Andrew NG
Model and cost function
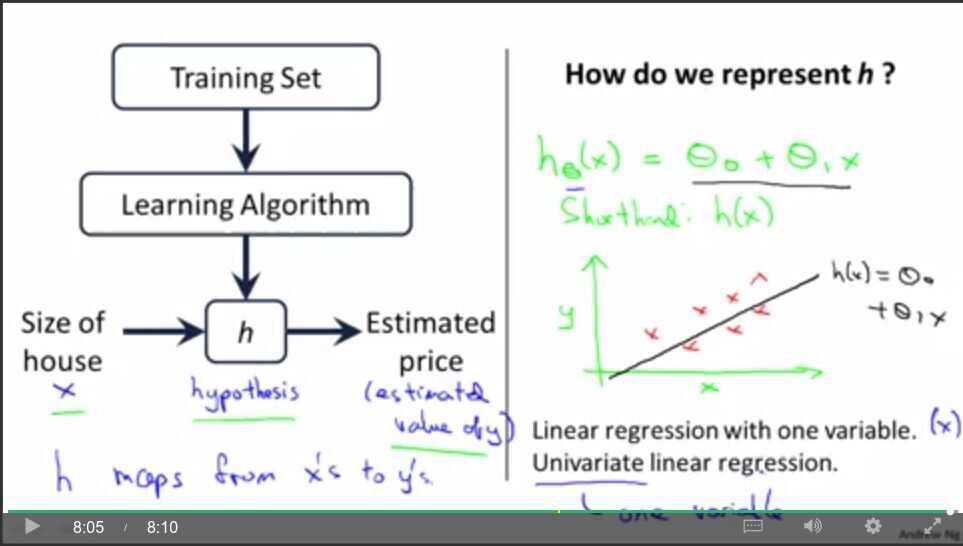
- Model representation - Linear regression using Training set
m - number of training examples
x's - input variables / features
y's - output variable / "target" variable
(x,y) - one training example
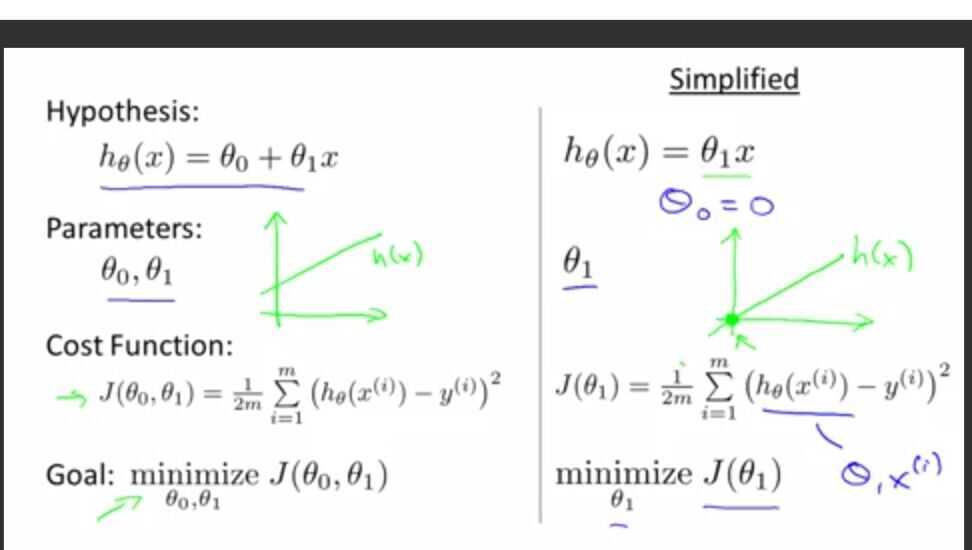
