AWS Lambda
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/lambda/latest/dg/lambda-edge.html
https://www.toptal.com/aws/service-oriented-architecture-aws-lambda
Managing applications in the AWS Lambda console - AWS Lambda
Run Your Code in Response to Events
# Stock Check Lambda function
# This function is triggered when values are inserted into the Inventory DynamoDB table.
# Inventory counts are checked, and if an item is out of stock, a notification is sent to an SNS topic.
# This handler is executed every time the Lambda function is triggered
def lambda_handler(event, context):
# Show the incoming event in the debug log
print("Event received by Lambda function: " + json.dumps(event, indent=2))
# For each inventory item added, check if the count is zero
for record in event['Records']:
newImage = record['dynamodb'].get('NewImage', None)
if newImage:
count = int(record['dynamodb']['NewImage']['Count']['N'])
if count == 0:
store = record['dynamodb']['NewImage']['Store']['S']
item = record['dynamodb']['NewImage']['Item']['S']
# Construct message to be sent
message = store + ' is out of stock of ' + item
print(message)
# Connect to SNS
sns = boto3.client('sns')
alertTopic = 'NoStock'
snsTopicArn = [t['TopicArn'] for t in sns.list_topics()['Topics']
if t['TopicArn'].lower().endswith(':' + alertTopic.lower())][0]
# Send message to SNS
sns.publish(
TopicArn=snsTopicArn,
Message=message,
Subject='Inventory Alert!',
MessageStructure='raw'
)
# Finished!
return 'Successfully processed {} records.'.format(len(event['Records']))
Slack notifications
import logging
import json
from urllib.parse import urlencode
from urllib.request import Request, urlopen
def lambda_handler(event, context):
webhook_url = "https://hooks.slack.com/services/xxx/org_id/api_key"
print(event)
message = json.loads(event["Records"][0]["Sns"]["Message"])
name = message["AlarmName"]
reason = message["NewStateReason"]
state = message["NewStateValue"]
if state == "ALARM":
color = "danger"
else:
color = "good"
slack_data = {
"channel": "monitoring",
"color": color,
"fields": [
{
"title": "Alarm: %s" % (name),
"value": "%s \n https://ap-south-1.console.aws.amazon.com/cloudwatch/home?region=ap-south-1#alarmsV2:alarm/%s?" % (reason, name),
}
]
}
request = Request(
webhook_url,
data=json.dumps(slack_data).encode(),
headers={"Content-Type": "application/json"},
)
response = urlopen(request)
return {"statusCode": response.getcode(), "body": response.read().decode()}
AWS Serverless Lambda Supports Response Streaming - YouTube
Features
- The maximum timeout for an AWS Lambda function is 900 seconds (15 minutes). You can configure this value in increments of 1 second, with a default of 3 seconds. This is a hard limit set by AWS and cannot be exceeded
- AWS Lambda functions can be configured with memory ranging from 128 MB to 10,240 MB (10 GB). The default memory setting is 128 MB, but you can increase it in 1-MB increments up to the maximum. Lambda allocates CPU power proportionally to the amount of memory configured, so a 256 MB function will have twice the processing power of a 128 MB function.
- Since AWS Lambda functions can scale extremely quickly, it's a good idea to deploy a Amazon CloudWatch Alarm that notifies your team when function metrics such as ConcurrentExecutions or Invocations exceeds the expected threshold
- If you intend to reuse code in more than one AWS Lambda function, you should consider creating an AWS Lambda Layer for the reusable code
- You can configure your AWS Lambda function to pull in additional code and content in the form of layers. A layer is a ZIP archive that contains libraries, a custom runtime, or other dependencies.
- With layers, you can use libraries in your function without needing to include them in your deployment package. Layers let you keep your deployment package small, which makes development easier. A function can use up to 5 layers at a time.
