Apache Iceberg
Iceberg is a high-performance format for huge analytic tables. Iceberg brings the reliability and simplicity of SQL tables to big data, while making it possible for engines like Spark, Trino, Flink, Presto, and Hive to safely work with the same tables, at the same time.
- Expressive SQL
- Full Schema Evolution
- Hidden Partitioning
- Time Travel and Rollback
- Data Compaction
Features
- Use SQL tables for big data
- Work with the same tables simultaneously using engines like Spark, Trino, Flink, Presto, Hive, Impala, StarRocks, Doris, and Pig
- Capture metadata information on the state of datasets as they change over time
- Partition large tables into smaller ones to speed up read and load times
- Run reproducible queries on the same table snapshot
- Reset tables to their previous state to easily walk back errors
- Enable ACID transactions at scale, allowing concurrent writers to work in tandem
- Track changes to a table over time
- Query historical data and verify changes between updates

- https://iceberg.apache.org
- Streaming from Apache Iceberg - Building Low-Latency and Cost-Effective Data Pipelines - YouTube
- A Data Engineer's Guide to PyIceberg | HackerNoon
- GitHub - apache/iceberg-python: Apache PyIceberg
- Apache Iceberg: What It Is and Why Everyone’s Talking About It. - YouTube
- What is Iceberg Versioning and How It Improves Data Reliability
Apache Iceberg V3
- Variant data type
- Deletion vectors
- Row lineage
- AWS re:Invent 2025 - [NEW LAUNCH] What's new in Apache Iceberg v3 and beyond (OPN201) - YouTube
Variant
Data Types
- Primitive types - Basic atomic data types that cannot be broken down into simpler types. Ex - Integer, String
- Structure types - Composed of other types, fixed schema. Ex - List, Map
- Semi-structured types - Flexibility to handle complex, hierarchical data structures such as JSON. Ex - Variant
Components of the variant data type
- Metadata - Enhanced metadata for type definitions in support of pruning
- Encoding - Binary encoding of semi-structured data to a files, metadata and values
- Shredding - Materialization of elements in the data to hidden columns
Variants benefits
- Performance and Cost
- Columnar storage
- Predicate pushdown
- Statistics
- Flexible Schema
- No predefined schema needed
- Evolves automatically
- Efficient storage
- Shredded format
- Compression
- Schema navigation
- Dot notation
- Nested access
Deletion Vectors
- Row level deletes
- Speeds up write operations
- Storage optimization
Write modes in Apache Iceberg
- Copy on write
- Merge on read
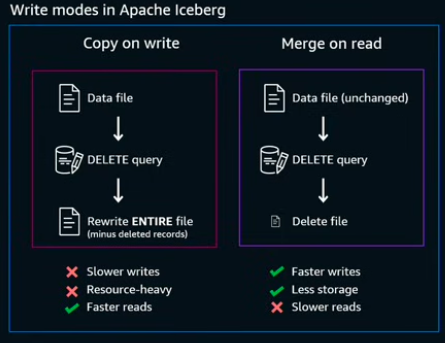
Row level deletes in Iceberg

Row lineage
- Write specification
- Writes record level row lineage information
- Inherits row lineage information from metadata
- Efficient reads
- New metadata columns
- Avoid full scans
_row_idmetadata column for row identity
- Streamlined operations
- On by default
- Record state information lives with the data
Queries
SELECT event_details:price::int as price
FROM tbl_sales_events
WHERE event_details:account_id::int = 12345
Optimizations
-
Compaction – Data compaction compacts small data files to reduce storage usage and improve read performance. Data files are merged and rewritten to remove obsolete data and consolidate fragmented data into larger, more efficient files. You can configure compaction to run automatically.
Binpack is the default compaction strategy in Apache Iceberg. It combines smaller data files into larger ones for optimal performance. Compaction also supports sort and Z-order strategies that cluster similar data together. Sort organizes data based on specified columns, improving query performance for filtered operations. Z-order creates sorted datasets that enhance query performance when multiple columns are queried simultaneously. All three compaction strategies - bincpak, sort, and Z-order - reduce the amount of data scanned by query engines, thereby lowering query processing costs.
-
Snapshot retention – Snapshots are timestamped versions of an Iceberg table. Snapshot retention configurations allow customers to enforce how long to retain snapshots and how many snapshots to retain. Configuring a snapshot retention optimizer can help manage storage overhead by removing older, unnecessary snapshots and their associated underlying files.
-
Orphan file deletion – Orphan files are files that are no longer referenced by the Iceberg table metadata. These files can accumulate over time, especially after operations like table deletions or failed ETL jobs. Enabling orphan file deletion allows AWS Glue to periodically identify and remove these unnecessary files, freeing up storage.
Optimizing Iceberg tables - AWS Glue