2. Cost function
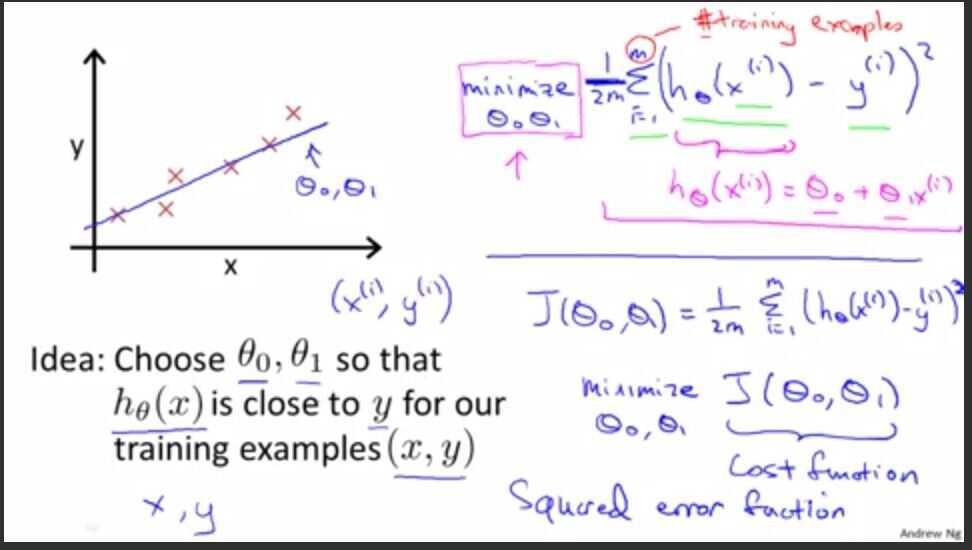
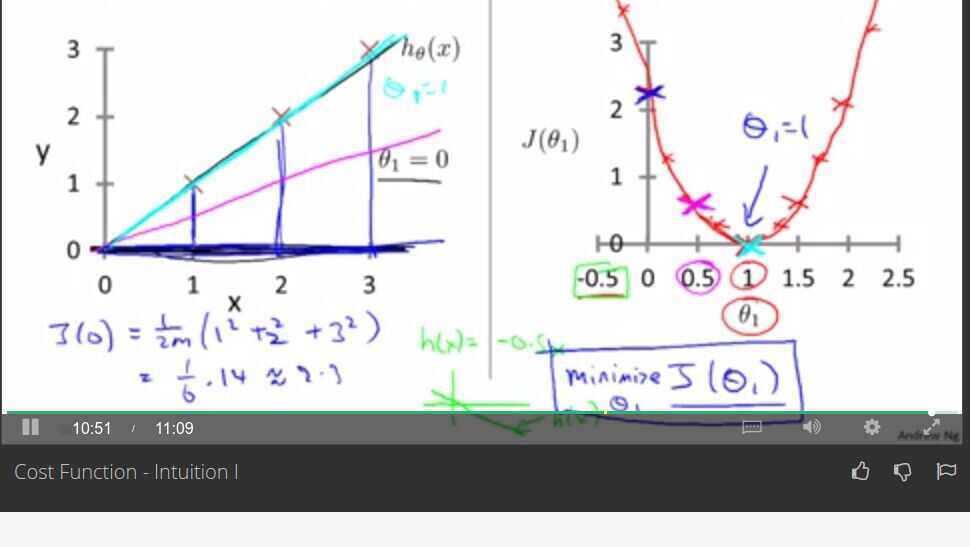
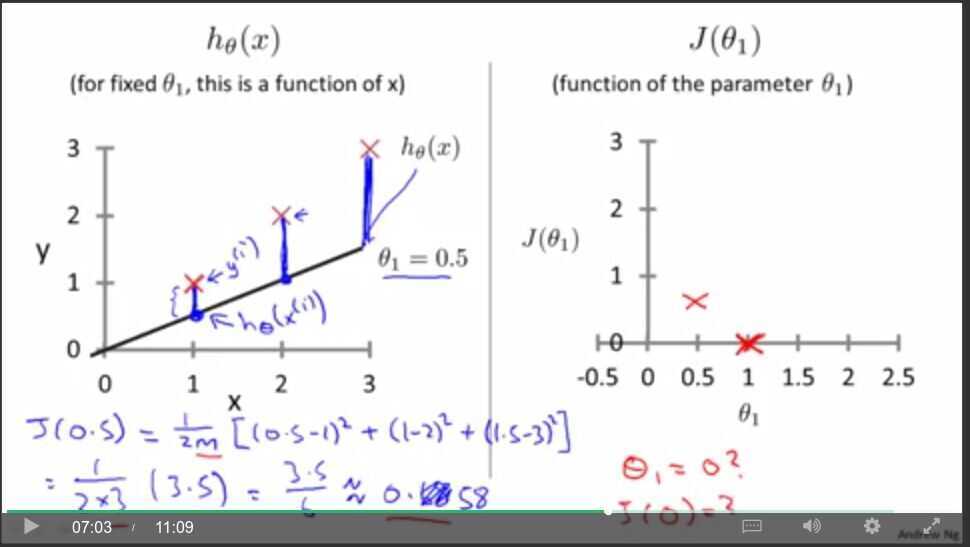
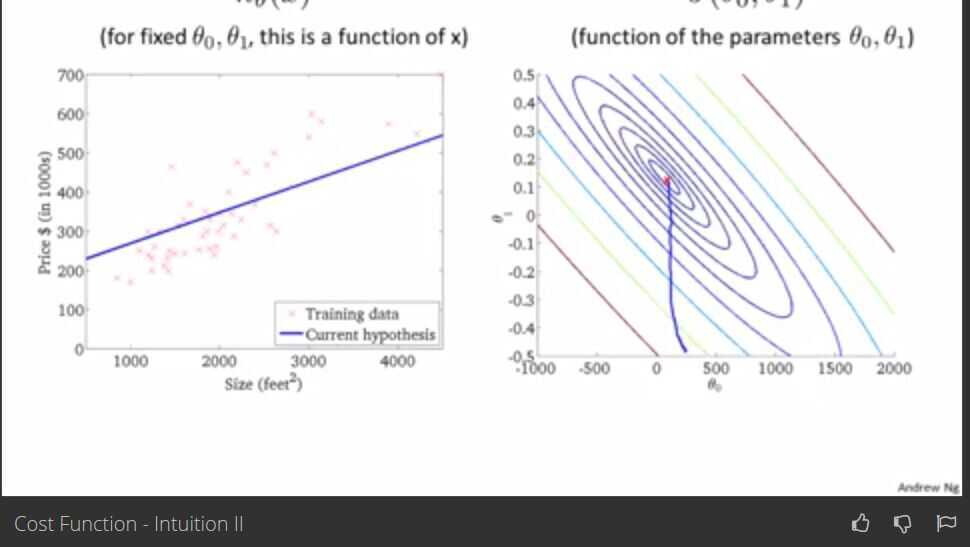
Cost function intuition -
Octave
- Singular Value Decomposition (SVD)
Every nxm matrix can be written as a product of three smaller matrices.
