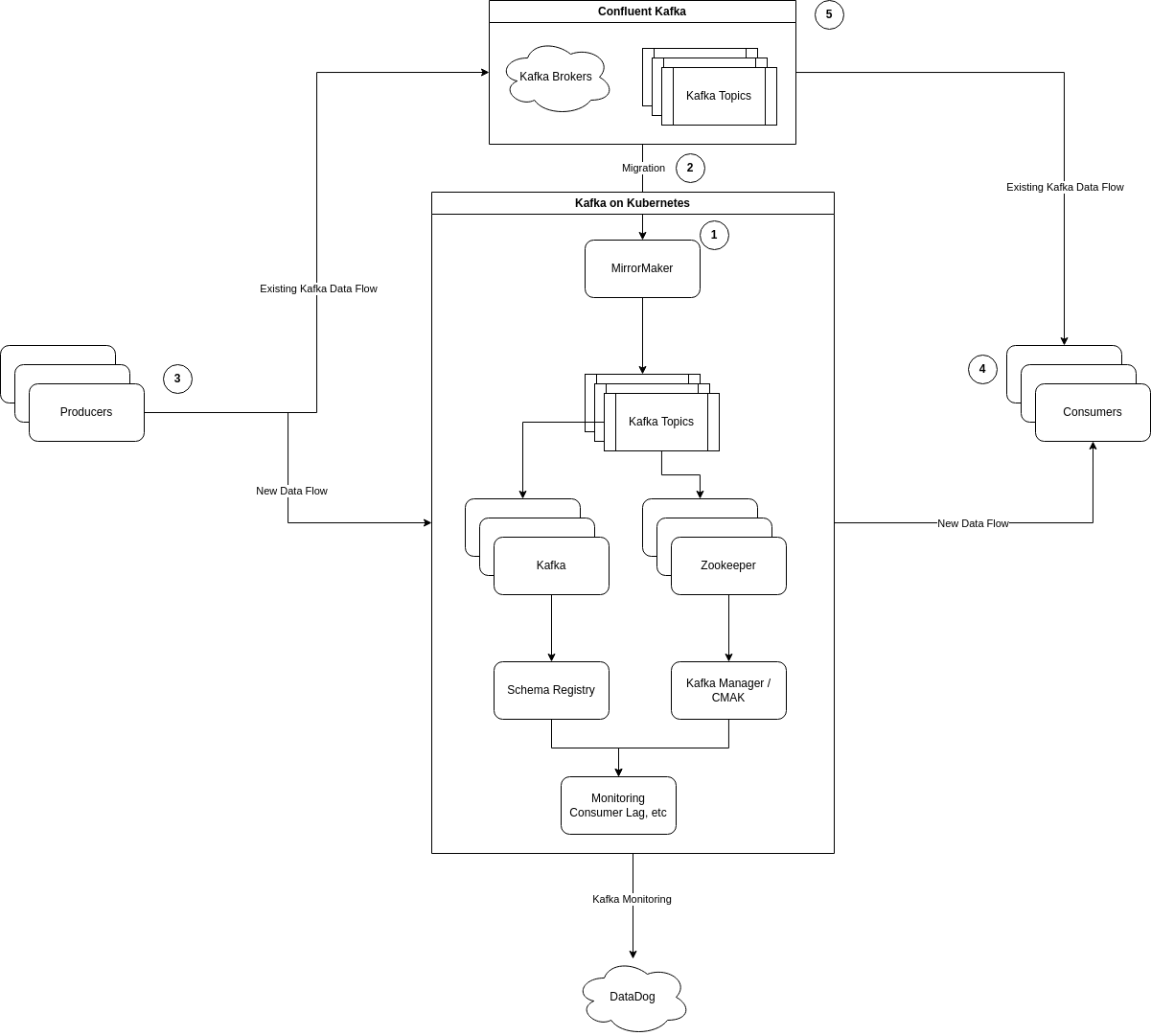
To ensure zero downtime during the migration of a Confluent Cloud Kafka cluster to a Kafka cluster deployed on Kubernetes using Strimzi and Kafka MirrorMaker, here are the steps:
- Setup Kafka MirrorMaker: Initially, set up Kafka MirrorMaker to replicate data between the Confluent Cloud Kafka cluster and the new Kafka cluster on Kubernetes. This step is crucial for ensuring data consistency and availability during the migration.
