SQL Data Types
SQL data type rules
Databricks uses several rules to resolve conflicts among data types:
- Promotion safely expands a type to a wider type.
- Implicit downcasting narrows a type. The opposite of promotion.
- Implicit crosscasting transforms a type into a type of another type family.
You can also explicitly cast between many types:
- cast function casts between most types, and returns errors if it cannot.
- try_cast function works like cast function but returns NULL when passed invalid values.
- Other builtin functions cast between types using provided format directives.
Type precedence graph
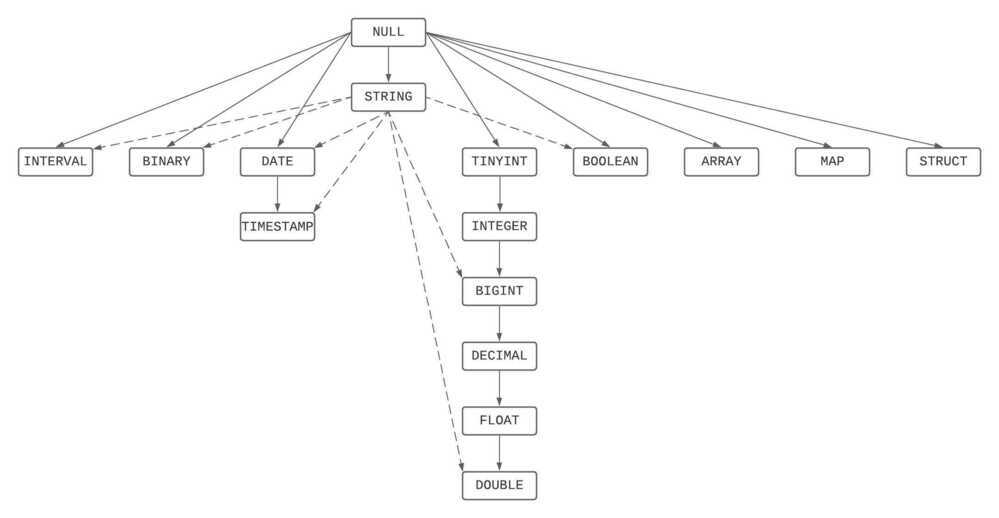
SQL data type rules | Databricks on AWS
Varchar vs NVarchar
The key difference between VARCHAR and NVARCHAR lies in their character encoding and how they handle different languages and characters. VARCHAR uses a single-byte character set, typically ASCII, and is best suited for data primarily in English or similar languages. NVARCHAR, on the other hand, uses Unicode (typically UTF-16) and can store characters from multiple languages and scripts.
Varchar vs Text
When a table has TEXT or BLOB columns, the table can't be stored in memory. This means every query (which doesn't hit cache) has to access the file system - which is orders of magnitude slower than the memory.
Therefore you should store this TEXT column in a seperate table which is only accessed when you actually need it. This way the original table can be stored in memory and will be much faster.
Think of it as separating the data into one "memory table" and one "file table". The reason for doing this is to avoid accessing of the filesystem except when neccessary (i.e. only when you need the text).
MySQL varchar(2000) vs text? - Stack Overflow