Change Data Capture (CDC)
In databases, change data capture(CDC) is a set of software design patterns used to determine (and track) the data that has changed so that action can be taken using the changed data. CDC is also an approach to data integration that is based on the identification, capture and delivery of the changes made to enterprise data sources.
CDC solutions occur most often in data-warehouse environments since capturing and preserving the state of data across time is one of the core functions of a data warehouse, but CDC can be utilized in any database or data repository system.
What Is Change Data Capture - Understanding Data Engineering 101 - YouTube
Change Data Capture for Microservices - YouTube
Understanding Change Data Capture (CDC): Definition, Methods, Benefits | Airbyte
Change Data Capture benefits
- CDC is efficient
- CDC enables near real-time processing
- CDC tracks delete operations in the source database
- CDC reduces the impact on the source database
Change Data Capture methods
Table metadata
This method keeps track of metadata across every row in a table, including when the row was created and updated. Using this method requires additional columns in the original table (such as created_at and updated_at) or a separate table to track these different metadata elements.
Tracking metadata is commonly used in incremental batch processing to identify new and updated rows.
There are many ways to identify new and updated rows in the source table. The most common way is to look at the updated_at column in the destination table before replication to know the latest update and then identify the rows with a later updated_at in the source table. The result is the new and updated rows that should be merged at the destination.
A detailed implementation in Python for PostgreSQL CDC can be found here.
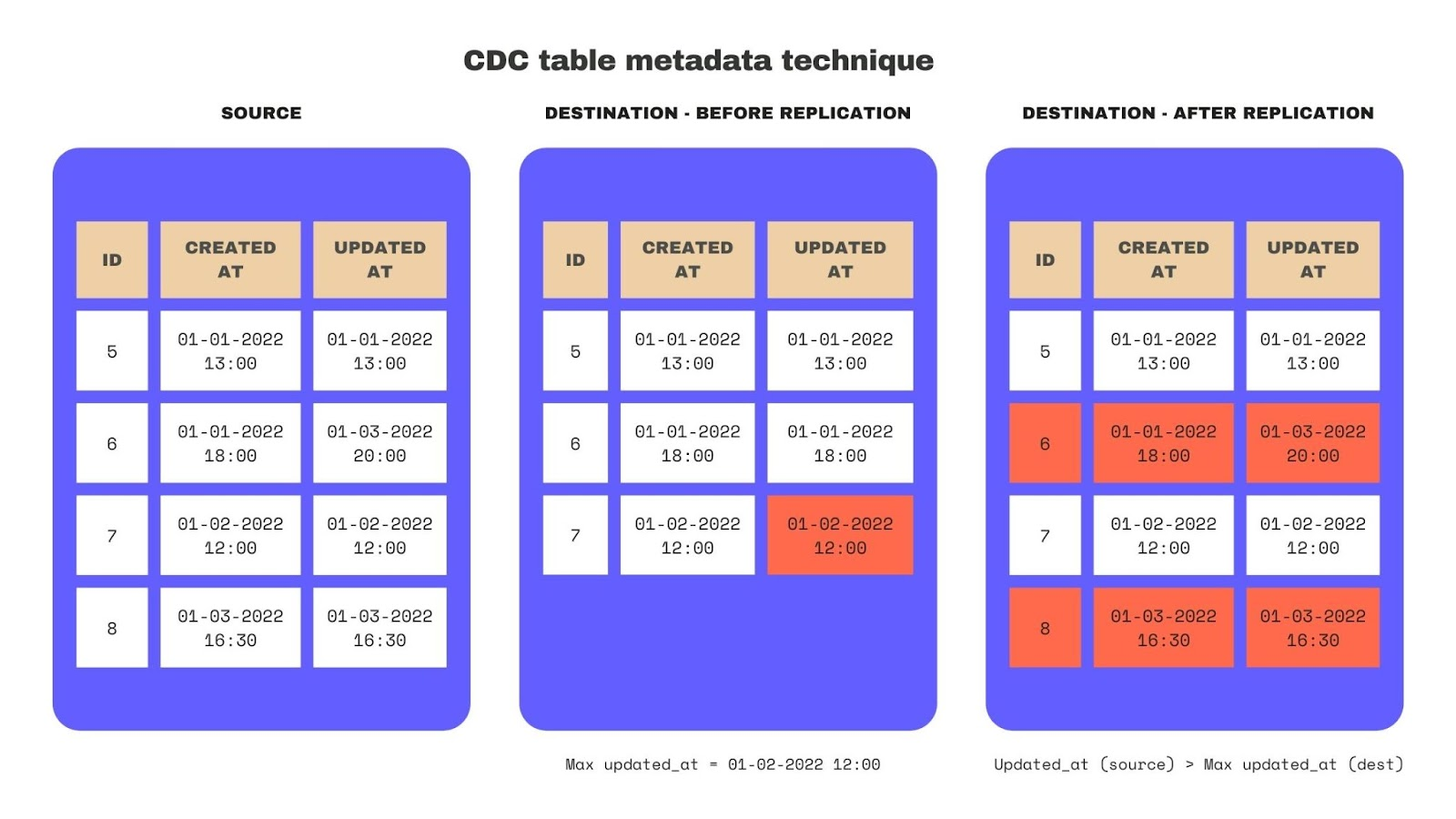
Key challenges:
- If there are hard deletes in the source database, it’s impossible to track them using this method.
- Regularly querying the source database to identify new and updated rows can overload it.
Table differences
This method identifies the difference between the source and the destination tables to detect new, updated, and even deleted rows. The difference can be calculated using a SQL query or specific utilities provided by the database (for example, SQL Server provides a tablediff utility).
