Android
Nocode
Judo brings server-driven UI to your iOS and Android apps. Build user interfaces visually in a fraction of time and publish them instantly without submitting to the app store.
Databases
- ObjectBox
- Firebase real time DB
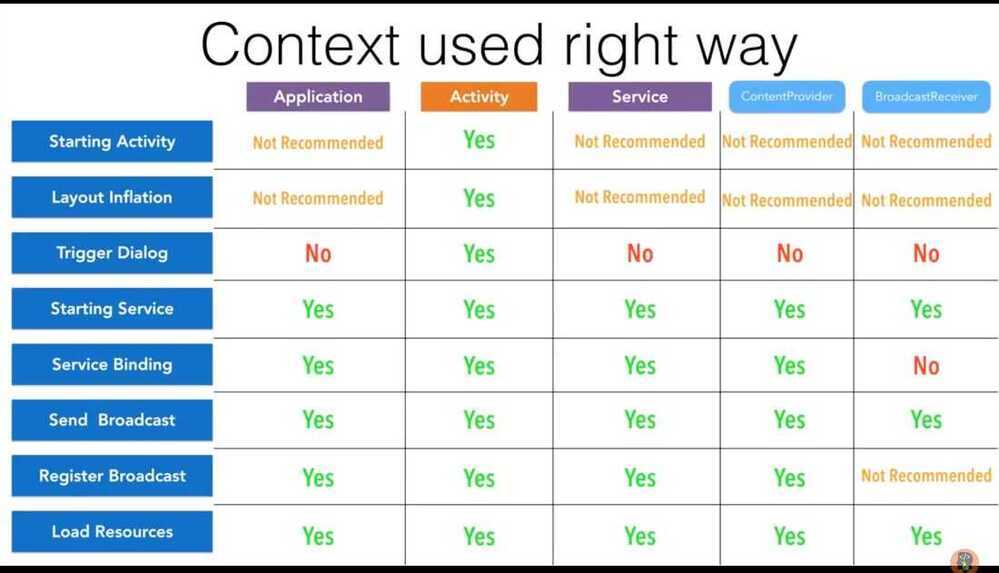
Contexts (Application Context)
https://blog.mindorks.com/understanding-context-in-android-application-330913e32514
Memory Leak - Part 1, Curious Case of Memory Leak
Contexts = Activities + Services + 1 Application Context
Libraries
Layouts
- Drawer layout
- Linear layout
- Relative layout
- Constraint layout
- Coordinator layout
- Tabbed layout
Eventbus greenbot
ORM greenbot
SQLite Database
How to corrupt - https://sqlite.org/howtocorrupt.html
RxJava GCM Mosquitto MQTT Broker
Serializable vs Parcelable
http://www.developerphil.com/parcelable-vs-serializable
Android Interface Description Language (AIDL)
AIDL (Android Interface Definition Language) allows you to define the programming interface that both the client and service agree upon in order to communicate with each other using interprocess communication (IPC). On Android, one process cannot normally access the memory of another process. So to talk, they need to decompose their objects into primitives that the operating system can understand, and marshall the objects across that boundary for you. The code to do that marshalling is tedious to write, so Android handles it for you with AIDL.
Architectural Styles
Clean Architecture
https://www.toptal.com/android/benefits-of-clean-architecture-android
Repository Pattern
https://medium.com/swlh/repository-pattern-in-android-c31d0268118c
https://developer.android.com/codelabs/kotlin-android-training-repository#0
https://medium.com/corebuild-software/android-repository-pattern-using-rx-room-bac6c65d7385
Why the Repository Pattern ?
- decouples the application from the data sources
- provides data from multiple sources (DB, API) without clients being concerned about this
- isolates the data layer
- single place, centralized, consistent access to data
- testable business logic via Unit Tests
- easily add new sources
MVI Pattern in Android without RxJava
https://proandroiddev.com/android-unidirectional-state-flow-without-rx-596f2f7637bb
HAL (Hardware Abstraction Layer)
https://source.android.com/devices/architecture/hal-types
HILT
Hilt provides a standard way to incorporate Dagger dependency injection into an Android application.
The goals of Hilt are:
- To simplify Dagger-related infrastructure for Android apps.
- To create a standard set of components and scopes to ease setup, readability/understanding, and code sharing between apps.
- To provide an easy way to provision different bindings to various build types (e.g. testing, debug, or release).
https://developer.android.com/codelabs/android-hilt
Others
- https://medium.com/snapp-mobile/android-keeping-release-and-debug-installed-all-the-time-43f5812d6637
- https://www.toptal.com/android/functional-reactive-programming-part-2
- GitHub - Genymobile/scrcpy: Display and control your Android device
- Deployment Patterns
- Soft Launch, Dark Launch, and Canary Release for Mobile Apps | Instabug
- Gradually roll out Firebase App Check using Firebase Remote Config
- How to Stage Rollout Features using Firebase Remote Config (Android & iOS) - Rebecca Franks - @riggaroo
- Android Developers Blog: Staged releases allow you to bring new features to your users quickly, safely and regularly.
- Android & Kotlin Development Masterclass – Full Course - YouTube