Indian States and UTs
India is a federal union comprising 28 states and 9 union territories, for a total of 37 entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into districts and smaller administrative divisions.
Adminstrative Divisions of India
Indian states and territories frequently use different local titles for the same level of subdivision (e.g., the mandals of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana correspond to tehsils of Uttar Pradesh and other Hindi-speaking states but to talukas of Gujarat, Goa, Karnataka, Kerala, Maharashtra, and Tamil Nadu).
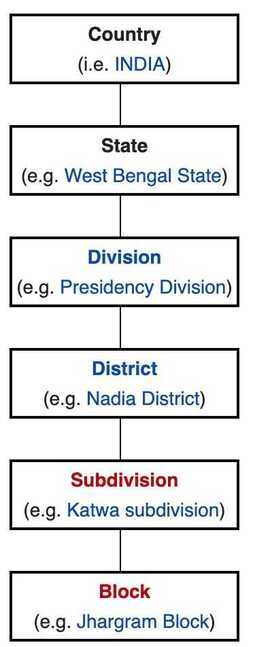
Tiers of India
Zones
The States have been grouped into six zones having an Advisory Council "to develop the habit of cooperative working" among these States.Zonal Councils were set up vide Part-III of the States Reorganisation Act, 1956. The North Eastern States' special problems are addressed by another statutory body - The North Eastern Council, created by the North Eastern Council Act, 1971. The present composition of each of these Zonal Councils is as under:
- Northern Zonal Council, comprising Chandigarh, Delhi, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Ladakh, Punjab, and Rajasthan;
- North Eastern Council, comprising Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland and Tripura; The State of Sikkim has also been included in the North Eastern Council vide North Eastern Council (Amendment) Act, 2002 notified on 23 December 2002.
- Central Zonal Council, comprising the States of Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Uttarakhand and Uttar Pradesh;
- Eastern Zonal Council, comprising Bihar, Jharkhand, Odisha, and West Bengal;
- Western Zonal Council, comprising Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Daman and Diu, Goa, Gujarat, and Maharashtra;
- Southern Zonal Council, comprising Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Puducherry, Tamil Nadu, and Telangana.
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Lakshadweep are not members of any of the Zonal Councils. However, they are presently special invitees to the Southern Zonal Council