Liquidity Mining
Liquidity mining is a process in decentralized finance (DeFi) that incentivizes users to provide liquidity to a liquidity pool by rewarding them with cryptocurrency tokens. Liquidity pools are used to facilitate decentralized trading and allow users to trade cryptocurrencies without relying on centralized exchanges.
In liquidity mining, users called liquidity providers (LPs) contribute their cryptocurrency assets to a liquidity pool and earn rewards in the form of a new cryptocurrency token. These rewards are typically a percentage of the trading fees generated by the liquidity pool, and they are distributed proportionally to each LP based on their share of the pool.
The goal of liquidity mining is to encourage users to provide liquidity to a pool, which in turn increases the liquidity of the pool and improves the efficiency of trading. This can help reduce price slippage and improve the overall trading experience for users.
Liquidity mining has become a popular feature of many DeFi protocols, including decentralized exchanges (DEXs), lending protocols, and yield farming platforms. Some of the most well-known liquidity mining protocols include Uniswap, Compound, and Aave.
Why is liquidity mining required?
Liquidity mining is needed in the first place to bootstrap liquidity in decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols. In traditional finance, market makers are typically responsible for providing liquidity by buying and selling assets on an exchange. However, in DeFi, there are no central authorities or market makers to provide liquidity.
Instead, liquidity pools are used to facilitate trading in a decentralized manner. These pools consist of funds deposited by users who act as liquidity providers (LPs). LPs are incentivized to provide liquidity to the pool through the opportunity to earn fees generated by trading in the pool.
However, in the early days of DeFi, it was challenging to attract LPs to these pools because they were relatively unknown, and the potential rewards were uncertain. To overcome this challenge, DeFi projects began to offer liquidity mining rewards to incentivize LPs to deposit funds into the pools. These rewards are typically distributed in the form of a new token or the native token of the protocol.
Liquidity mining has proven to be an effective way to attract liquidity to DeFi protocols and has played a significant role in the growth of the DeFi ecosystem. By providing incentives for LPs to contribute funds to liquidity pools, liquidity mining has helped increase the liquidity and efficiency of decentralized trading, making DeFi more accessible and attractive to users.
How liquidity mining generates rewards?
Liquidity mining generates rewards by distributing a portion of the transaction fees generated by a liquidity pool to liquidity providers (LPs) who have deposited funds into the pool.
When a user trades on a decentralized exchange (DEX) or uses a DeFi protocol that utilizes a liquidity pool, they pay a fee for the transaction. These fees are collected by the protocol and then distributed to the LPs who have provided liquidity to the pool. The rewards are typically distributed proportionally to the amount of liquidity provided by each LP.
In addition to transaction fees, some DeFi protocols may also generate rewards through token issuance. In these cases, a new cryptocurrency token is created specifically for liquidity mining. LPs who provide liquidity to the pool receive a portion of this new token as a reward, in addition to any transaction fees generated by the pool.
The amount of rewards that can be earned through liquidity mining can vary depending on a number of factors, including the size of the liquidity pool, the trading volume, and the volatility of the assets in the pool. However, in general, the more liquidity a user provides to a pool, the greater their potential rewards.
It is important to note that liquidity mining rewards are not guaranteed and can fluctuate over time based on market conditions and other factors. Users should carefully evaluate the risks and rewards of liquidity mining before participating in any DeFi protocol.
Volatility Loss / Impermanent Loss
In decentralized finance (DeFi), volatility loss refers to the potential loss that can occur when a liquidity provider (LP) provides liquidity to a liquidity pool that contains volatile assets.
When an LP provides liquidity to a pool, they receive liquidity provider tokens (LP tokens) representing their share of the pool. These LP tokens can be used to withdraw their share of the underlying assets in the pool. However, if the price of one or more of the assets in the pool experiences significant volatility, the value of the LP tokens may also fluctuate, resulting in a potential loss for the LP.
For example, if an LP provides liquidity to a pool containing equal amounts of Ether (ETH) and a stablecoin like USDC, and the price of ETH drops significantly, the value of the LP tokens may also decrease. If the LP decides to withdraw their share of the assets at this point, they may receive fewer assets than they originally deposited, resulting in a loss of value.
To mitigate volatility loss, LPs can choose to provide liquidity to pools containing less volatile assets or use strategies such as impermanent loss protection, which compensates LPs for any losses incurred due to volatility.
What Is IMPERMANENT LOSS? DEFI Explained - Uniswap, Curve, Balancer, Bancor - YouTube
What is Impermanent Loss in Crypto? (Animated + Examples) - YouTube
6 Ways to Avoid Impermanent Loss (Crypto Liquidity Pools) - YouTube
Liquidity
Liquidity is a measure of resource sufficiency as it concerns a cryptocurrency market or a custodial institution. For tradable assets, it translates to investors’ freedom to make trades in any direction without significant slippage. For custodial institutions, it is the ability to satisfy withdrawal requests without significant delays or friction. A sufficiently liquid market or institution should be able to sustain this in harsh market conditions.
What is Liquidity in Crypto? | CoinGecko
Liquidity Provider Tokens (LP Tokens)
Liquidity provider tokens or LP tokens are tokens issued to liquidity providers on a decentralized exchange (DEX) that run on an automated market maker (AMM) protocol.
LP tokens are used to track individual contributions to the overall liquidity pool, as LP tokens held correspond proportionally to the share of liquidity in the overall pool.
At the most basic level, LP tokens work on the following formula:
Total Value of Liquidity Pool / Circulating Supply of LP Tokens = Value of 1 LP Token
The relationship between LP tokens and the proportional share of a liquidity pool is used most commonly in at least two cases:
- To determine the liquidity provider’s share of transaction fees accumulated during the duration of liquidity provision.
- To determine how much liquidity is returned to liquidity providers from the liquidity pools when LPs decide to redeem their LP tokens.
There are many other use cases for LP tokens that are emerging on modern DeFi platforms. These include:
- Staking LP tokens to earn further rewards as a way to incentivize LPs to lock their liquidity into pools. Sometimes, this is called farming.
- Using LP tokens values as a qualifying factor to access initial DEX offering (IDOs), i.e., to participate in certain IDOs, one must hold a certain value of LP tokens.
Liquidity Provider Tokens (LP Tokens) Definition | CoinMarketCap
Yield Farming
Yield farming involves maximizing returns on cryptocurrency holdings by moving them between different DeFi protocols to take advantage of the highest yield opportunities. This can involve lending, staking, or liquidity provision.
- Leveraged Lending
Is Yield Farming DEAD? Are There ANY Good Opportunities Left? DEFI Explained - YouTube
What Is YIELD FARMING? DEFI Explained (Compound, Balancer, Curve, Synthetix, Ren) - YouTube
What is Yield Farming in Crypto? (Animated + 4 Examples) - YouTube
What are Degen Yield Farms? (Animated) - Crypto Pyramid Schemes - YouTube
Differences
Yield Farming vs. Liquidity Mining: What's the Difference? - B2Bbroker
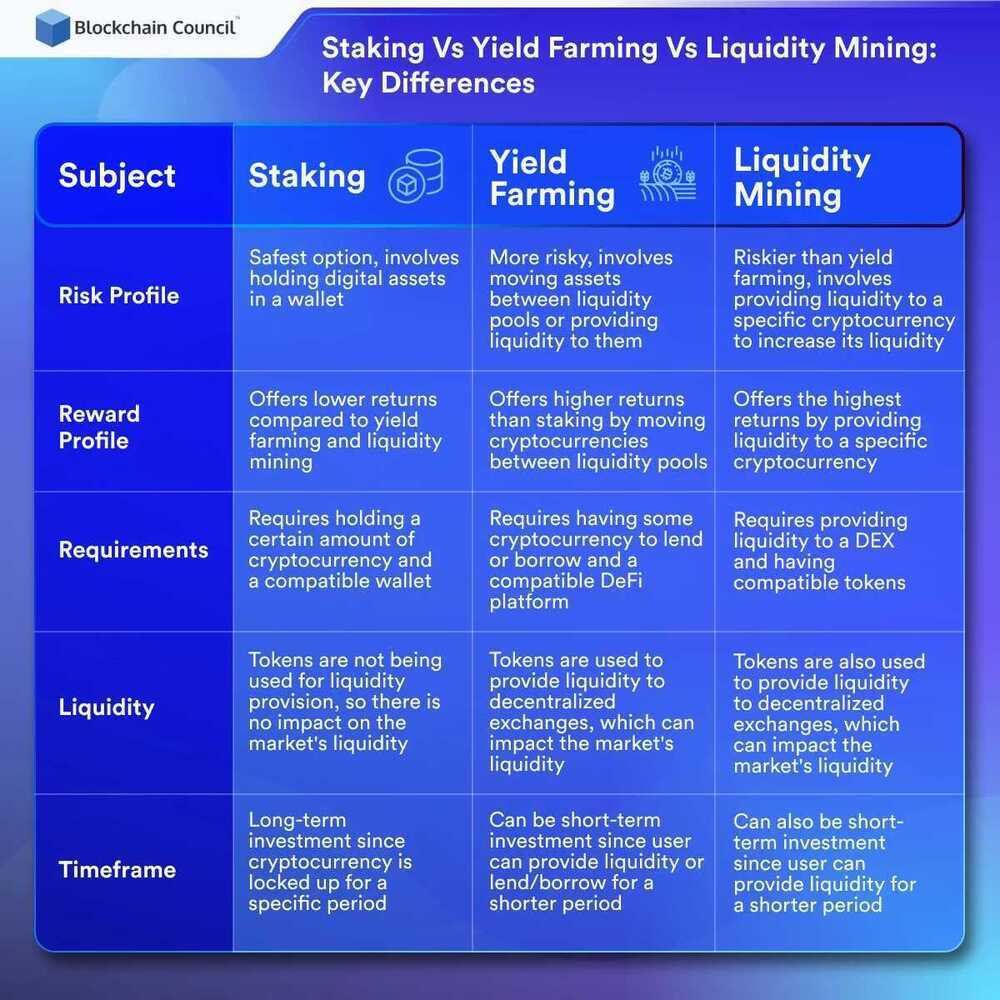
Staking vs Yield Farming vs Liquidity Mining- What's The Difference? - Blockchain Council
Curve Finance
Gauges
The gauge system
On Curve Finance, the inflation is going to users who provide liquidity. This usage is measured with gauges. The liquidity gauge measures how much a user is providing in liquidity.
The liquidity gauge measures how many dollars you have provided in a Curve pool. Each Curve pool has its own liquidity gauge where you can stake your liquidity provider tokens
The weight system
Each gauge also has a weight and a type. Those weights represent how much of the daily CRV inflation will be received by the liquidity gauge.
The DAO
The weight systems allow the Curve DAO to dictate where the CRV inflation should go.
Understanding Gauges - Curve Finance
Curve Finance: Deposit & stake liquidity | Lido Finance - YouTube
Understanding Curve Pools - Curve Resources
What is Curve Finance? I'm earning 25% AND protecting against a crash - YouTube
Links
- Harvest - Web3 Platform to Earn on Your Crypto
- The top five liquidity trackers and analytic tools | by International Token Standardization Association | Medium
- The 7 Most Frequently Asked Questions About Liquidity Mining
- Impermanent Loss & other Liquidity Mining risks explained - Dr. Julian Hosp - The Blockchain Expert
- How do LIQUIDITY POOLS work? (Uniswap, Curve, Balancer) | DEFI Explained - YouTube
- What Is BANCOR V2? CHAINLINK Integration And Dynamic Automated Market Maker Explained | DEFI - YouTube
- Top LP Tokens Coins by Market Cap | CoinGecko
- Top 10 Liquidity Pool (LP) Tokens: Unleashing the Power of DeFi - CryptoTicker
- What are liquidity provider (LP) tokens, and how do they work?
- What is a Liquidity Pool in Crypto? (Animated) - YouTube
- What is a Mining Pool in Crypto? (Animated + Examples) - YouTube
- What is a Dark Pool in Crypto? When + Why + How to use one! - YouTube
- Providing Crypto Liquidity: What Does Liquidity Mean In Crypto
- Liquidity Score (Market Pair, Exchange) - CoinMarketCap