Cloud Based SAAS Data Platform
Question
Scenario
Developing a Cloud-Based SaaS Data Platform. The platform will serve diverse clients, such as e-commerce businesses, healthcare providers, factories, and financial institutions needing scalable, secure, and efficient data handling.
Problem Statement
Design and develop an architecture for a cloud-based SaaS data platform that offers a service to ingest, map, store, and secure large-scale datasets.
Requirements
- Data Ingestion:
- Support real-time ingestion of data streams from APIs, message queues, and batch uploads.
- Data formats include JSON, CSV, XML, and Parquet.
- Ensure data validation during ingestion and handle schema evolution for dynamic datasets.
- Data Mapping and Transformation:
- Allow users to define mappings between raw data fields and standardised formats through a no-code/low-code UI.
- Implement ETL pipelines that scale for both real-time and batch data processing.
- Include data quality checks and deduplication mechanisms.
- Data Storage:
- Use a scalable cloud-based storage solution that supports structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data.
- Optimise for query performance, ensuring low-latency access to frequently used datasets.
- Data Retrieval
- Provide REST and Streaming APIs for data access.
- Implement advanced search capabilities with filters and aggregation functions.
- Support time-series queries and ad-hoc analytics.
- Non-Functional Requirements
- Scalability: Scale horizontally to handle millions of transactions per second.
- Security: Implement end-to-end encryption, user authentication, and role-based access control.
- Cost Optimization: Use serverless or autoscaling architectures to optimise cost for varying workloads.
- High Availability: Ensure 99.9% uptime with disaster recovery mechanisms.
- Additional Features
- Multi-Tenancy: Isolate data and configurations for different clients.
- Monitoring & Logging: Include comprehensive dashboards for monitoring system health and debugging issues.
- Compliance: Ensure compliance with data regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA.
- Stretch Goal (Optional)
- Describe how your platform could integrate with ML workflows, such as automated feature engineering or model serving.
Deliverables
- High-level block diagram detailing the data flow and key components.
- Choice of cloud services (e.g., AWS, Azure, or GCP) with justification for each.
- Explanation of how you would handle:
- Data schema evolution.
- Scaling challenges.
- Ensuring data security.
- (Optional) Brief discussion of trade-offs made in the design.
Solution
1. High-Level Block Diagram
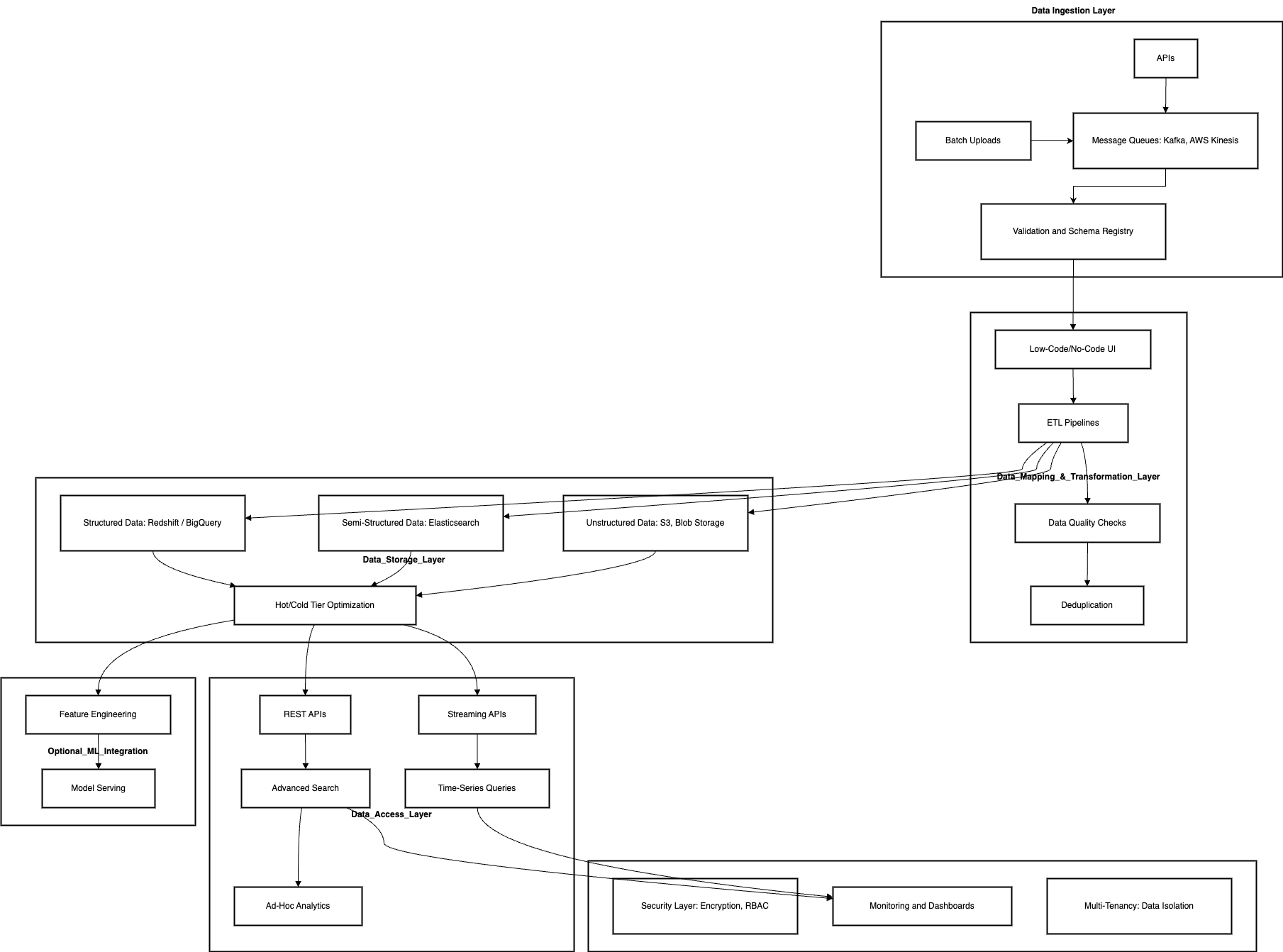
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1Kk1_INbeBsGtxDgAVCBjlUDcSLd-B2_D/view?usp=drive_link
2. Data Flow Overview
- Data Ingestion Layer:
- Real-time data ingestion: APIs, Message Queues (e.g., Kafka, AWS Kinesis).
