Questions
Activity Lifecycle
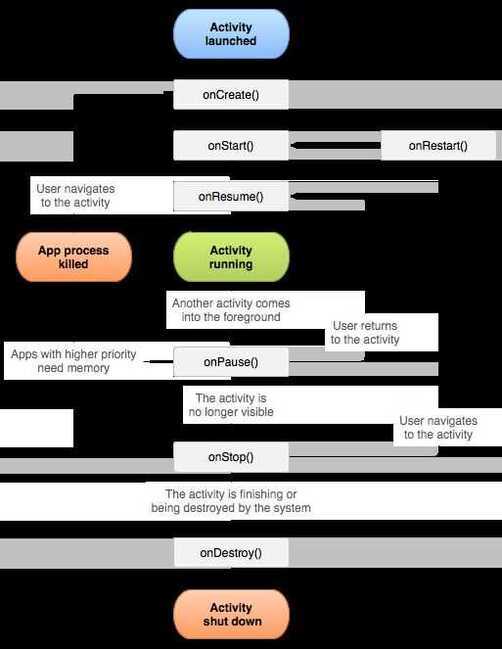
https://developer.android.com/guide/components/activities/activity-lifecycle
What is a ContentProvider and what is it typically used for?
AContentProvidermanages access to a structured set of data. It encapsulates the data and provide mechanisms for defining data security.ContentProvideris the standard interface that connects data in one process with code running in another process.
Describe three common use cases for using an Intent
Common use cases for using an Intent include:
- To start an activity: You can start a new instance of an Activity by passing an Intent tostartActivity()method.
- To start a service: You can start a service to perform a one-time operation (such as download a file) by passing an Intent tostartService().
- To deliver a broadcast: You can deliver a broadcast to other apps by passing an Intent tosendBroadcast(), sendOrderedBroadcast(), orsendStickyBroadcast().
What is DDMS? Describe some of its capabilities
DDMS is theDalvik Debug Monitor Serverthat ships with Android. It provides a wide array of debugging features including:
- port-forwarding services
- screen capture
- thread and heap information
- network traffic tracking
- incoming call and SMS spoofing
- simulating network state, speed, and latency
- location data spoofing
What is the relationship between the life cycle of an AsyncTask and an Activity? What problems can this result in? How can these problems be avoided?
An AsyncTask is not tied to the life cycle of the Activity that contains it. So, for example, if you start an AsyncTask inside an Activity and the user rotates the device, the Activity will be destroyed (and a new Activity instance will be created) but the AsyncTask will not die but instead goes on living until it completes.
Then, when the AsyncTask does complete, rather than updating the UI of the new Activity, it updates the former instance of the Activity (i.e., the one in which it was created but that is not displayed anymore!). This can lead to an Exception (of the type java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: View not attached to window manager if you use, for instance, findViewById to retrieve a view inside the Activity).
There's also the potential for this to result in a memory leak since the AsyncTask maintains a reference to the Activty, which prevents the Activity from being garbage collected as long as the AsyncTask remains alive.
For these reasons, using AsyncTasks for long-running background tasks is generally a bad idea . Rather, for long-running background tasks, a different mechanism (such as a service) should be employed.
What is an Intent? Can it be used to provide data to a ContentProvider? Why or why not?
The Intentobject is a common mechanism for starting new activity and transferring data from one activity to another. However, you cannot start a ContentProvider using an Intent.
When you want to access data in aContentProvider, you must instead use the ContentResolver object in your application's Context to communicate with the provider as a client. The Content Resolver object communicates with the provider object, an instance of a class that implements ContentProvider. The provider object receives data requests from clients, performs the requested action, and returns the results.
What is the difference between a fragment and an activity? Explain the relationship between the two
An activity is typically a single, focused operation that a user can perform (such as dial a number, take a picture, send an email, view a map, etc.). Yet at the same time, there is nothing that precludes a developer from creating an activity that is arbitrarily complex.
Activity implementations can optionally make use ofthe Fragment classfor purposes such as producing more modular code, building more sophisticated user interfaces for larger screens, helping scale applications between small and large screens, and so on. Multiple fragments can be combined within a single activity and, conversely, the same fragment can often be reused across multiple activities. This structure is largely intended to foster code reuse and facilitate economies of scale.
A fragment is essentially a modular section of an activity, with its own lifecycle and input events, and which can be added or removed at will. It is important to remember, though, that a fragment's lifecycle is directly affected by its host activity's lifecycle; i.e., when the activity is paused, so are all fragments in it, and when the activity is destroyed, so are all of its fragments.
What is difference between Serializable and Parcelable ? Which is best approach in Android ?
Serializable is a standard Java interface. You simply mark a class Serializable by implementing the interface, and Java will automatically serialize it in certain situations.
Parcelable is an Android specific interface where you implement the serialization yourself. It was created to be far more efficient than Serializable, and to get around some problems with the default Java serialization scheme.
What is the difference between Service and IntentService? How is each used?
Serviceis the base class for Android services that can be extended to create any service. A class that directly extendsServiceruns on the main thread so it will block the UI (if there is one) and should therefore either be used only for short tasks or should make use of other threads for longer tasks.
IntentService is a subclass of Servicethat handles asynchronous requests (expressed as "Intents") on demand. Clients send requests throughstartService(Intent)calls. The service is started as needed, handles eachIntentin turn using a worker thread, and stops itself when it runs out of work. Writing anIntentServicecan be quite simple; just extend theIntentServiceclass and override the onHandleIntent(Intent intent)method where you can manage all incoming requests.
What is ANR, and why does it happen?
'ANR' in Android is 'Application Not Responding.' It means when the user is interacting with the activity, and the activity is in theonResume()method, a dialog appears displaying "application not responding."
It happens because we start a heavy and long running task like downloading data in the main UI thread. The solution of the problem is to start your heavy tasks in the backbround using Async Task class.
Which method is called only once in a fragment life cycle?
onAttached()
Is it possible to create an activity in Android without a user interface ?
Yes, an activity can be created without any user interface. These activities are treated as abstract activities.
What is a broadcast receiver?
The broadcast receiver communicates with the operation system messages such as "check whether an internet connection is available," what the battery label should be, etc.