Use the Confluent Cloud Console with Private Networking
Access Confluent Cloud with private networking | Confluent Documentation
Configure a VPC Peered Cluster (Hands-On Tutorial)
In Confluent Cloud clusters with private networking, cluster endpoints used by some Confluent Cloud workflows, including topic management and ksqlDB query management, are not publicly accessible. For example, you cannot view Kafka topic data/message from the Confluent Cloud Console running on a workstation outside of the private network.
Note - If you’ve configured access to Confluent resources as described in this topic, but you still cannot view topics on private clusters in the Confluent Cloud Console using Google Chrome and you get the message, “This Cluster is protected by a private network”, you must enable the Local Network Access setting in Chrome. Chrome recently added the Local Network Access check as explained in Google’s documentation. For more information and the workaround, see the Confluent Support knowledge base article.
To view and manage your Confluent resources on a private network in Confluent Cloud Console with a client computer, you have the following options:
-
Enable the Resource metadata access option
If you only need to view topics and their metrics information, or if you need to use the Stream Lineage feature on the Confluent Cloud Console, you can enable the Resource metadata access option on the Confluent Cloud Console.
This option does not allow you to view topics data/messages.
-
Create a connection to the network that hosts the private cluster endpoints
For your Confluent clients (Confluent Cloud Console, REST API, CLI, Terraform, and Kafka API) from outside the private network to have access to the full functionality of Confluent Cloud, create and use a connection to the network that hosts the private endpoints.
For example, to manage topics (create/update/delete), to produce to/consume from topics, or to manage ksqlDB queries, create a connection to the network that hosts the private cluster endpoints, and then update your DNS configuration for topics or ksqlDB endpoints to use that connection.
Note - This option involves configuring external components, such as proxies, SSH tunnels, and DNS in your network.
CIDR for creating new AWS VPC - 10.0.0.0/16
CIDR for Confluent Cloud, when creating network in confluent cloud - 10.1.0.0/16
Create a connection to the network that hosts the private cluster endpoints
For single-cluster deployments, you can leverage managed services offered by your cloud provider — such as load balancers and gateways — to enable access to Confluent resources in private networking environments. These resources can then be managed and accessed using the Confluent Cloud Console or the Confluent CLI.
For large scale centralized architectures, you need a component with more advanced SNI routing than what the cloud provider load balancers and gateways can provide. NGINX remains the best technical solution.
Configure a proxy
To enable access to Confluent services in a privately-networked Confluent Cloud cluster from your local machine, you can use a proxy (NGINX, HAProxy, Envoy, or others). The proxy relays communication between your local clients and Confluent Cloud resources.
Confluent Cloud hostnames must be maintained over a TCP proxy. Otherwise, TLS hostname validation will fail, and TLS will not be established. You must have a DNS record, or an entry in your /etc/hosts file, that points to the IP address of the proxy instance that routes to the appropriate Confluent endpoint.
In the following example topology, the client runs outside of a VPC or VNet and uses an NGINX proxy to connect to Confluent Cloud.