- Batch ingestion: Bulk uploads (via SFTP, HTTP endpoints, etc.).
- Validation and Schema Registry.
- Data Mapping & Transformation Layer:
- Low-code/no-code UI for data mapping.
- Scalable ETL pipelines (real-time and batch).
- Data quality checks and deduplication.
- Data Storage Layer:
- Storage for structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data.
- Query-optimized storage for frequent access (e.g., hot and cold storage tiers).
- Data Access Layer:
- REST APIs for CRUD operations.
- Streaming APIs for real-time data access.
- Advanced search and analytics (e.g., filters, aggregations, time-series queries).
- Supporting Components:
- Security Layer: Authentication (OAuth2, JWT), role-based access control, and encryption.
- Monitoring & Logging: Real-time dashboards, alerts, and audit trails.
- Multi-Tenancy: Data isolation per client via namespace or account-level separation.
- Compliance Manager: Validation against regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
3. Choice of Cloud Services
- Compute:
- AWS Lambda / GCP Cloud Functions / Azure Functions for serverless ingestion and transformation.
- AWS Fargate / GCP Cloud Run for containerized microservices (batch jobs or long-running tasks).
- Data Ingestion:
- AWS Kinesis / GCP Pub/Sub / Azure Event Hubs for real-time data streams.
- APIs: API Gateway (AWS, GCP, or Azure) for ingesting RESTful data.
- Batch uploads: AWS S3 / GCP Cloud Storage / Azure Blob Storage for bulk files.
- Data Storage:
- AWS S3 / GCP Cloud Storage / Azure Blob Storage for unstructured data.
- AWS Redshift / GCP BigQuery / Azure Synapse for structured and semi-structured data.
- Elasticsearch / OpenSearch for advanced search capabilities.
- AWS DynamoDB / GCP Firestore for metadata or key-value pairs.
- Data Transformation:
- Apache Spark on EMR / Dataproc / Azure HDInsight for large-scale ETL.
- Schema evolution: AWS Glue Schema Registry / Confluent Schema Registry.
- Data Access:
- Amazon API Gateway / GCP Endpoints / Azure API Management for REST APIs.
- Kinesis Data Analytics / Apache Flink for real-time streaming analytics.
- Security:
- Encryption: AWS KMS / Azure Key Vault / GCP KMS.
- IAM: Role-based access control with cloud-native tools.
- Audit: AWS CloudTrail / Azure Monitor / GCP Operations Suite.
- Monitoring & Logging:
- AWS CloudWatch / GCP Operations Suite / Azure Monitor.
- Prometheus and Grafana for custom dashboards.
4. Handling Specific Challenges
Data Schema Evolution
- Implement a schema registry (AWS Glue Schema Registry or Confluent Schema Registry).
- Use versioning to support backward compatibility.
- Dynamically validate and transform incoming data based on schema versions.
Scaling Challenges
- Use autoscaling for serverless services like AWS Lambda or Kubernetes.
- Partitioning and sharding strategies for message queues and databases.
- Design storage with hot/cold tiering for cost efficiency and scalability.
Ensuring Data Security
- End-to-end encryption: Encrypt data at rest and in transit (e.g., TLS, AES-256).
- Role-based access control: Use cloud-native IAM services.
- Secure data isolation with namespaces for multi-tenancy.
5. Integration with ML Workflows
- Feature Engineering:
- Use ETL pipelines to automate feature extraction (e.g., AWS Glue + SageMaker).
- Model Serving:
- Host pre-trained models with SageMaker Endpoints / Vertex AI / Azure ML.
- Integration:
- Enable seamless access to processed data for ML workflows via APIs.
- Automate data labeling and validation using services like AWS Rekognition or custom ML pipelines.
6. Trade-Offs
- Serverless vs. Containerized Services: Serverless solutions reduce operational overhead but may have execution time limits; containers provide more control for long-running tasks.
- Hot/Cold Storage Optimization: Improves cost efficiency but may introduce latency for accessing cold storage.
- Schema Evolution Complexity: Adds design overhead but ensures flexibility for clients with diverse and changing datasets.