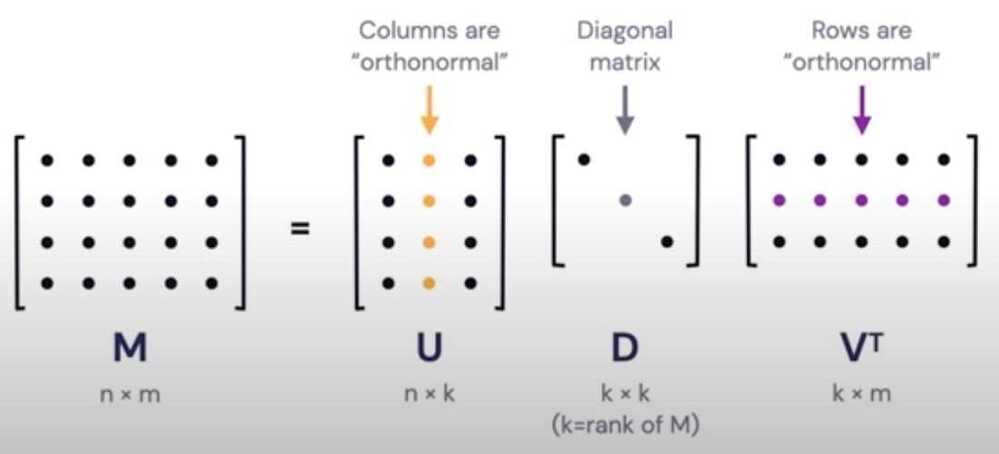
- SVD appreas in lots of places
- Statistics (PCA)
- Chemical physics
- Image processing
- Genomics
- Robotics
- Quantum physics (entanglement)
- Data embeddings / vector embeddings
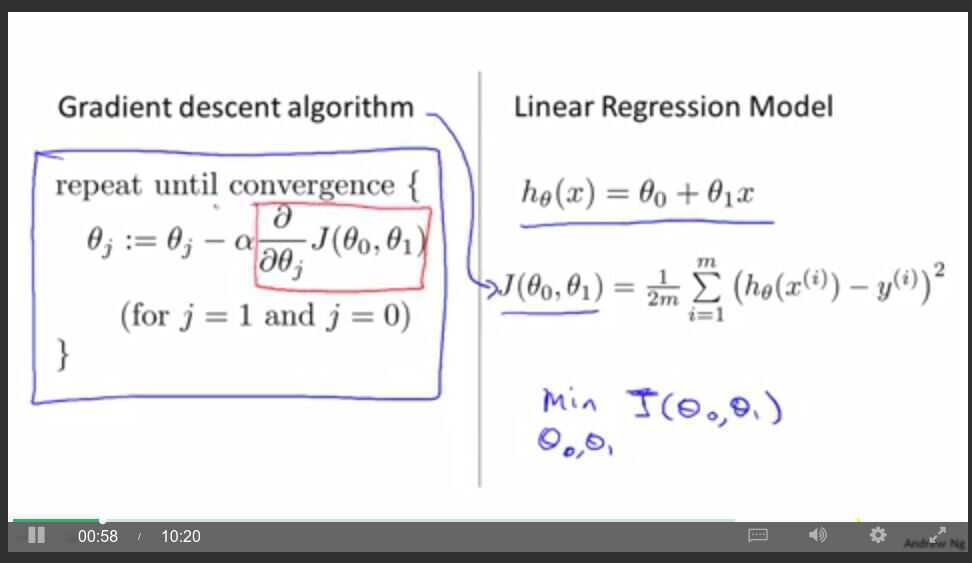
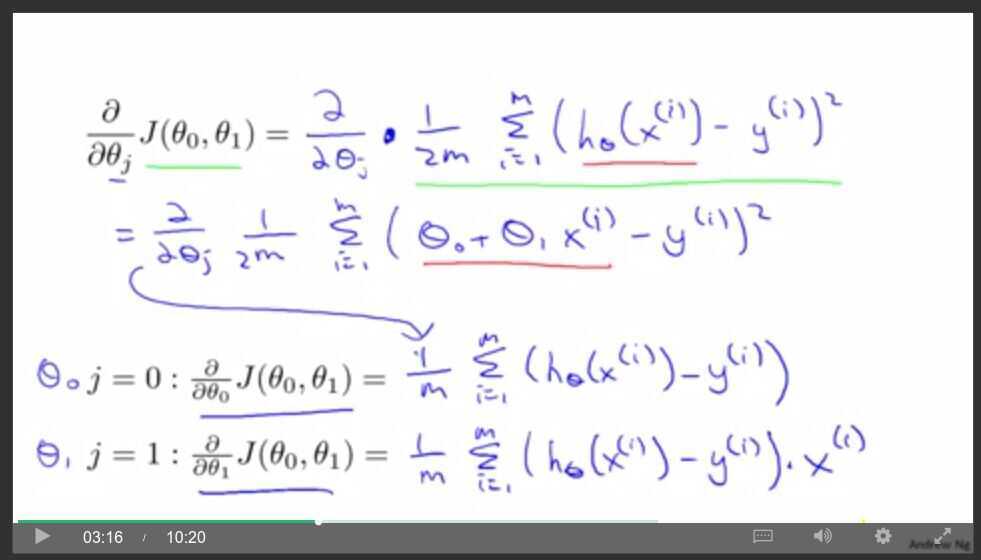
