Upgrades
Ethereum vision | ethereum.org
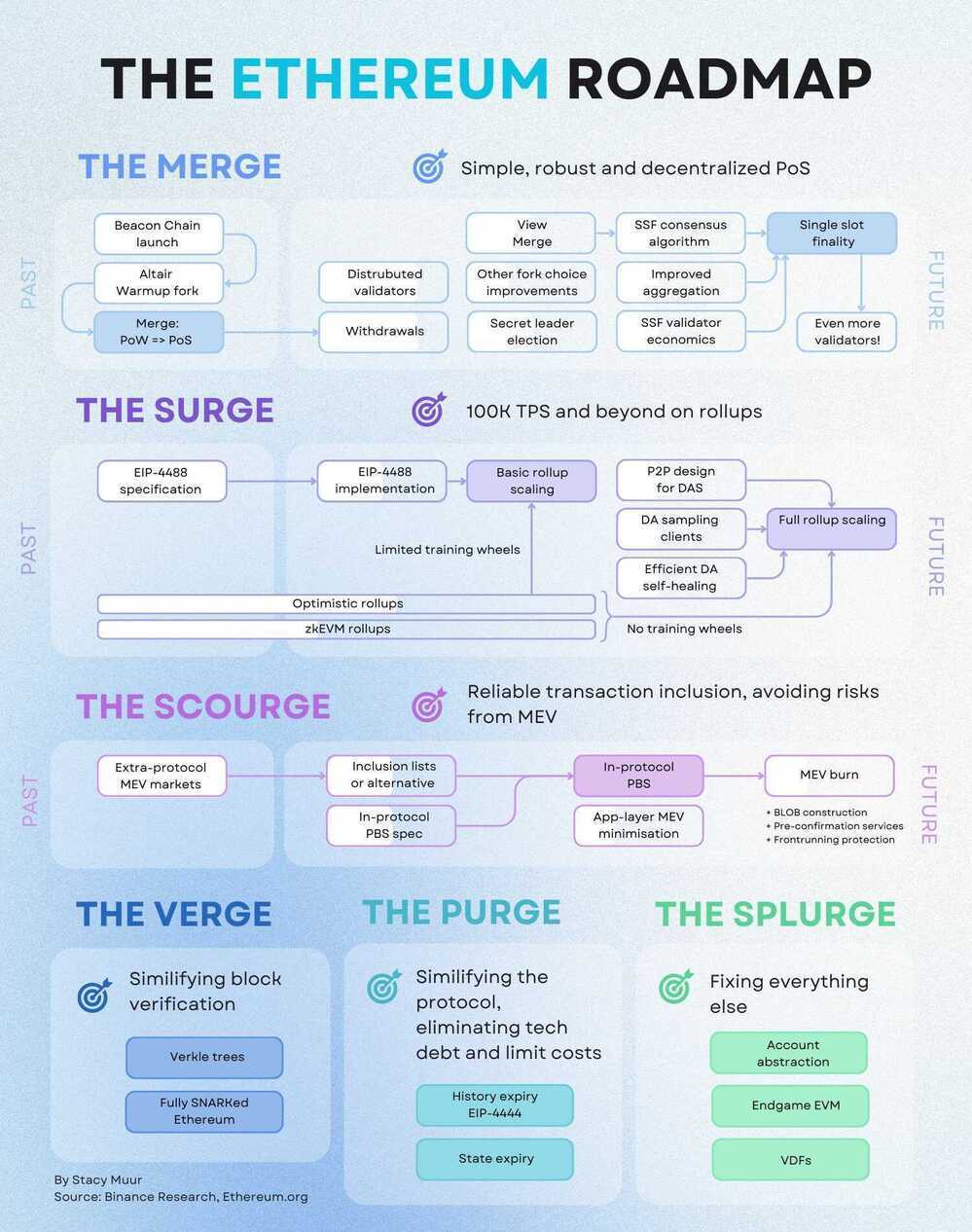
The Merge | ethereum.org
-
The upgrade from the original proof-of-work mechanism to proof-of-stake was called The Merge.
