Data Warehousing
In computing, a data warehouse (DW or DWH), also known as an enterprise data warehouse (EDW), is a system used for reporting and data analysis, and is considered a core component of business intelligence. DWs are central repositories of integrated data from one or more disparate sources. They store current and historical data in one single place that are used for creating analytical reports for workers throughout the enterprise.
The data stored in the warehouse is uploaded from the operational systems (such as marketing or sales). The data may pass through an operational data store and may require data cleansing for additional operations to ensure data quality before it is used in the DW for reporting.
Extract, transform, load (ETL) and Extract, load, transform (E-LT) are the two main approaches used to build a data warehouse system.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Data_warehouse
Data Warehouse vs Database
A data warehouse is specially designed for data analytics, which involves reading large amounts of data to understand relationships and trends across the data. A database is used to capture and store data, such as recording details of a transaction.
| Characteristics | Data Warehouse | Transactional Database |
|---|---|---|
| Suitable workloads | Analytics, reporting, big data | Transaction processing |
| Data source | Data collected and normalized from many sources | Data captured as-is from a single source, such as a transactional system |
| Data capture | Bulk write operations typically on a predetermined batch schedule | Optimized for continuous write operations as new data is available to maximize transaction throughput |
| Data normalization | Denormalized schemas, such as the Star schema or Snowflake schema | Highly normalized, static schemas |
| Data storage | Optimized for simplicity of access and high-speed query performance using columnar storage | Optimized for high throughout write operations to a single row-oriented physical block |
| Data access | Optimized to minimize I/O and maximize data throughput | High volumes of small read operations |
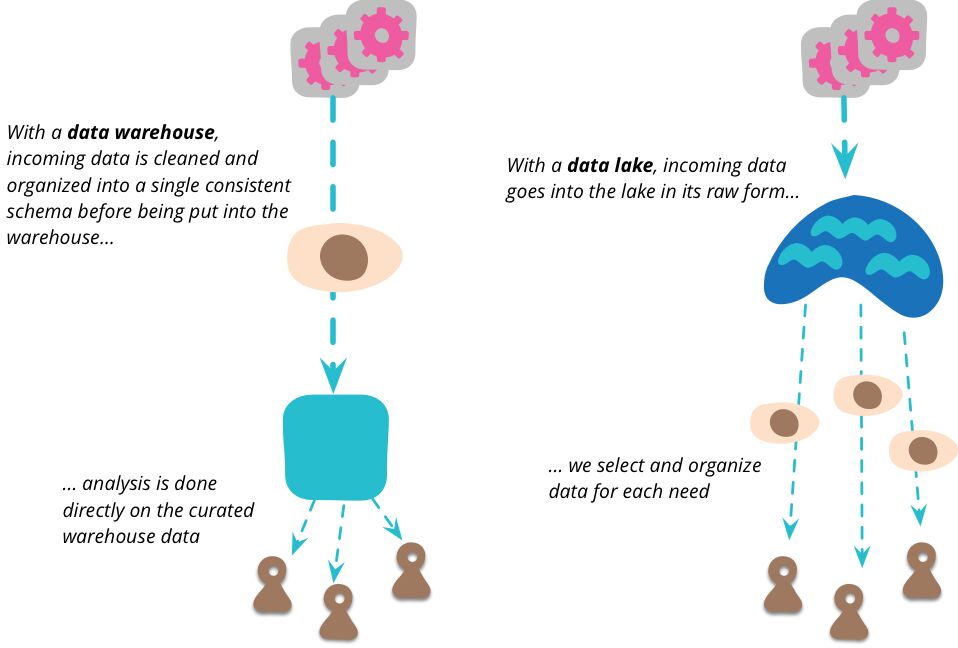
Data Warehouse vs Data Lake
Unlike a data warehouse, a data lake is a centralized repository for all data, including structured and unstructured. A data warehouse utilizes a pre-defined schema optimized for analytics. In a data lake, the schema is not defined, enabling additional types of analytics like big data analytics, full text search, real-time analytics, and machine learning.