Gradient Descent for Linear regression with one variable
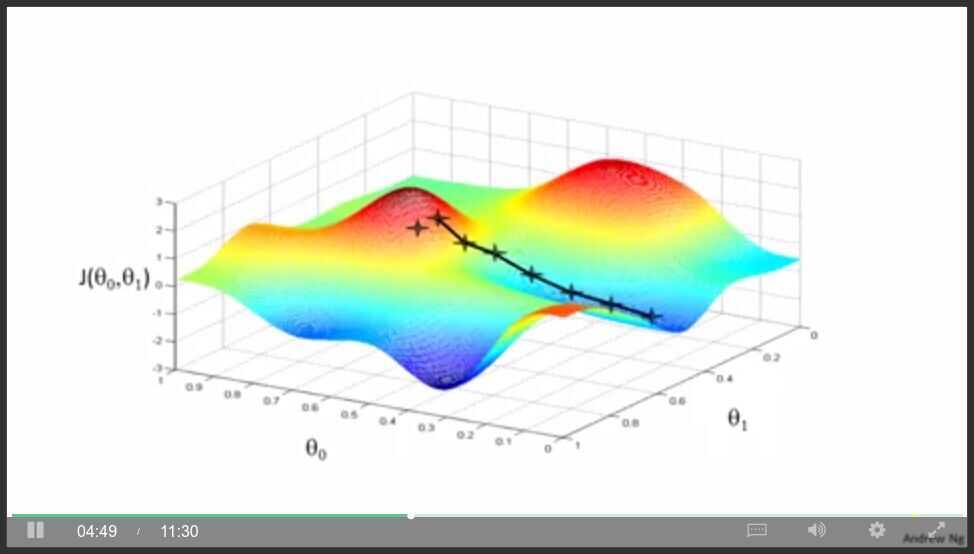
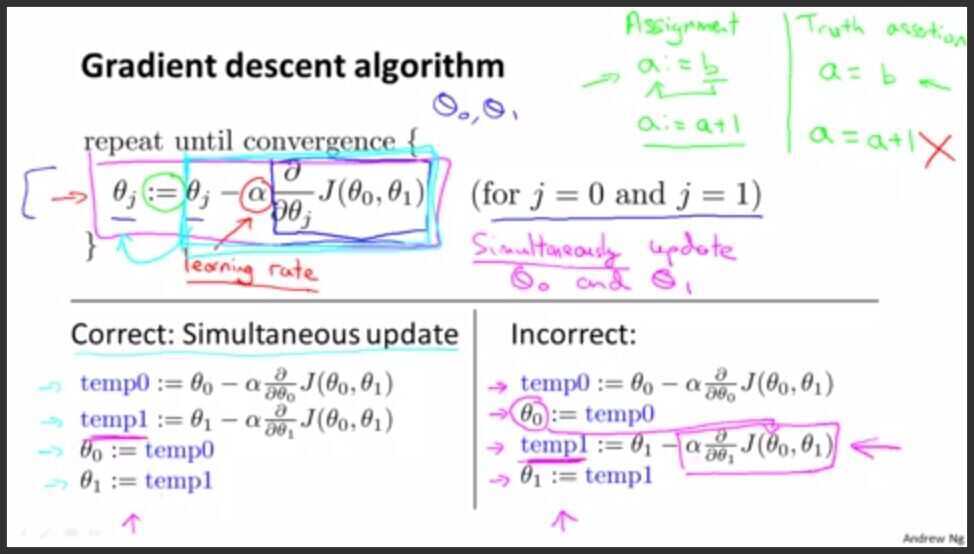
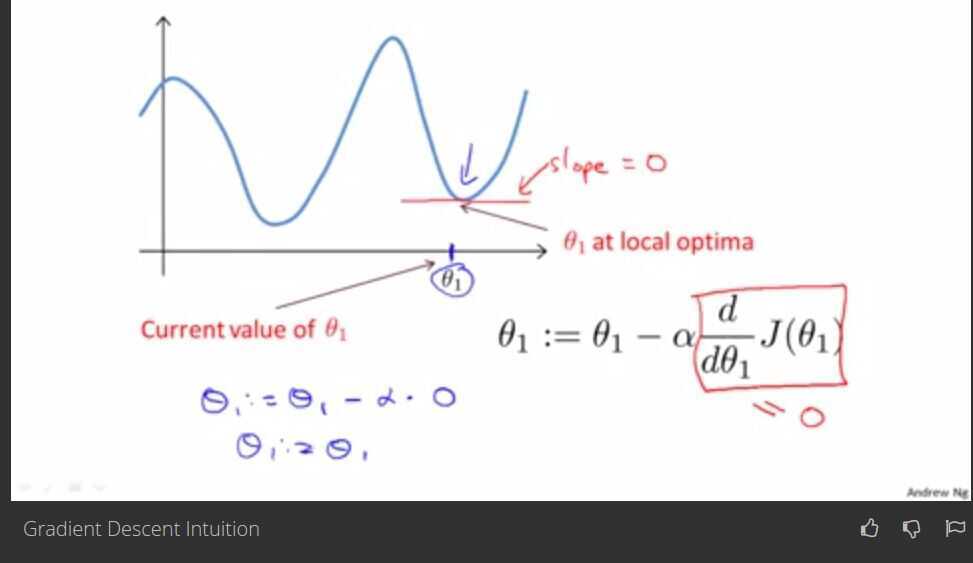
Gradient descent intuition
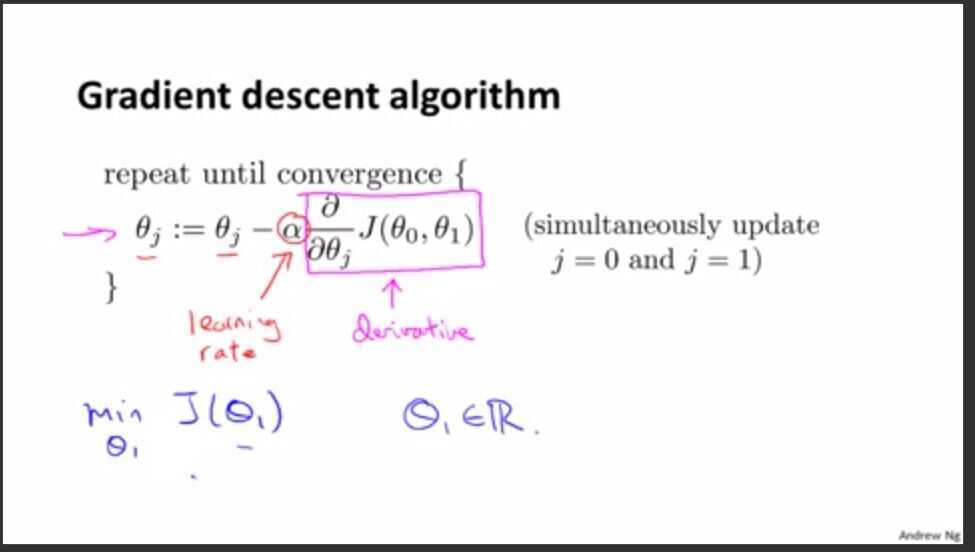
Derivative term
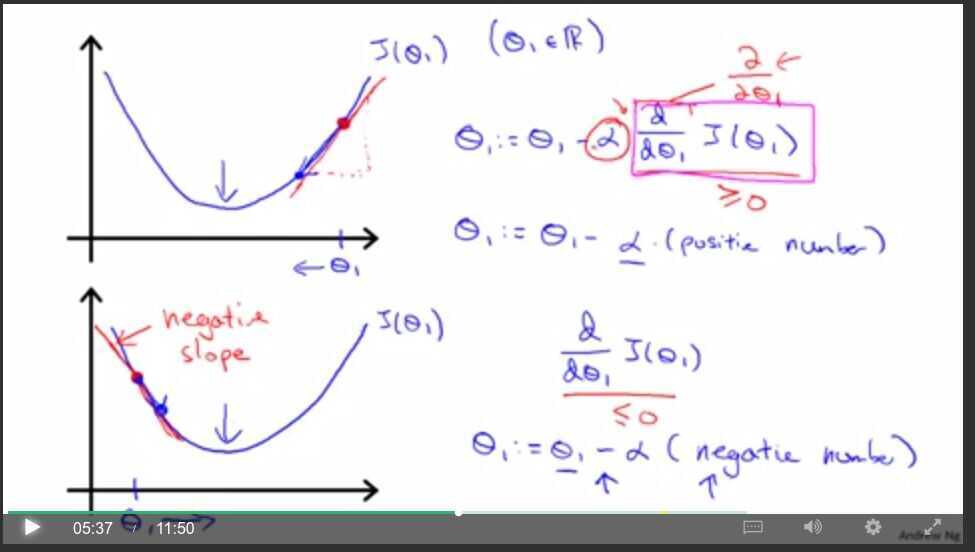