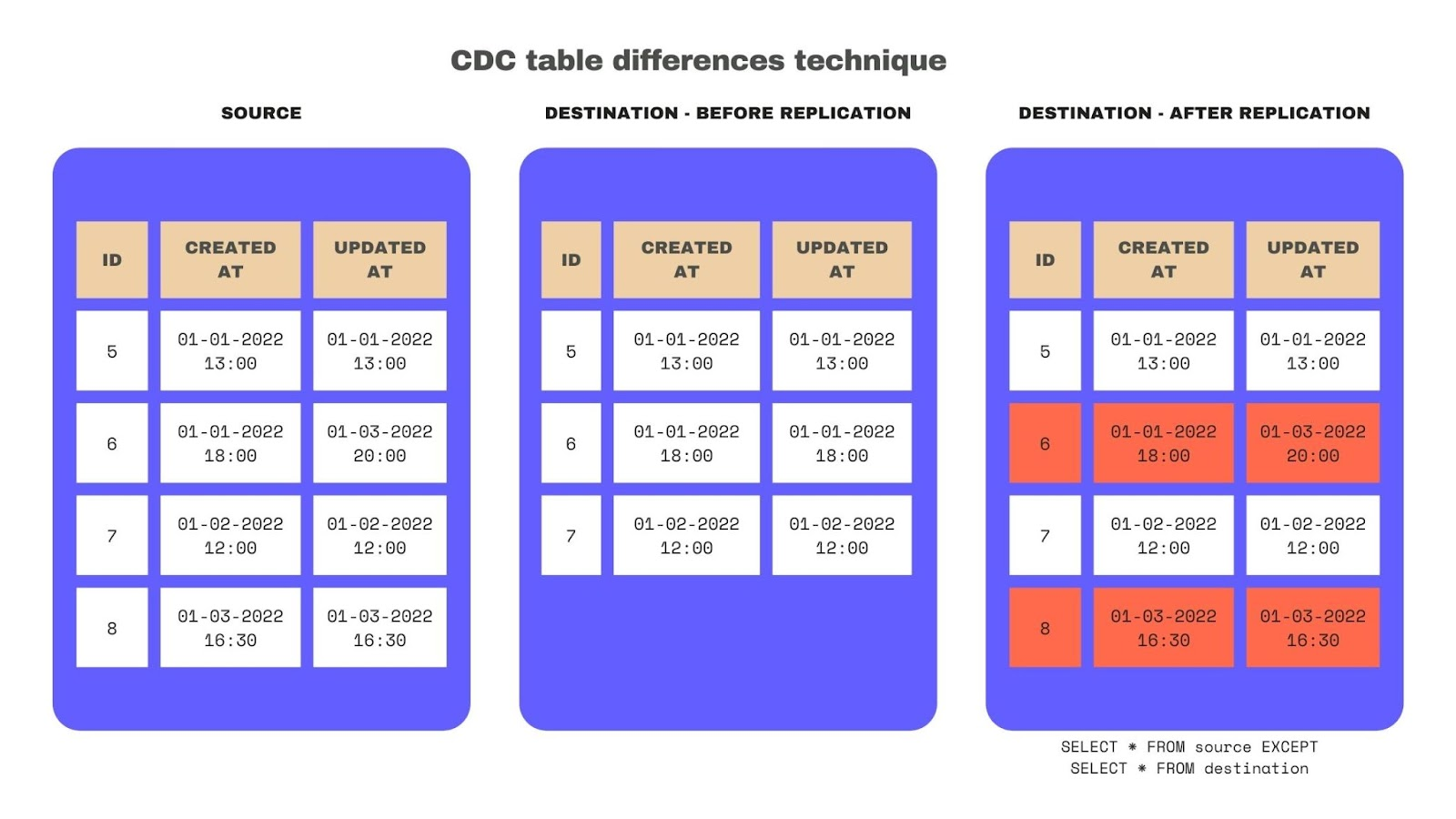
Key challenges:
- Comparing tables row-by-row to identify differences requires extensive computational resources, and it’s not scalable.
Database triggers (Trigger-based CDC)
This method requires the creation of database triggers with logic to manage the metadata within the same table or in a separate book-keeping table, often called a shadow table.
Most databases allow the creation of triggers; you can see how to create a trigger for PostgreSQL.
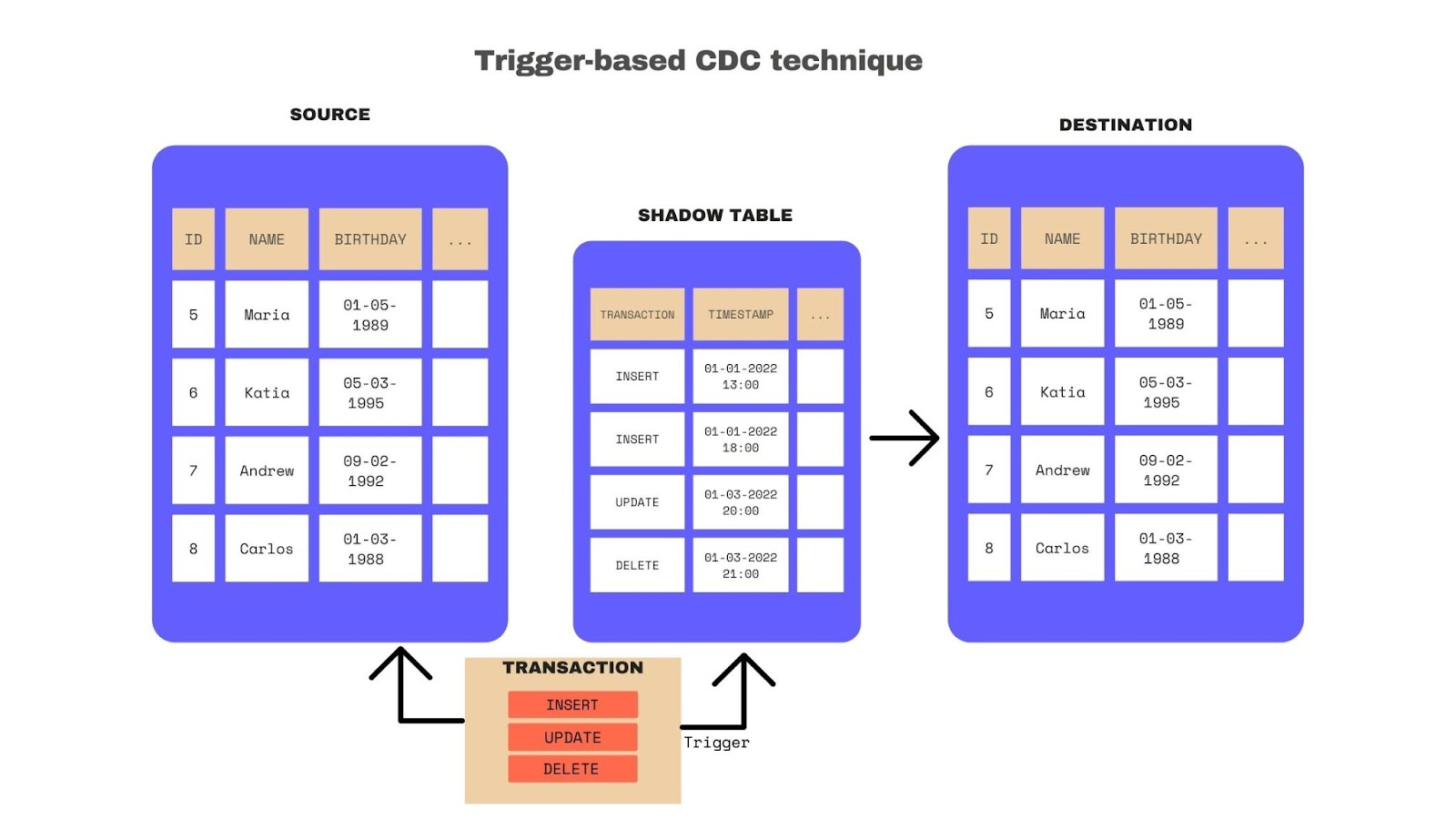
Key challenges:
- If a transaction fails, roll-back logic may need to be implemented to remove the operation from the shadow table.
- The trigger needs to be modified in case of table schema changes.
- Triggers cannot be reused for other databases, given the differences in SQL language.
- The use of triggers can slow down the transactional workload.
Database transaction log (Log-based CDC)
Log-based CDC uses the transaction logs that some databases - such as Postgres, MySQL, SQL Server, and Oracle - implement natively as part of their core functionality.