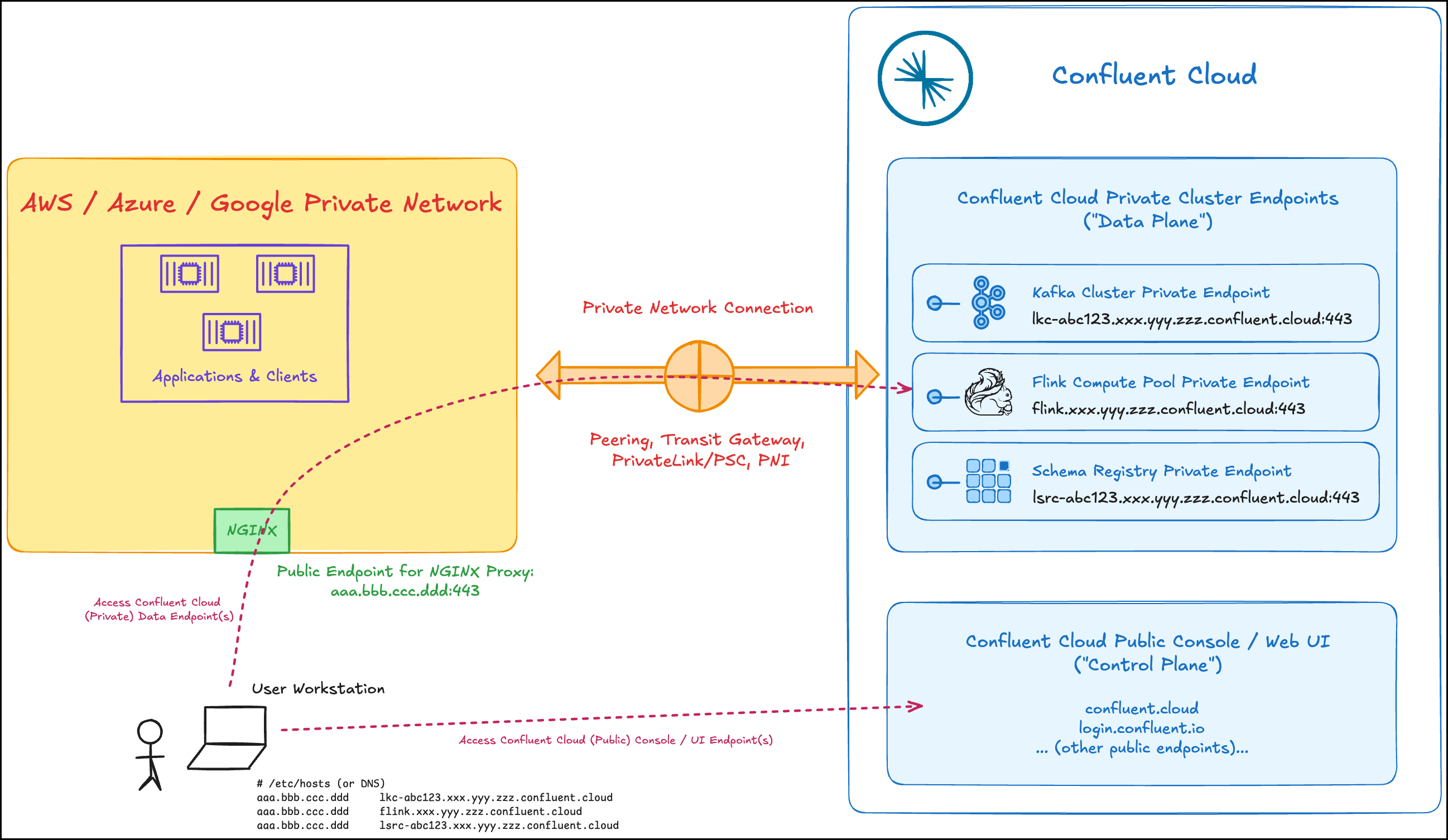
To install and configure the proxy, complete the following steps. The configuration steps use NGINX as an example:
- Provision a Virtual Machine (VM) in your VPC or VNet that is connected to Confluent Cloud.
- Install NGINX on an instance in the VPC or VNet connected to Confluent Cloud.
sudo apt update
sudo apt install nginx
# Test the NGINX configuration. NGINX checks the configuration for correct syntax and tries to open files referred to in the configuration
nginx -t
# for loading load_module /usr/lib/nginx/modules/ngx_stream_module.so;
sudo apt install nginx-extras
nginx -t
- Update the NGINX configuration file (
/etc/nginx/nginx.conf) to use SNI from incoming TLS sessions for routing traffic to the appropriate servers on ports443and9092.
events {}
stream {
map $ssl_preread_server_name $targetBackend {
default $ssl_preread_server_name;
}
server {
listen 9092;
proxy_connect_timeout 1s;
proxy_timeout 7200s;
resolver 127.0.0.53;
proxy_pass $targetBackend:9092;
ssl_preread on;
}
server {
listen 443;
proxy_connect_timeout 1s;
proxy_timeout 7200s;
resolver 127.0.0.53;
proxy_pass $targetBackend:443;
ssl_preread on;
}
log_format stream_routing '[$time_local] remote address $remote_addr'
'with SNI name "$ssl_preread_server_name" '
'proxied to "$upstream_addr" '
'$protocol $status $bytes_sent $bytes_received '
'$session_time';
access_log /var/log/nginx/stream-access.log stream_routing;
}
- Verify the resolver
nslookup <ConfluentCloud_BootstrapHostname> 127.0.0.53
- Restart NGINX to pick up the latest configuration (
/etc/nginx/nginx.conf).
sudo systemctl restart nginx
sudo systemctl status nginx
- Configure your DNS provider to resolve requests to Confluent Cloud to the proxy server.