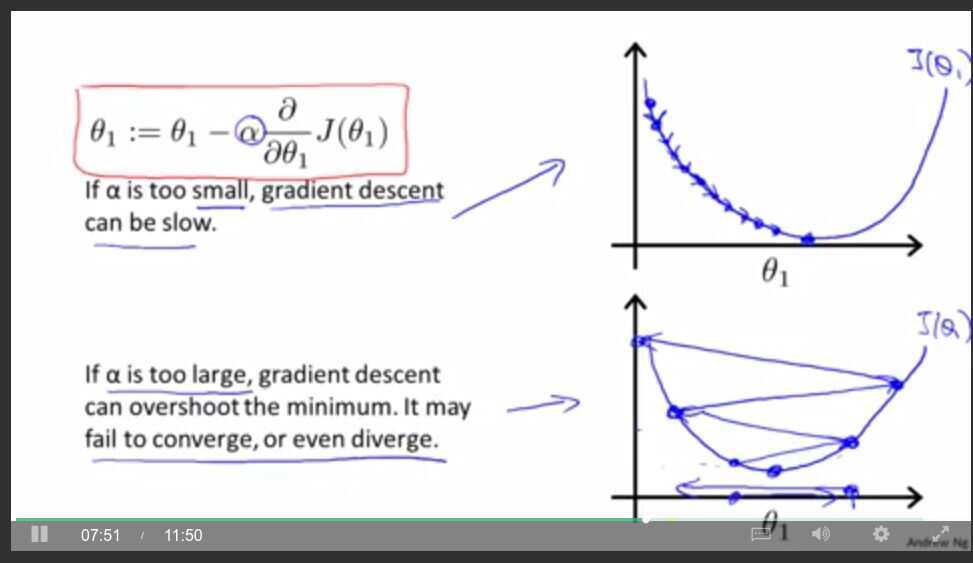
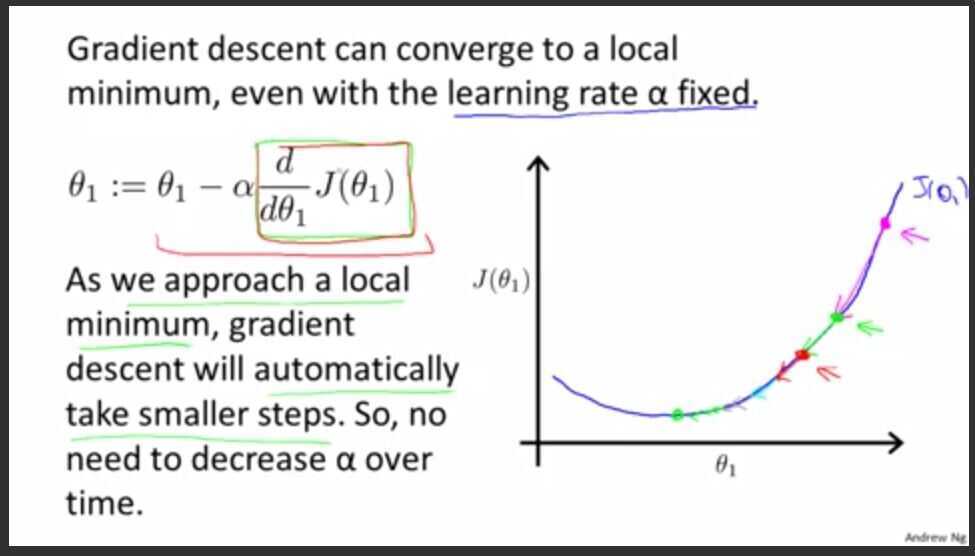
Alpha
Gradient Descent for Linear Regression
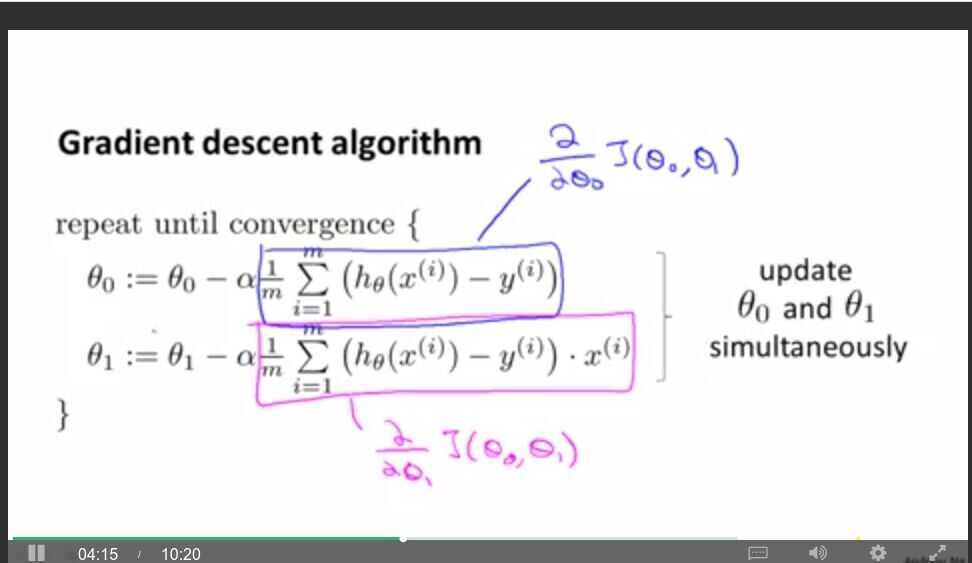
Gradient descent is a convex function (Global minimum)
Also called (Batch gradient descent) becauses look at all training sample.