- Synchronize Clusters: Use MirrorMaker to continuously synchronize data from the Confluent Cloud Kafka cluster to the Strimzi Kafka cluster. This synchronization should be monitored closely to ensure data integrity.
- Monitor Synchronization Process: Regularly monitor the synchronization process to ensure that data is being replicated accurately and in real-time. This step is vital to prevent data loss or inconsistency.
- Switch Producers to Strimzi Kafka: Gradually redirect the data producers from the Confluent Cloud Kafka cluster to the new Strimzi Kafka cluster. This step should be done in phases to minimize the impact on the production environment.
- Monitor Producers for Stability: After switching the producers, monitor them for stability and performance. Ensure that they are functioning correctly and there are no issues in data production.
- Switch Consumers to Strimzi Kafka: Once the producers are stable, start redirecting the consumers to the new Kafka cluster. This step should also be done gradually to ensure a smooth transition.
- Monitor Consumers for Stability: After switching, monitor the consumers to ensure they are reading data correctly from the new Kafka cluster and there are no performance issues.
- Decommission Confluent Cloud Kafka Cluster: Once the new Kafka cluster is fully operational and all producers and consumers are switched over without any issues, you can safely decommission the old Confluent Cloud Kafka cluster.
Astronomer to Airflow on K8s Migration
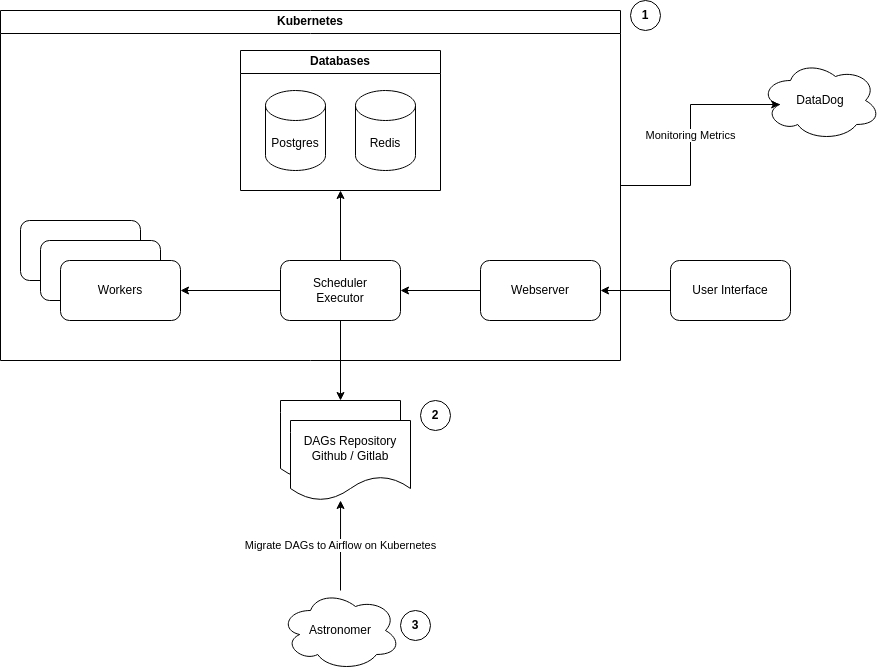
To ensure a smooth migration from Astronomer to Airflow on K8s, here are the steps:
- Airflow Deployment on K8s: We can use the official helm chart to deploy Airflow in k8s. Once the deployment is done, we can create the necessary modules - Postgres/MySQL, Redis, Airflow Scheduler, Airflow Web, Airflow worker. Based on the current pool and node sizes, nodes will be added. We’ll set up auto-scaling according to DAG loads. Move dags to new Airflow in batches.
- Decommission Astronomer: Once everything is set up and running, we can decommission Astronomer.