##
# Host Database
#
# localhost is used to configure the loopback interface
# when the system is booting. Do not change this entry.
##
127.0.0.1 localhost
255.255.255.255 broadcasthost
::1 localhost
<Public IP Address of VM instance> <Kafka-REST-Endpoint>
<Public IP Address of VM instance> <Flink-private-endpoint>
<Public IP Address of VM instance> <Flinkpls-private-endpoint>
<Public IP Address of VM instance> <Schema-registry-private-endpoint>
The example above resolves both the Kafka bootstrap server host and the Kafka REST host. The host addresses of the Kafka bootstrap server and the REST endpoint are the same, and only the port numbers differ.
- For AWS Enterprise clusters only, set the cluster endpoint as described in Select a Kafka endpoint for AWS Enterprise clusters.
- Go to the Confluent Cloud Console and verify that topics and ksqlDB query management are now visible under the Topics and ksqlDB tabs for your cluster.
Enable or disable the Resource metadata access option
The Resource metadata access option enables you to connect to the clusters with private networking to view resources. Specifically, the following features are enabled when you turn on the option:
- Viewing topics metadata and configuration. Avoid turning on this option if topic names are considered sensitive.
- Viewing consumer lags and other topic-level metrics
- Viewing and configuring Schema Registry
- Using Stream Lineage
- Listing existing topics during connector creation
You can toggle the option at the cluster level or at the organization level. The cluster-level toggle overrides the organization-level toggle.
Note that the Resource metadata access option only controls access on the Confluent Cloud Console. Resource metadata is not accessible using Confluent Cloud APIs, Confluent CLI, or Terraform even when the option is enabled.
The Resource metadata access option is read-only. Even if you have the DeveloperWrite access or above on a topic and have the Resource metadata access option enabled, you cannot create, edit, or delete topics. Management operations (create, update, and delete) still require setting up a proxy or SSH as described in Create a connection to the network that hosts the private cluster endpoints.
Before you enable the Resource metadata access option, review the following information:
- You access topic metadata (name and settings) on the Confluent Cloud Console over the public network using the TLS-enabled connections.
- No one outside of your organization will be able to see the topic information, and the information will be protected by the RBAC permissions you configure.
- The topic data will still not be accessible over the internet.
- Topic-level DENY ACLs will not prevent users from reading topic metadata (name and settings).
- The RBAC roles that allow users to read topic metadata for individual topics (such as DeveloperRead and ResourceOwner), or the roles that allow users to read topic metadata on individual clusters (such as CloudClusterAdmin) will not be sufficient to use this feature. See the list below for roles that enable this feature.
To enable or disable the Resource metadata access:
- Log into Confluent Cloud as an administrator with the OrganizationAdmin role. Only the OrganizationAdmin role has the permission to toggle the Resource metadata access both at the cluster level and organization level.
- Make sure the Stream Governance package is turned on in your Confluent Cloud environment. You can use any package of Stream Governance, including the free Essentials package. For more information about Stream Governance, see Stream Governance on Confluent Cloud.
- Enable or disable Resource metadata access.
- To enable or disable the option at the cluster level, toggle Resource Metadata Access on or off in the Security tab on the Cluster Settings page.
- You can also enable Resource metadata access when you create a cluster at the Networking setup step.
- To enable or disable the option at the organization level, toggle Resource Metadata Access on or off on the Organizations page.
- To enable or disable the option at the cluster level, toggle Resource Metadata Access on or off in the Security tab on the Cluster Settings page.
- If you enabled the Resource metadata access option, navigate to your cluster’s topics and Stream Lineage pages to view them.