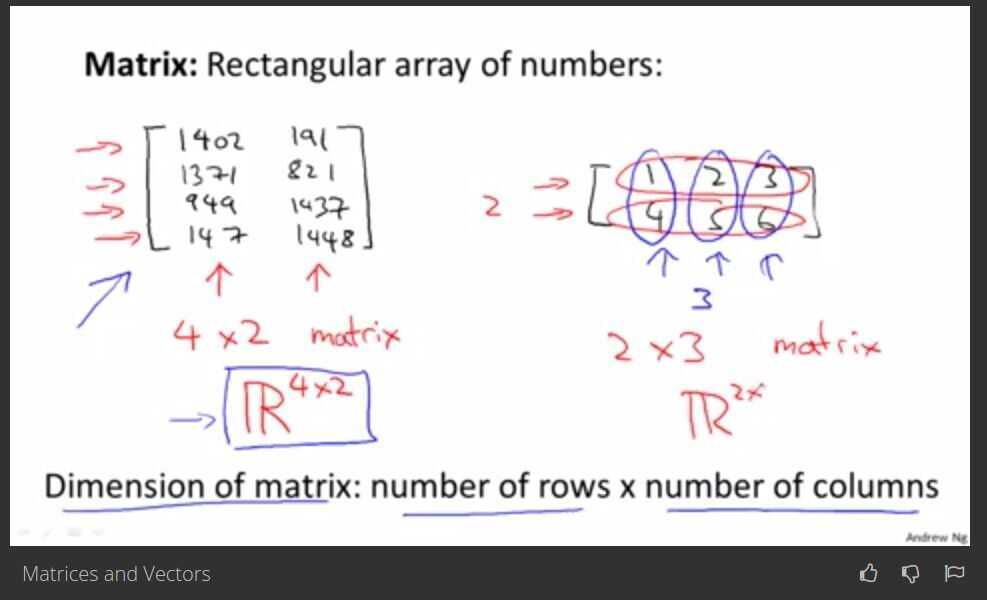
Linear Algebra Review
Matrix - Rectangular array of numbers.
Dimension of matrix : number of rows * number of columns
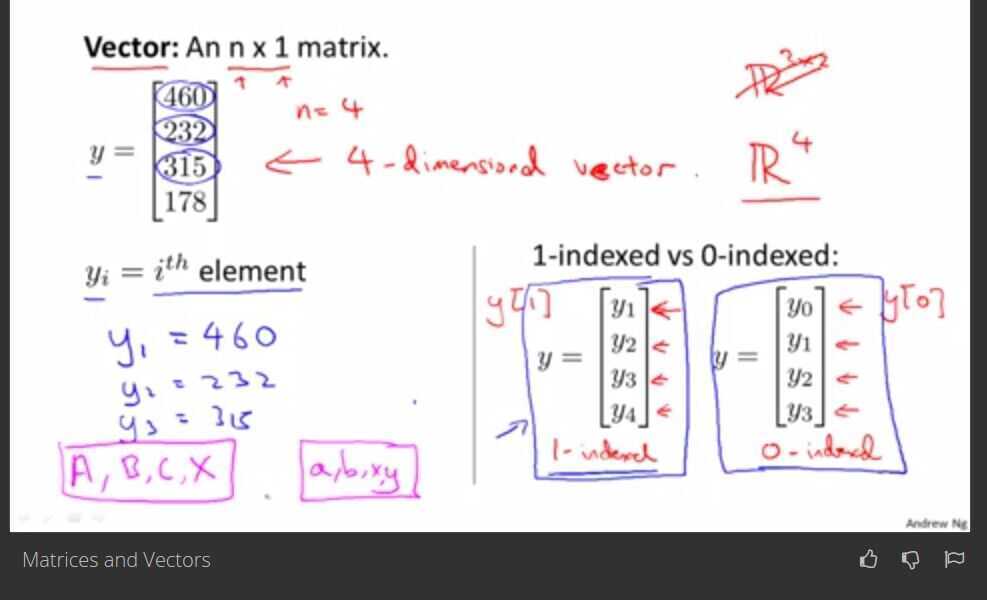
Vector - is a matrix with one column (n*1 matrix)
Uppercase for matrices
Lower case for others variables, vectors, etc.