| Characteristics | Data Warehouse | Data Lake |
|---|---|---|
| Data | Relational data from transactional systems, operational databases, and line of business applications | Non-relational and relational data from IoT devices, web sites, mobile apps, social media, and corporate applications |
| Schema | Designed prior to the data warehouse implementation (schema-on-write) | Written at the time of analysis (schema-on-read) |
| Price/Performance | Fastest query results using higher cost storage | Query results getting faster using low-cost storage |
| Data Quality | Highly curated data that serves as the central version of the truth | Any data that may or may not be curated (i.e. raw data) |
| Users | Business analysts, data scientists, and data developers | Data scientists, data developers, and business analysts (using curated data) |
| Analytics | Batch reporting, BI, and visualizations | Machine learning, predictive analytics, data discovery, and profiling |
| Tasks | Typically read-only queries for aggregating and summarizing data | Storing data and big data analytics, like deep learning and real-time analytics |
| Size | Only stores data relevant to analysis | Stores all data that might be used - can take up petabytes! |
| Tightly coupled compute and storage | Seperation of compute and storage | |
| Written at the time of analysis (Schema on write) | Designed prior to the data warehouse implementation (Schema on read) | |
| Great for storing frequently accessed data as well as data aggregates and summary | Great for storing granular data; raw as well as processed data |
Data Warehouse vs Data Mart
A data mart is a data warehouse that serves the needs of a specific team or business unit, like finance, marketing, or sales. It is smaller, more focused, and may contain summaries of data that best serve its community of users.
A data mart is an access layer which is used to get data out to the users. It is presented as an option for large size data warehouse as it takes less time and money to build. However, there is no standard definition of a data mart is differing from person to person.
In a simple word Data mart is a subsidiary of a data warehouse. The data mart is used for partition of data which is created for the specific group of users.
Data marts could be created in the same database as the Datawarehouse or a physically separate Database.
| Characteristics | Data Warehouse | Data Mart |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Centralized, multiple subject areas integrated together | Decentralized, specific subject area |
| Users | Organization-wide | A single community or department |
| Data source | Many sources | A single or a few sources, or a portion of data already collected in a data warehouse |
| Size | Large, can be 100's of gigabytes to petabytes | Small, generally up to 10's of gigabytes |
| Design | Top-down | Bottom-up |
| Data detail | Complete, detailed data | May hold summarized data |
Characteristics of a Data Warehouse
- Subject-Oriented: A data warehouse uses a theme, and delivers information about a specific subject instead of a company’s current operations. In other words, the data warehousing process is more equipped to handle a specific theme. Examples of themes or subjects include sales, distributions, marketing, etc.
- Integrated: Integration is defined as establishing a connection between large amount of data from multiple databases or sources. However, it is also essential for the data to be stored in the data warehouse in a unified manner. The process of data warehousing integrates data from multiple sources, such as a mainframe, relational databases, flat files, etc. Furthermore, it helps maintain consistent codes, attribute measures, naming conventions, and, formats.
- Time-variant: Time-variant in a DW is more extensive as compared to other operating systems. Data stored in a data warehouse is recalled with a specific time period and provides information from a historical perspective.
- Non-volatile: In the non-volatile data warehouse, data is permanent i.e. when new data is inserted, previous data is not replaced, omitted, or deleted. In this data warehouse, data is read-only and only refreshes at certain intervals. The two data operations performed in the data warehouse are data access and data loading.
Functions of a Data Warehouse
Data warehouse functions as a repository. It helps organizations avoid the cost of storage systems and backup data at an enterprise level. The prominent functions of the data warehouse are:
- Data Cleaning
- Data Integration
- Data Mapping
- Data Extraction
- Data Transformation
- Data Loading
- Refreshing
Reference
https://dzone.com/refcardz/data-warehousing
https://medium.com/@rchang/a-beginners-guide-to-data-engineering-part-ii-47c4e7cbda71
https://medium.com/@rchang/a-beginners-guide-to-data-engineering-the-series-finale-2cc92ff14b0
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/dwh/index.htm
https://www.guru99.com/data-warehouse-architecture.html
https://aws.amazon.com/data-warehouse
Data Warehouse Concepts: Kimball vs. Inmon Approach | Astera