-
The Merge refers to the original Ethereum Mainnet merging with a separate proof-of-stake blockchain called the Beacon Chain, now existing as one chain.
-
The Merge reduced Ethereum's energy consumption by ~99.95%.
-
'Eth1' is now the 'execution layer', which handles transactions and execution.
-
'Eth2' is now the 'consensus layer', which handles proof-of-stake consensus.
In order to simplify and maximize focus on a successful transition to proof-of-stake, The Merge upgrade did not include certain anticipated features such as the ability to withdraw staked ETH. The Shanghai upgrade is planned to follow The Merge, which will enable the ability for stakers to withdraw.
'What Happens After the Merge' - Vitalik Buterin - YouTube
ETHEREUM MERGE - The Most Anticipated Event In Crypto Explained - YouTube
Terminal Total Difficulty (TTD) specifies the final, terminal Proof of Work block, after which the Proof of Stake consensus (implemented in the Beacon Chain) takes over.
ETH issuance tldr
- Before transitioning to proof-of-stake, miners were issued approximately 13,000 ETH/day
- Stakers are issued approximately 1,700 ETH/day, based on about 14 million total ETH staked
- The exact staking issuance fluctuates based on the total amount of ETH staked
- Since The Merge, only the ~1,700 ETH/day remains, dropping total new ETH issuance by ~88%
- The burn: This fluctuates according to network demand. If an average gas price of at least 16 gwei is observed for a given day, this effectively offsets the ~1,700 ETH that is issued to validators and brings net ETH inflation to zero or less for that day.
The Beacon Chain | ethereum.org
'What Happens After the Merge' - Vitalik Buterin - YouTube
How The Merge impacted ETH supply | ethereum.org
The Shanghai/Capella Upgrade
PROTO-DANKSHARDING
The Ethereum community is scaling to global accessibility through Layer-2s (L2s). L2s increase the total block space available to users while still maintaining the security offered by the Ethereum Layer 1 (L1).
L2s publish a lot of data on Ethereum, and the network currently charges high fees for doing so. To fix this, Ethereum will create a new data layer, often referred to as sharding. This provides what is called "data availability" guarantees to L2 users. The L1 only holds the data for a limited time, which means we can scale the chain without sacrificing decentralization for smaller L1 node operators.
The current leading design for this is called Danksharding. The rollout for this will happen in several steps, with the first one being EIP-4844, also known as ProtoDanksharding.
Proto-danksharding (aka EIP-4844) is a planned change to the Ethereum protocol which introduces ephemeral data storage. Because the data does not need to be stored by the network forever, it will be cheaper to use than on-chain storage (i.e. CALLDATA). Rollups (Layer 2s) can use this storage to post transaction data or proofs back to Layer 1 (mainnet). The benefits are lower transaction fees on the L2, greater scalability and more accessibility to more people!
Proto-danksharding requires a new cryptographic scheme: KZG Commitments. This ceremony, sometimes called a "Trusted Setup", will generate a structured reference string (SRS) which is needed for the commitments to work. An SRS is secure as long as at least one participant in the ceremony successfully conceals their secret.
Don't overload Ethereum's consensus
Dual-use of validator staked ETH, while it has some risks, is fundamentally fine, but attempting to "recruit" Ethereum social consensus for your application's own purposes is not.
Ethereum social consensus, for other purposes:
- The ultimate oracle: a proposal where users can vote on what facts are true by sending ETH, with a SchellingCoin mechanism: everyone who sent ETH to vote for the majority answer gets a proportional share of all the ETH sent to vote for the minority answer. The description continues: "So in principle this is an symmetric game. What breaks the symmetry is that a) the truth is the natural point to coordinate on and more importantly b) the people betting on the truth can make a credible thread of forking Ethereum if they loose."
- Re-staking: a set of techniques, used by many protocols including EigenLayer, where Ethereum stakers can simultaneously use their stake as a deposit in another protocol. In some cases, if they misbehave according to the other protocol's rules, their deposit also gets slashed. In other cases, there are no in-protocol incentives and stake is simply used to vote.