Addition and Scalar Multiplication
Scalar multiplication is 3matrix (nmatrix).
Scalar division is ⅓ * matrix
Matrix Vector Multiplication
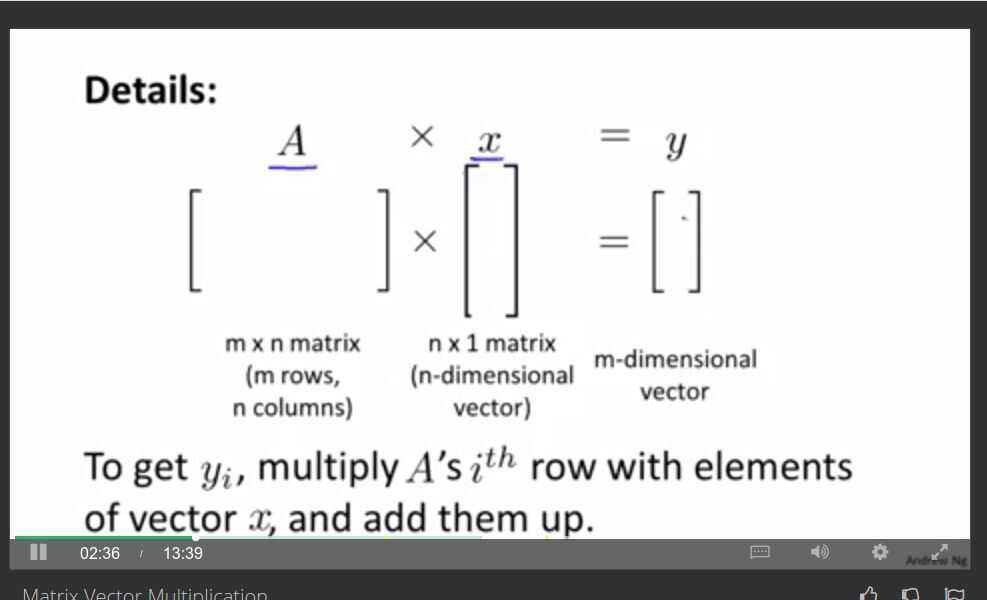
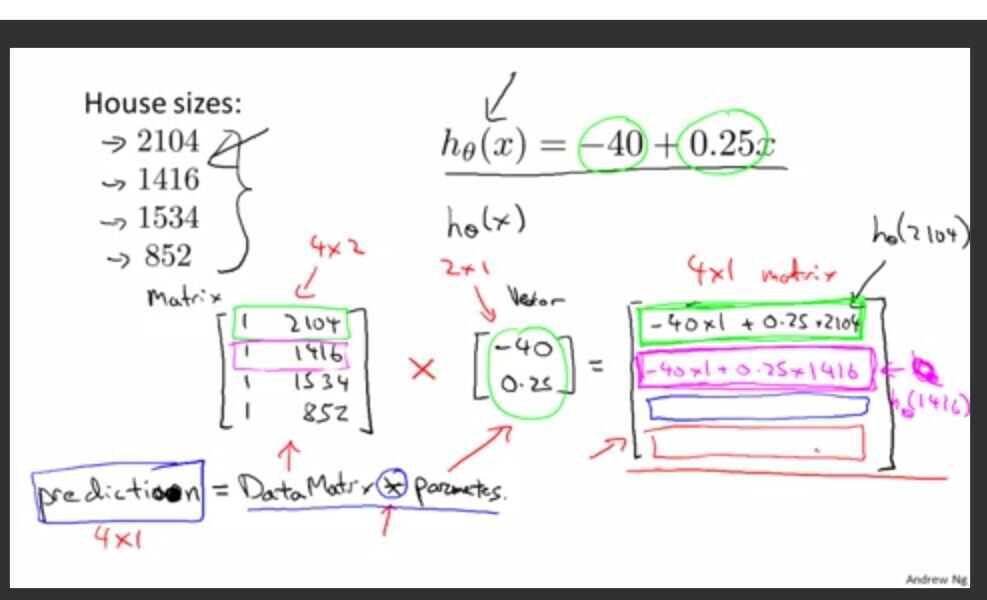
Calculating hypothesis using matrix-vector multiplication in octave its easy
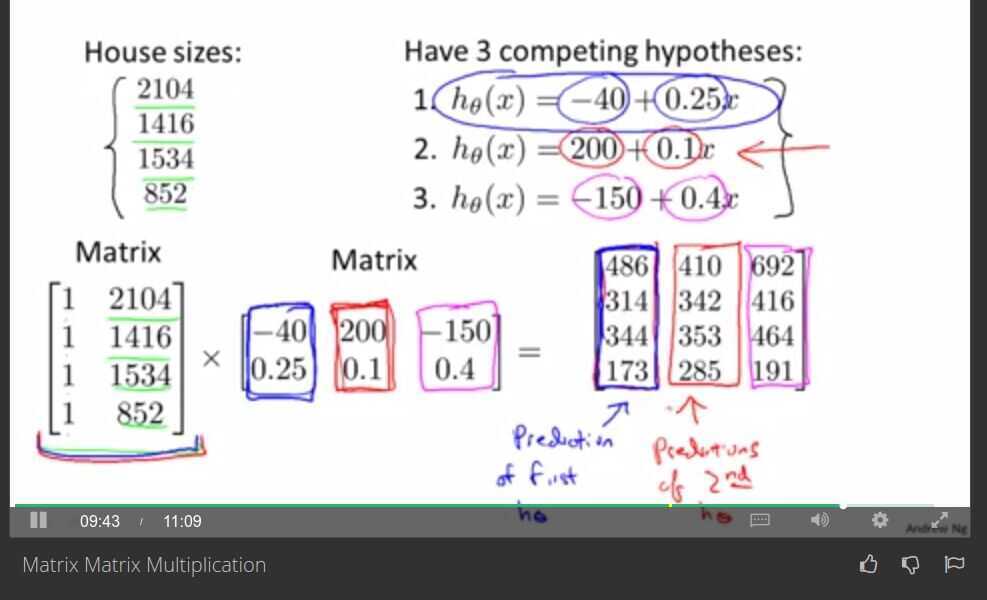
Matrix - Matrix multiplication
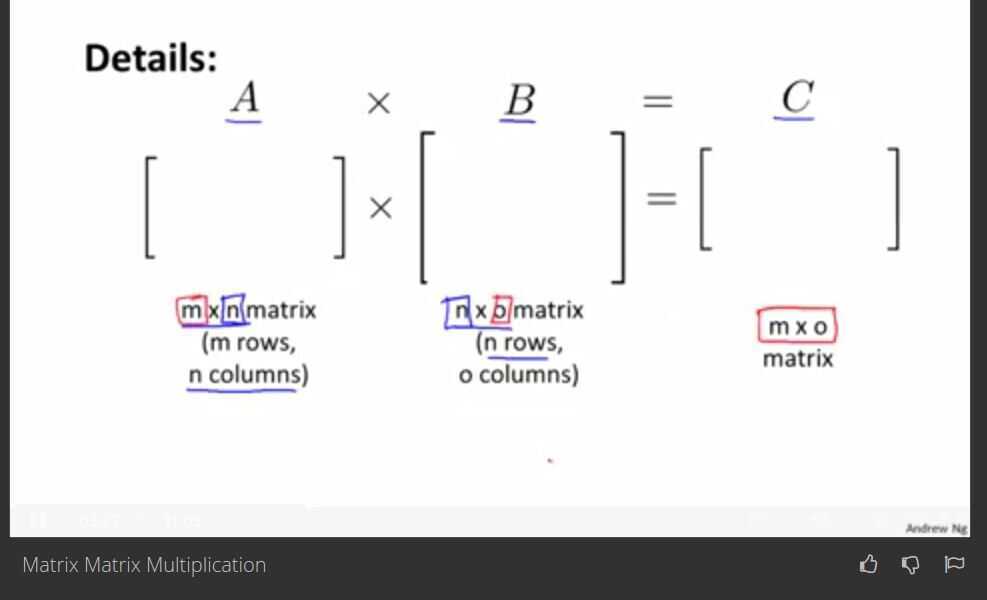
If we have 3 hypothesis with 4 houses then,
