Amazon EBS
EBS Usage
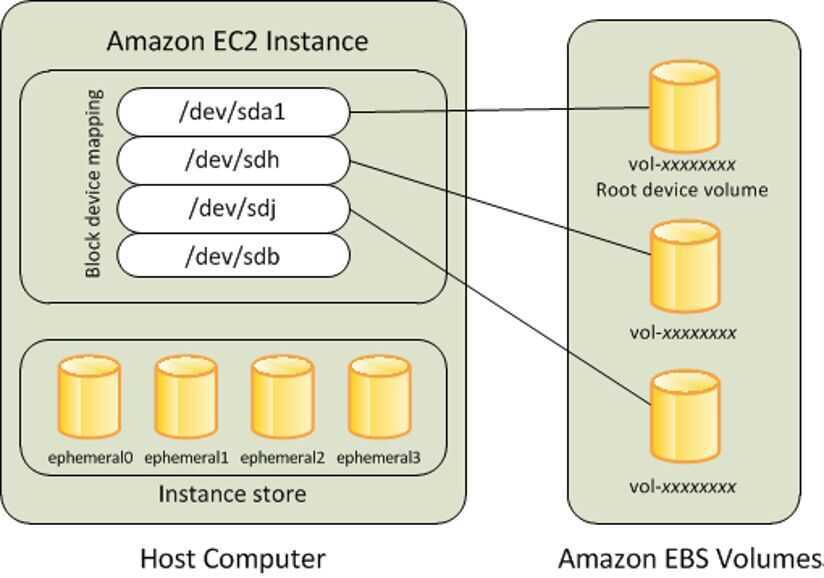
EBS volumes are network-attached storage that persists independently from the running life of a single EC2 instance. After an EBS volume is attached to an EC2 instance, you can use the EBS volume similar to a physical hard drive -- typically by formatting it with the file system of your choice and using the file I/O interface provided by the instance operating system. Multiple EBS volumes can be attached to a single EC2 instance and it allows you to dynamically increase capacity, tune performance, and change the type of any new or existing current generation volume with no downtime or performance impact. Furthermore EBS provides the ability to save point-in-time snapshots of your volumes. Each separate volume can be configured as EBS General Purpose (SSD), Provisioned IOPS (SSD), Throughput Optimized (HDD), or Cold (HDD) as needed
The volumes types fall into two categories:
- SSD-backed volumes optimized for transactional workloads involving frequent read/write operations with small I/O size, where the dominant performance attribute is IOPS
- HDD-backed volumes optimized for large streaming workloads where throughput (measured in MiB/s) is a better performance measure than IOPS
Amazon EBS volume types - Amazon EBS
Durability & availability
Amazon EBS cloud service is designed to be highly available and reliable. As mentioned earlier EBS volumes data is replicated across multiple servers within availability zones. Taking snapshots of your EBS volumes increases the durability of the data stored on your EBS volumes. Furthermore, EBS volumes are designed for an Annual Failure Rate (AFR)of between 0.1 and 0.2 percent, where failure refers to a complete or partial loss of the volume, depending on the size and performance of the volume.
Termination
When you launch an instance, the root device volume contains the image used to boot the instance. You can choose between AMIs backed by Amazon EC2 instance store and AMIs backed by Amazon EBS.
By default, the root volume for an AMI backed by Amazon EBS is deleted when the instance terminates. You can change the default behavior to ensure that the volume persists after the instance terminates. Non-root EBS volumes remain available even after you terminate an instance to which the volumes were attached.
Security
IAM service enables access to EBS volumes, allowing you to specify who can access which EBS volumes. EBS encryption enables data-at-rest and data-in-motion security. It offers seamless encryption of both EBS boot volumes and data volumes as well as snapshots. Access control plus encryption offers a strong defense-in-depth security strategy for your data.
Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS) provides block-level storage volumes for use with Amazon EC2 instances. When you create an encrypted Amazon EBS volume and attach it to a supported instance type, data stored at rest on the volume, data moving between the volume and the instance, snapshots created from the volume and volumes created from those snapshots are all encrypted. It uses AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS) customer master keys (CMK) when creating encrypted volumes and snapshots. Encryption operations occur on the servers that host Amazon EC2 instances, ensuring the security of both data-at-rest and data-in-transit between an instance and its attached Amazon EBS storage.