- L1-driven recovery of L2 projects: it has been proposed on many occasions that if an L2 has a bug, the L1 could fork to recover it. One recent example is this design for using L1 soft forks to recover L2 failures.
Three Transitions for Ethereum Future
- The L2 scaling transition - everyone moving to rollups
- The wallet security transition - everyone moving to smart contract wallets
- The privacy transition - making sure privacy-preserving funds transfers are available, and making sure all of the other gadgets that are being developed (social recovery, identity, reputation) are privacy-preserving
Deeper dive on cross-L2 reading for wallets and other use cases
Pectra Upgrade (May 7, 2025)
Ethereum Pectra Upgrade | Coinbase
Ethereum Pectra Upgrade: Everything you need to know
Key Innovations of the Pectra Upgrade
- Enhanced Scalability: The Pectra Upgrade introduces mechanisms that increase the network’s transaction capacity. This allows Ethereum to process more transactions per second, which is crucial for supporting the growing number of decentralized applications (dApps) and users on the platform.
- Reduced Transaction Fees: By optimizing data processing and storage management, gas fees are expected to decrease. This makes transactions more affordable for users and encourages broader adoption and use of Ethereum-based applications.
- Improved Security: The upgrade implements advanced cryptographic techniques to further enhance the security of smart contracts and user data. This ensures a more robust and secure environment for all network participants.
- Introduction of Smart Accounts: The Pectra Upgrade makes Ethereum accounts more flexible to use. Regular user accounts, which previously could only perform simple transactions, can now be temporarily converted into Smart Accounts. This allows users to execute multiple transactions simultaneously and even pay gas fees with different cryptocurrencies. These improvements make Ethereum easier and cheaper to use while opening new possibilities for future innovations.
Key Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs) in the Pectra Upgrade
- EIP-7251: Increase of Maximum Validator Balance This EIP raises the maximum balance for validators from 32 ETH to 2,048 ETH. This allows validators to stake larger amounts more efficiently. It also reduces the number of validators needed, which decreases network load and improves blockchain efficiency.
- EIP-7702: Introduction of Account Abstraction This proposal allows externally owned accounts (EOAs) to be temporarily converted into smart contract accounts. This enables functions like transaction bundling and paying gas fees with alternative tokens. It improves user-friendliness and lays the groundwork for future developments in account management.
- EIP-7742: Dynamic Adjustment of Blob Capacity This EIP enables dynamic adjustment of the maximum and target number of blobs per block. It prepares the network for future scaling measures and improves data availability for Layer 2 solutions.
- EIP-6110: On-Chain Processing of Validator Deposits By moving validator deposit processing directly onto the consensus layer, this EIP reduces potential security risks and shortens the wait time for new validators. This makes it easier for new validators to join and increases the network's security.
- EIP-7002: Smart Contract-Controlled Staking Withdrawals This EIP allows smart contracts to directly trigger validator withdrawals. This offers staking pools and other applications greater flexibility in managing withdrawal processes and automates certain operations. Users gain more rights and security when using third-party staking services.
- EIP-7691: Blob scaling This EIP doubles the number of blobs that can be processed per block, allowing Ethereum to handle significantly more data and process it more efficiently. This enhances the network’s scalability—especially for layer-2 rollups —resulting in consistently lower transaction costs even during periods of high demand.
Is Ethereum Ready for a Major Comeback in 2025? (New Upgrades!) - YouTube
Massive Ethereum Upgrade Coming Soon on this date - what you must know - YouTube
ETH To Skyrocket In 2025? Pectra Explained - YouTube
Ethereum in 2025: Major Upgrades and DevCon Insights You Need to Know - YouTube
Future Upgrades
Fusaka Upgrade
- binance.com/en/academy/articles/ethereum-fusaka-upgrade-all-you-need-to-know
- Fulu-Osaka (Fusaka) | ethereum.org
Others
Intro to ERC 6551 - Token Bound Accounts - Jayden Windle - YouTube
Vitalik Buterin ETHGlobal Waterloo III Keynote - YouTube
Should Ethereum be okay with enshrining more things in the protocol?