Log-based and trigger-based CDC are very similar - both keep a log of changes every time a database operation happens - so the shadow table and the transaction log contain the same information. The difference between log-based and trigger-based CDC is that the first one uses a core functionality of the database (transaction log); meanwhile, the triggers are created and defined by the user.
Since database logs are updated in every transaction, the experience is transparent, which means log-based CDC does not require any logical changes in database objects or the application running on top of the database. A system reads data directly from the database Change Data Capture logs to identify changes in a database, minimizing the impact of the capture process.
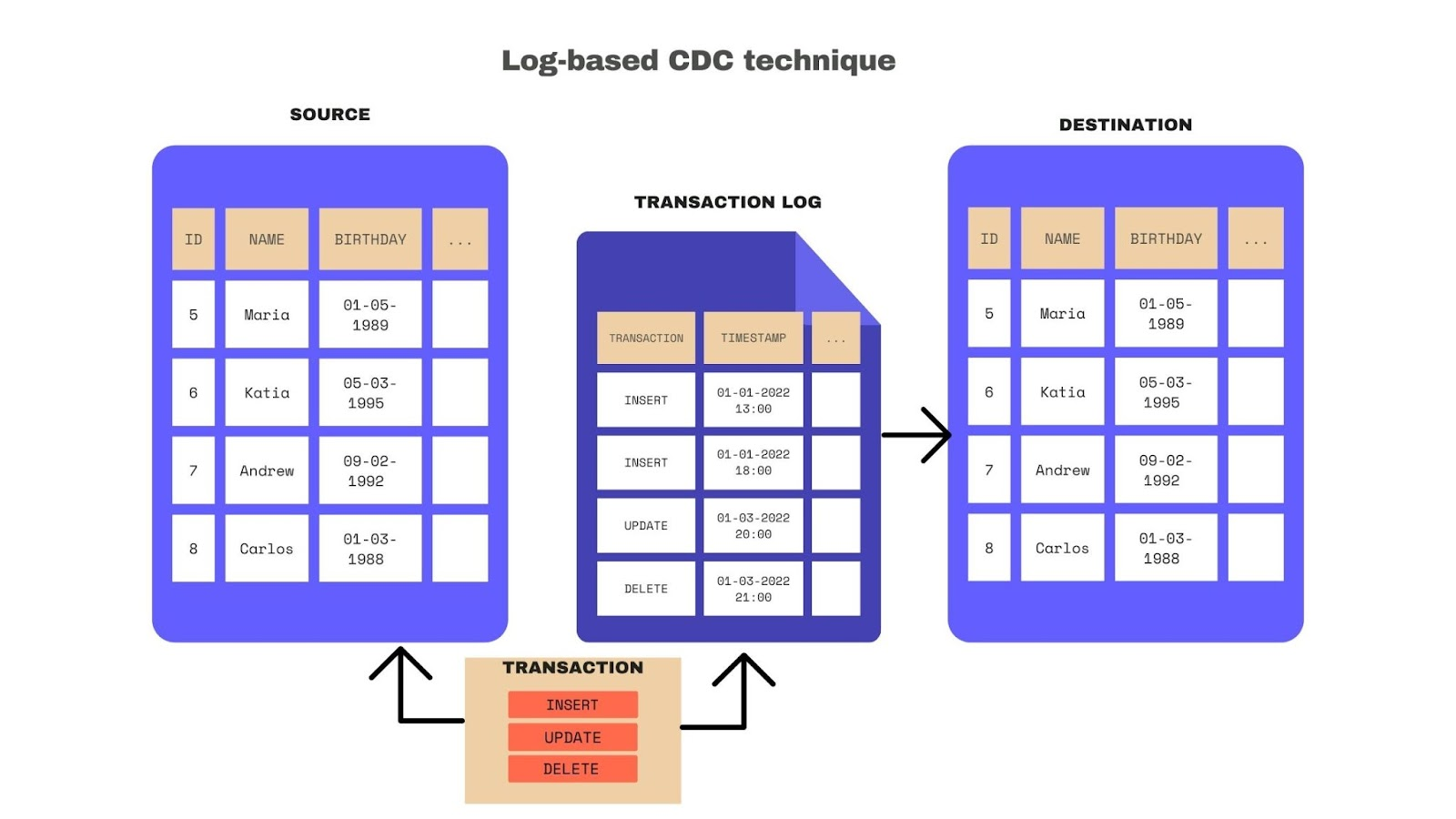
Key challenges:
- Some database operations are not captured in the CDC logs, such as ALTER or TRUNCATE. In that case, additional logic needs to be configured to force the logging of those operations.
- If the destination datastore is down, transaction logs must be kept intact until the subsequent replication happens.
Tools
Debezium
AWS DMS (Data Migration Service)
aws-database-migration-service-dms
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Change_data_capture
Maxwell
This is Maxwell's daemon, a change data capture application that reads MySQL binlogs and writes data changes as JSON to Kafka, Kinesis, and other streaming platforms.
Maxwell is a CDC (Changelog Data Capture) tool that can stream changes in real-time from MySQL into Kafka, Kinesis and other streaming connectors. Maxwell provides a unified format schema for changelog and supports to serialize messages using JSON.
What's it for?
- ETL of all sorts
- maintaining an audit log of all changes to your database
- cache building/expiring
- search indexing
- inter-service communication
GitHub - zendesk/maxwell: Maxwell's daemon, a mysql-to-json kafka producer
Others
- airbyte
- debezium
- attunity (now Qlik replicate)
- fivetran
- Talend
- Matillion
- Integrate.io
- Panoply
- Informatica
- Singer.io
- Hadoop
- Dataddo
- AWS Glue
- Stitch
- Hevo Data
- upsolver
- archion
- CloudQuery | Data Fabric for Cloud and Security Teams
12 best data migration tools of 2023
11 Best Data Migration Tools for 2023
6 Popular CDC Tools, Compared (July 2023 Edition)