Scaling
Replication/Clustering
Default: Master-Slave
When installing the chart withcluster.enabled=true, it will deploy a Redis master StatefulSet (only one master node allowed) and a Redis slave StatefulSet. The slaves will be read-replicas of the master. Two services will be exposed:
- Redis Master service: Points to the master, where read-write operations can be performed
- Redis Slave service: Points to the slaves, where only read operations are allowed.
In case the master crashes, the slaves will wait until the master node is respawned again by the Kubernetes Controller Manager.
Master-Slave with Sentinel
When installing the chart with cluster.enabled=true and sentinel.enabled=true, it will deploy a Redis master StatefulSet (only one master allowed) and a Redis slave StatefulSet. In this case, the pods will contain en extra container with Redis Sentinel. This container will form a cluster of Redis Sentinel nodes, which will promote a new master in case the actual one fails. In addition to this, only one service is exposed:
- Redis service: Exposes port 6379 for Redis read-only operations and port 26379 for accesing Redis Sentinel.
For read-only operations, access the service using port 6379. For write operations, it's necessary to access the Redis Sentinel cluster and query the current master using the command below (using redis-cli or similar:
SENTINEL get-master-addr-by-name mymaster
This command will return the address of the current master, which can be accessed from inside the cluster.
In case the current master crashes, the Sentinel containers will elect a new master node.
https://redis.io/topics/sentinel
Redis Cluster
https://redis.io/topics/cluster-tutorial
https://redis.io/topics/cluster-spec
Replication - One leader many followers model
Clustering - Shard data across multiple nodes
https://redis.io/topics/cluster-tutorial
Hybrid - Replication + Clustering
Sentinel - https://redis.io/topics/sentinel
keydb - Multithreaded fork of redis
https://docs.keydb.dev/blog/2019/10/07/blog-post
twenproxy (by twitter)
twemproxy (pronounced "two-em-proxy"), aka nutcracker is a fast and lightweight proxy for memcached and redis protocol. It was built primarily to reduce the number of connections to the caching servers on the backend. This, together with protocol pipelining and sharding enables you to horizontally scale your distributed caching architecture.
https://github.com/twitter/twemproxy
codis
Proxy based Redis cluster solution supporting pipeline and scaling dynamically
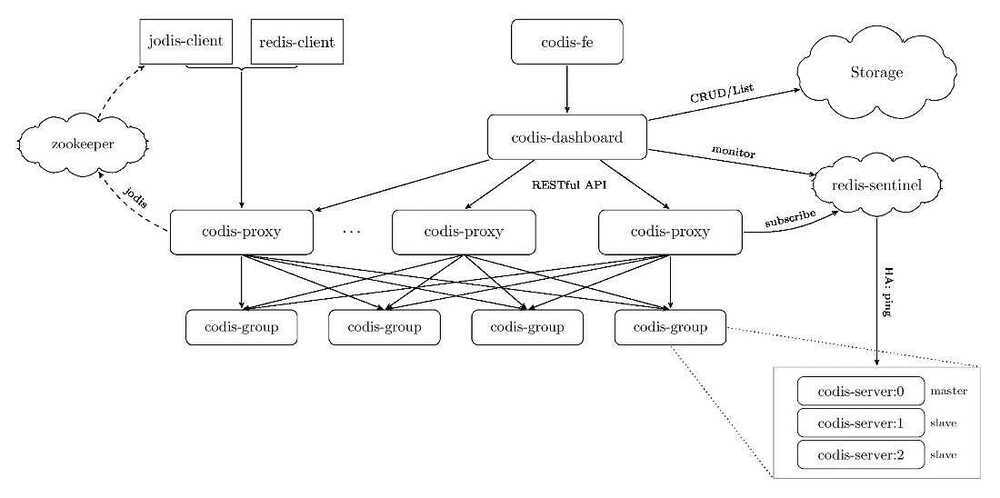
https://github.com/CodisLabs/codis
| Codis | Twemproxy | Redis Cluster | |
|---|---|---|---|
| resharding without restarting cluster | Yes | No | Yes |
| pipeline | Yes | Yes | No |
| hash tags for multi-key operations | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| multi-key operations while resharding | Yes | - | No(details) |
| Redis clients supporting | Any clients | Any clients | Clients have to support cluster protocol |
Redis vs Memcached
Both Redis and MemCached are in-memory, open-source data stores. Memcached, a high-performance distributed memory cache service, is designed for simplicity while Redis offers a rich set of features that make it effective for a wide range of use cases.
| Memcached | Redis | |
|---|---|---|
| Sub-millisecond latency | Yes | Yes |
| Developer ease of use | Yes | Yes |
| Data partitioning | Yes | Yes |
| Support for a broad set of programming languages | Yes | Yes |
| Advanced data structures | - | Yes |
| Multithreaded architecture | Yes | - |
| Snapshots | - | Yes |
| Replication | - | Yes |
| Transactions | - | Yes |
| Pub/Sub | - | Yes |
| Lua scripting | - | Yes |
| Geospatial support | - | Yes |
https://aws.amazon.com/elasticache/redis-vs-memcached
Memcached Tutorial for Beginners - YouTube
DragonFly
Dragonfly is a drop-in Redis replacement, designed to meet the performance and efficiency requirements of modern cloud-based applications. Organizations that switch to Dragonfly require less hardware and achieve dramatically improved data performance.
- Dragonfly - The Fastest In-Memory Data Store
- Redis vs. Dragonfly Scalability and Performance
- GitHub - dragonflydb/dragonfly: A modern replacement for Redis and Memcached
- DragonflyDB Architecture Overview, Internals, and Trade-offs - hitting 6.43 million ops/sec - YouTube
Other in-memory database
- facebook rocksdb
- memcached - Memcached Architecture - Crash Course with Docker, Telnet, NodeJS - YouTube
- GitHub - paypal/junodb: JunoDB is PayPal's home-grown secure, consistent and highly available key-value store providing low, single digit millisecond, latency at any scale.
- Dissecting Juno DB - YouTube
- Aerospike
- GitHub - DiceDB/dice: A drop-in replacement of Redis with SQL-based realtime reactivity.