- You can create layers, or use layers published by AWS and other AWS customers. Layers support resource-based policies for granting layer usage permissions to specific AWS accounts, AWS Organizations, or all accounts. The total unzipped size of the function and all layers can't exceed the unzipped deployment package size limit of 250 megabytes.
- By default, AWS Lambda functions always operate from an AWS-owned VPC and hence have access to any public internet address or public AWS APls. Once an AWS Lambda function is VPC-enabled, it will need a route through a Network Address Translation gateway (NAT gateway) in a public subnet to access public resources.
- You should only enable your functions for VPC access when you need to interact with a private resource located in a private subnet. An Amazon RDS instance is a good example.
- AWS Lambda functions always operate from an AWS-owned VPC. By default, your function has the full ability to make network requests to any public internet address — this includes access to any of the public AWS APls. For example, your function can interact with AWS DynamoDB APIs to PutItem or Query for records. You should only enable your functions for VPC access when you need to interact with a private resource located in a private subnet. An Amazon RDS instance is a good example.
- Once your function is VPC-enabled, all network traffic from your function is subject to the routing rules of your VPC/Subnet. If your function needs to interact with a public resource, you will need a route through a NAT gateway in a public subnet.
- AWS Lambda allocates compute power in proportion to the memory you allocate to your function. This means you can over-provision memory to run your functions faster and potentially reduce your costs. However, AWS recommends that you should not over provision your function time out settings. Always understand your code performance and set a function time out accordingly. Overprovisioning function timeout often results in Lambda functions running longer than expected and unexpected costs.
- The bigger your deployment package, the slower your AWS Lambda function will cold-start. Hence, AWS suggests packaging dependencies as a separate package from the actual AWS.
- Lambda package - This statement is incorrect and acts as a distractor. All the dependencies are also packaged into the single Lambda deployment package.