- Data at rest inside the volume is encrypted
- Data moving between the volume and the instance is encrypted
- Any snapshot created from the volume is encrypted
| Volume type | General Purpose SSD (gp2) | Provisioned IOPS SSD (io1) | Throughput Optimized HDD (st1) | Cold HDD (sc1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Description | General purpose SSD volume that balances price and performance for a wide variety of workloads | Highest-performance SSD volume for mission-critical low-latency or high-throughput workloads | Low-cost HDD volume designed for frequently accessed, throughput-intensive workloads | Lowest cost HDD volume designed for less frequently accessed workloads |
| Use cases | Recommended for most workloads; System boot volumes; Virtual desktops; Low-latency interactive apps; Development and test environments; Critical business applications that require sustained IOPS performance, or more than 16,000 IOPS or 250 MiB/s of throughput per volume; Large database workloads, such as:; MongoDB; Cassandra; Microsoft SQL Server; MySQL; PostgreSQL; Oracle; Streaming workloads requiring consistent, fast throughput at a low price; Big data; Data warehouses; Log processing; Cannot be a boot volume; Throughput-oriented storage for large volumes of data that is infrequently accessed; Scenarios where the lowest storage cost is important; Cannot be a boot volume | |||
| Pricing | $0.114per GB-month of provisioned storage | $0.131per GB-month of provisioned storage AND$0.068per provisioned IOPS-month | $0.051per GB-month of provisioned storage | $0.029per GB-month of provisioned storage |
Pricing
EBS Pricing - 100 GB - $11.4 per month
S3 Pricing - 100 GB - $2.5 per month
S3 Pricing - First 50 TB / Month - $0.025per GB
S3 Standard - Infrequent Access* - For long lived but infrequently accessed data that needs millisecond access - $0.019per GB
S3 Glacier** - For long-term backups and archives with retrieval option from 1 minute to 12 hours - $0.005per GB
S3 Glacier Deep Archive** - For long-term data archiving that is accessed once or twice in a year and can be restored within 12 hours - $0.002per GB
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/ebs-volume-types.html
Amazon EBS Multi-Attach
Amazon EBS Multi-Attach enables you to attach a single Provisioned IOPS SSD (io1 or io2) volume to multiple instances that are in the same Availability Zone. You can attach multiple Multi-Attach enabled volumes to an instance or set of instances. Each instance to which the volume is attached has full read and write permission to the shared volume. Multi-Attach makes it easier for you to achieve higher application availability in clustered Linux applications that manage concurrent write operations.
Multi-Attach is supported exclusively on Provisioned IOPS SSD volumes.
Multi-Attach is now available on Amazon EBS Provisioned IOPS volume type, io2. Launched in August 2020, io2 is the newest generation of our Provisioned IOPS volume type designed for 99.999% durability (100x io1) and 500:1 IOPS:GiB (10x io1). Multi-Attach lets you share access to an EBS data volume between up to 16 Nitro-based EC2 instances within the same Availability Zone (AZ). Each attached instance has full read and write permission to the shared volume. Multi-Attach is intended to make it easier to achieve higher application availability for customers that want to deploy applications that manage storage consistency from multiple writers in shared storage infrastructure.
Attach an EBS volume to multiple EC2 instances using Multi-Attach - Amazon EBS
- Multi-Attach enabled volumes can be attached to up to 16 instances built on the Nitro System that are in the same Availability Zone.
Provisioned IOPS SSD (io1)
Provisioned IOPS SSD (io1) is backed by solid-state drives (SSDs) and is a high-performance Amazon EBS storage option designed for critical, I/O intensive database and application workloads, as well as throughput-intensive database workloads. io1 is designed to deliver a consistent baseline performance of up to 50 IOPS/GB to a maximum of 64,000 IOPS and provide up to 1,000 MB/s of throughput per volume. Therefore, the io1 volume type would be able to meet the requirement of 25,000 IOPS per volume for the given use-case.
gp2 vs gp3
| Volume Type | gp3 | gp2 |
|---|---|---|
| Short Description | Lowest cost SSD volume that balances price performance for a wide variety of transactional workloads | General Purpose SSD volume that balances price performance for a wide variety of transactional workloads |
| Durability | 99.8% - 99.9% durability | 99.8% - 99.9% durability |
| Use Cases | Virtual desktops, medium sized single instance databases such as Microsoft SQL Server and Oracle, latency sensitive interactive applications, boot volumes, and dev/test environments | Virtual desktops, medium sized single instance databases such as Microsoft SQL Server and Oracle, latency sensitive interactive applications, boot volumes, and dev/test environments |
| API Name | gp3 | gp2 |
| Volume Size | 1 GB - 16 TB | 1 GB - 16 TB |
| Max IOPS/Volume | 16,000 | 16,000 |
| Max Throughput*/Volume | 1,000 MB/s | 250 MB/s |
| Max IOPS/Instance | 260,000 | 260,000 |
| Max Throughput/Instance | 12,500 MB/s | 7,500 MB/s |
| Price | $0.08/GB-month; 3,000 IOPS free and; $0.005/provisioned IOPS-month over 3,000;; 125 MB/s free and; $0.04/provisioned MB/s-month over 125 | $0.10/GB-month |
General Purpose SSD (gp2) volumes offer cost-effective storage that is ideal for a broad range of workloads. These volumes deliver single-digit millisecond latencies and the ability to burst to 3,000 IOPS for an extended duration. Between a minimum of 100 IOPS (at 33.33 GiB and below) and a maximum of 16,000 IOPS (at 5,334 GiB and above), baseline performance scales linearly at 3 IOPS per GiB of volume size. AWS designs gp2 volumes to deliver a provisioned performance of 99% uptime. A gp2 volume can range in size from 1 GiB to 16 TiB.
Migrate your Amazon EBS volumes from gp2 to gp3 and save up to 20% on costs | AWS Storage Blog
- It might take up to 24 hours for a new configuration to take effect, and in some cases more, such as when the volume has not been fully initialized. Typically, a fully used 1-TiB volume takes about 6 hours to migrate to a new performance configuration. Transitional volume performance will be no less than the source volume performance. If you are downgrading IOPS, transitional volume performance is no less than the target volume performance.
Changing RDS storage from gp2 to gp3 | AWS re:Post
- There is no downtime associated but always plan to make modifications at the time when clusters is expected to be least busy. There wouldn't be downtime, you may see "Storage Optimization" status.
gp2 to gp3 migration for Amazon RDS | by Rajesh Kantamani | Medium
Underutilized EBS
Neglecting Underutilized EBS Volumes: A Costly Oversight in AWS | by puggy | Medium
Is there a way to programmatically find unused EBS Volume usage? : r/aws
Decreasing Size
Can I reduce an over-sized EBS volume? | AWS re:Post
Increasing Size
Extend the file system after resizing an Amazon EBS volume - Amazon EBS
# xen based instance
sudo lsblk
sudo growpart /dev/xvda 1
df -hT
sudo resize2fs /dev/root
Amazon EBS Snapshot
You can back up the data on your Amazon EBS volumes to Amazon S3 by taking point-in-time snapshots. Snapshots are incremental backups, which means that only the blocks on the device that have changed after your most recent snapshot are saved. This minimizes the time required to create the snapshot and saves on storage costs by not duplicating data. When you delete a snapshot, only the data unique to that snapshot is removed. Each snapshot contains all of the information that is needed to restore your data (from the moment when the snapshot was taken) to a new EBS volume.
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/EBSSnapshots.html
EBS volumes provide durable block-level storage for use with EC2 instances in the AWS cloud. Volumes are automatically replicated within Availability Zones for high availability and durability.
Amazon EBS fast snapshot restore (FSR)
Amazon EBS fast snapshot restore (FSR) enables you to create a volume from a snapshot that is fully initialized at creation. This eliminates the latency of I/O operations on a block when it is accessed for the first time. Volumes that are created using fast snapshot restore instantly deliver all of their provisioned performance.
To get started, enable fast snapshot restore for specific snapshots in specific Availability Zones. Each snapshot and Availability Zone pair refers to one fast snapshot restore. When you create a volume from one of these snapshots in one of its enabled Availability Zones, the volume is restored using fast snapshot restore.
You must explicitly enable fast snapshot restore for each snapshot. For example, if you create a new snapshot from a volume that was restored from a fast snapshot restore-enabled snapshot, the new snapshot is not automatically enabled for fast snapshot restore. If you copy a snapshot that is enabled for fast snapshot restore, the snapshot copy is not automatically enabled for fast snapshot restore.