Multiplication Properties
- Multiplication is not commutative ( AB not equal to BA)
- Multiplication is Associative ( a*(bc) = (ab)*c)
- Identity matrix (A.I = I.A = A)
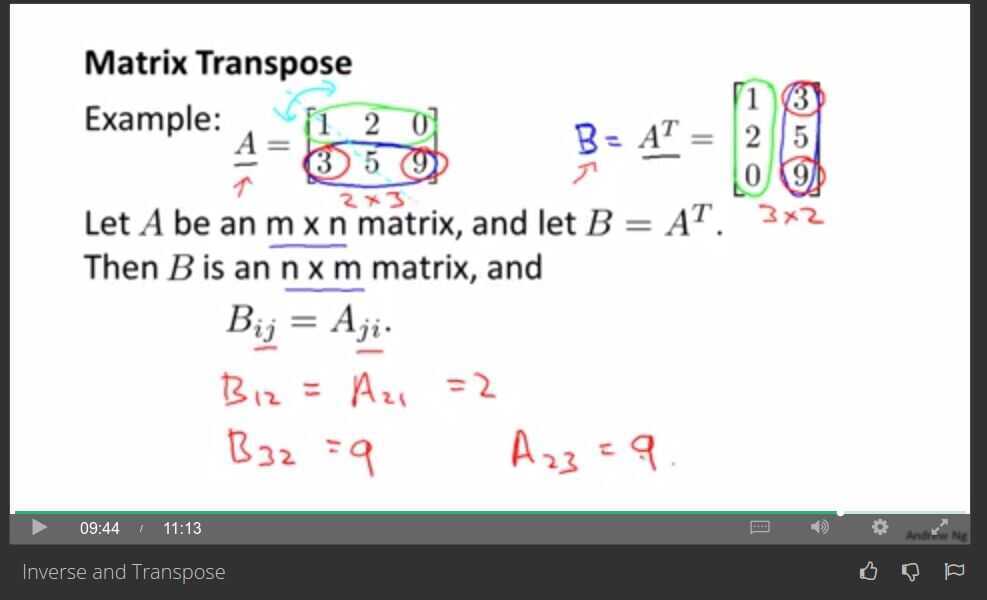
Matrix Inverse and Transpose
Matrix Inverse:
- 0 does not have an inverse.
- 3 inverse is 3-1
- Matrix inverse ( A * A-1 = Identity)
- Matrix that don't have an inverse are singular or degenerate matrix
- Ex- 0 matrix doesn't have inverse.
Matrix Transpose: