Design of Key-Value Stores
- We will discuss the design and insight of key-value/NoSQL stores for today's cloud storage systems.
- We will also discuss Apache Cassandra and different consistency solutions
The Key-Value Abstration
-
(Business) Key -> Value
-
(flipkart.com) item number -> information about it
-
(easemytrip.com) Flight number -> information about flight, e.g., availability
-
(twitter.com) tweet id -> information about tweet
-
(mybank.com) account number -> information about it
-
It's a dictionary datastructure
- Insert, lookup, and delete by key
- Example: hash table, binary tree
-
But distributed
-
Seems familiar? Remember Distributed Hash Tables (DHT) in P2P systems
-
Key-value stores reuse many techniques from DHTs
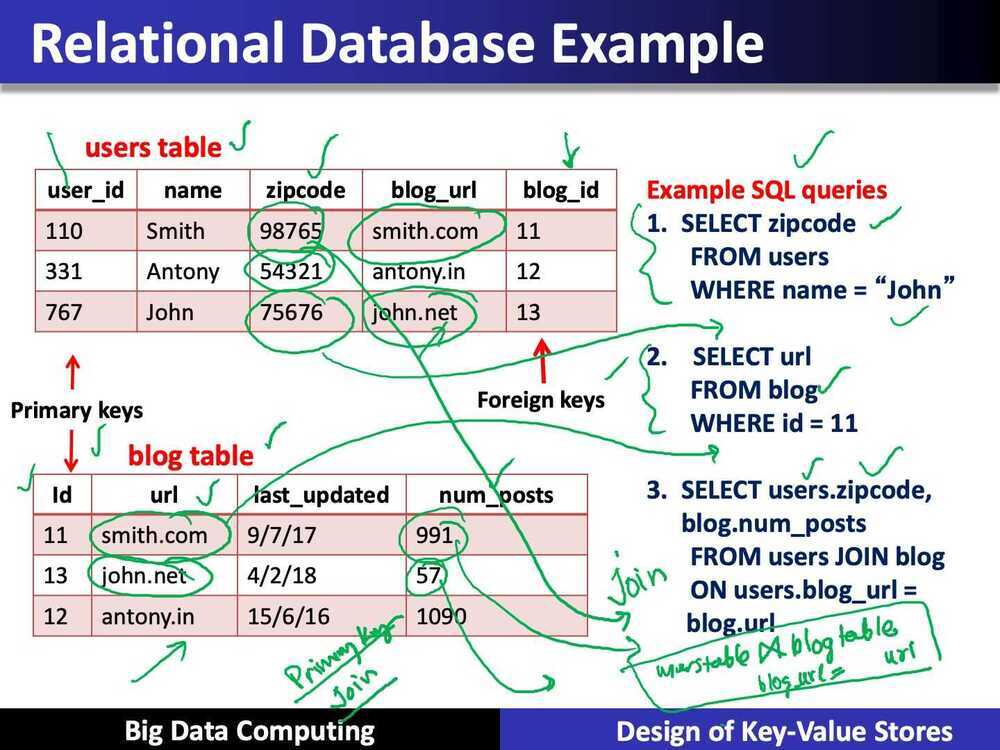
Is it a kind of database?
- RDMSs have been around for ages
- MySQL is the most popular among them
- Data stored in tables
- Schema-based, i.e., structured tables
- Each row (data item) in a table has a primary key that is unique within that table
- Queried using SQL (Structured Query Language)
- Supports joins
Mismatch with today's workloads
- Data: Large and unstructured: Difficult to come out with schemas where the data can fit
- Lots of random reads and writes: Coming from millions of clients
- Sometimes write-heavy: Lot more writes compare to read
- Foreign keys rarely needed
- Joins infrequent
Needs of Today's Workloads
- Speed (Lightning fast writes)
- Avoid Single Point of Failuer (SPoF) (Fault tolerant)
- Low TCO (Total cost of operation and Total cost of ownership)
- Fewer system administrators
- Incremental Scalability
- Adding more nodes adds linear capabilities
- Scale out, not scale up
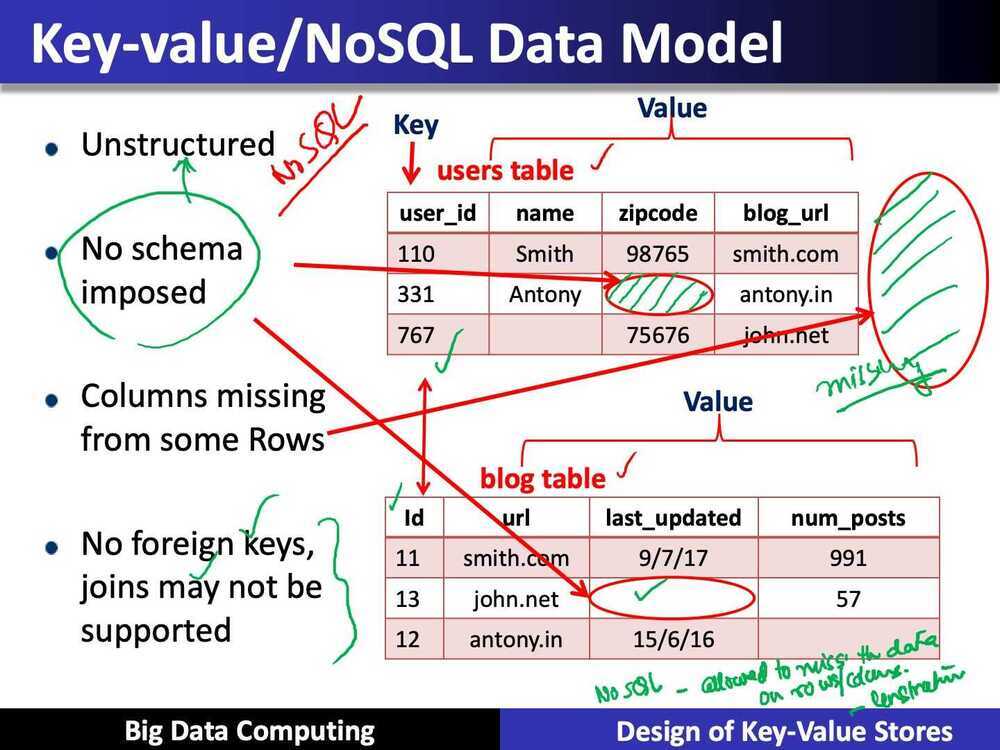
Key-value / NoSQL Data Model
- NoSQL = Not Only SQL
- Necessaary API operations: get(key) and put(key, value)
- And some extended operations, e.g., "CQL" in Cassandra key-value store
- Tables
- Column families in Cassandra, Table in HBase, Collection in MongoDB
- Like RDBMS tables, but ...
- May be unstructured: May not have schemas
- Some columns may be missing from some rows
- Don't always support joins or have foreign keys
- Can have index tables, just like RDBMSs
Column-Oriented Storage
NoSQL systems often use column-oriented storage
- RDMSs store an entire row together (on disk or at a server)
- NoSQL systems typically store a column together (or a group of columns)
- Entries within a column are indexed and easy to locate, given a key
- Why useful?
- Range searches within a column are fast since you don't need to fetch the entire database
- E.g., Get me all blog_ids from the blog table that were updated within the past month
- Search in the last_updated column, fetch corresponding blog_id column
- Don't need to fetch the other columns