- Serverless architecture and containers complement each other but you cannot package and deploy AWS Lambda functions as container images
- This statement is incorrect. You can now package and deploy AWS Lambda functions as container images.
Cost
| Metric | EC2 Spot Instance (including EBS) | Lambda (7 requests/hr) | Lambda (8 requests/hr) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monthly Cost (USD) | $41.50892 | $38.33 | $43.80 |
| Cost Breakdown | |||
| EC2 Spot Instance | $0.87892 | ||
| EBS Storage | $40.63 | ||
| Lambda Compute | $38.33 | $38.33 |
- Lambda can be cheaper than EC2 Spot Instance (including EBS) when the Lambda workload is lower (7 requests per hour).
- Lambda becomes more expensive than EC2 Spot Instance (including EBS) when the Lambda workload increases (8 requests per hour).
Lambda vs EC2 cost - AWS Pricing Calculator
Working
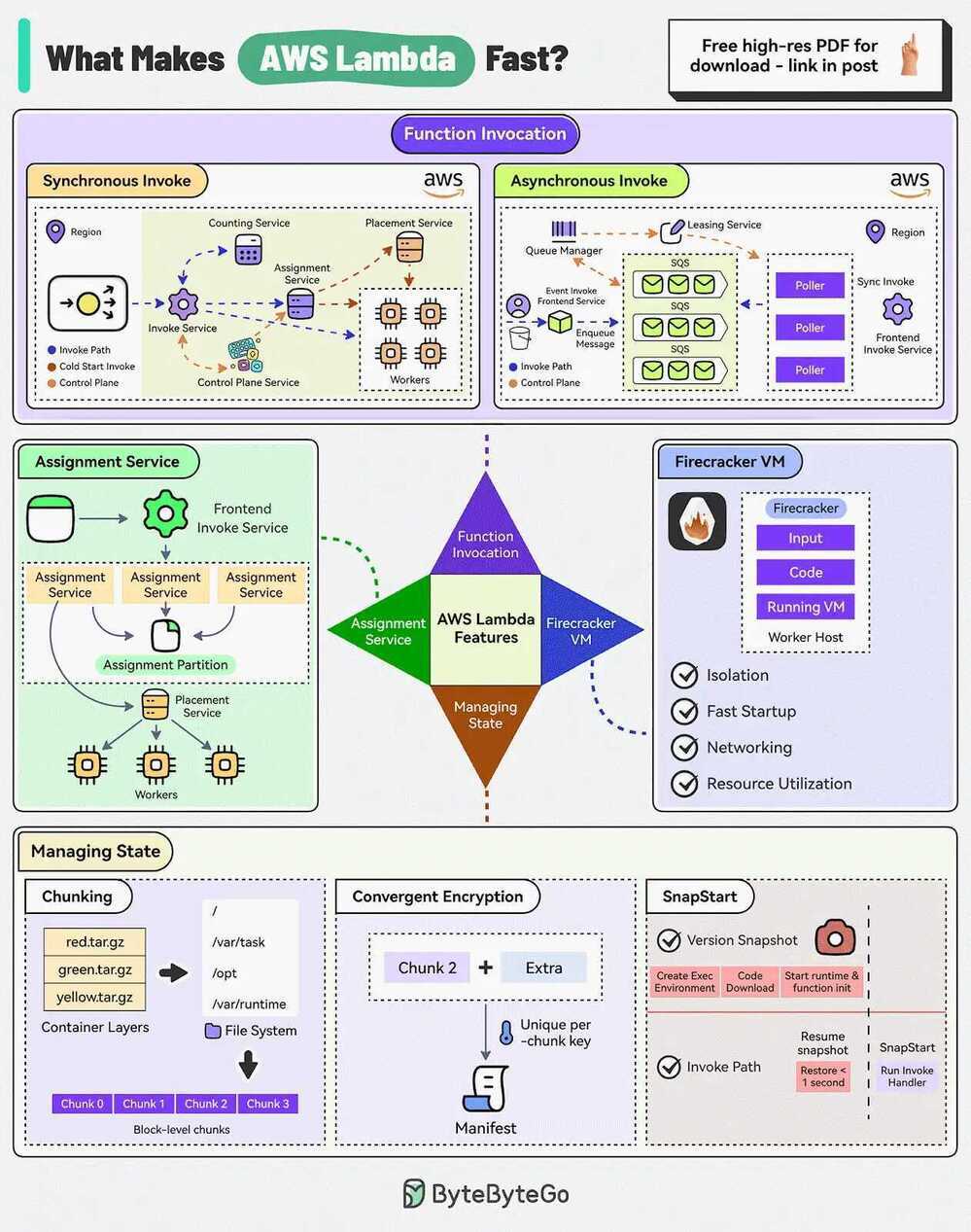
What makes AWS Lambda so fast?
There are 4 main pillars:
1 - Function Invocation
AWS Lambda supports synchronous and asynchronous invocation.
In synchronous invocation, the caller directly calls the Lambda function using AWS CLI, SDK, or other services.
In asynchronous invocation, the caller doesn’t wait for the function’s response. The request is authorized and an event is placed in an internal SQS queue. Pollers read messages from the queue and send them for processing.
2 - Assignment Service
The Assignment Service manages the execution environments.
The service is written in Rust for high performance and is divided into multiple partitions with a leader-follower approach for high availability.
The state of execution environments is written to an external journal log.
3 - Firecracker MicroVM
Firecracker is a lightweight virtual machine manager designed for running serverless workloads such as AWS Lambda and AWS Fargate.
It uses Linux’s Kernel-based virtual machine to create and manage secure, fast-booting microVMs.
4 - Component Storage
AWS Lambda also has to manage the state consisting of input data and function code.
To make it efficient, it uses multiple techniques:
- Chunking to store the container images more efficiently.
- Using convergent encryption to secure the shared data. This involves appending additional data to the chunk to compute a more robust hash.
- SnapStart feature to reduce cold start latency by pre-initializing the execution environment