Storage Cost Optimisation
Recommendation: Move from Logical to Physical Storage
Physical vs Logical Storage
In BigQuery, "logical storage" refers to the uncompressed size of your data, including any data retained for time travel and fail-safe storage, while "physical storage" represents the actual compressed size of the data stored on disk, meaning it's the amount of space the data physically occupies on Google's servers; essentially, logical storage is the "apparent" size of your data, while physical storage is the "real" size after compression, with logical storage usually being cheaper per gigabyte than physical storage.
Key differences
- Size Calculation: Logical storage is the uncompressed data size, whereas physical storage reflects the compressed size after data optimization.
- Billing: By default, BigQuery charges based on logical storage, which means you are not billed for the compression savings. However, you can choose to switch to physical storage billing if you want to pay based on the actual disk space used.
- Time Travel and Fail-Safe Storage: When using logical storage, time travel and fail-safe storage are included in the price, but when using physical storage, these features are billed separately at the "active storage" rate.
When to use which
- Logical Storage (default): Use this if you want the simplest billing model and are not overly concerned about optimizing for storage costs, especially if you utilize features like time travel frequently.
- Physical Storage: If you have very large datasets with high compression potential and want to minimize storage costs, consider switching to physical storage billing.
Charges
BigQuery charges based on active logical storage, which is often higher compared to physical storage due to the compression factor. Here’s how you can optimize this:
- Understand Compression Benefits: BigQuery's physical storage cost is based on compressed storage. Depending on the compression ratio of your data, you can potentially reduce storage costs significantly. For example, if your data compresses well (as per Bigquery Tables scan), you may only pay a fraction of the logical storage cost.
- Compression Strategy: Evaluate all your BigQuery Tables and choose appropriate Tables that will help reduce your overall cost of storage and query performance. For highly compressible data, the cost savings can be substantial (up to 30-40% savings compared to logical storage costs).
Example:
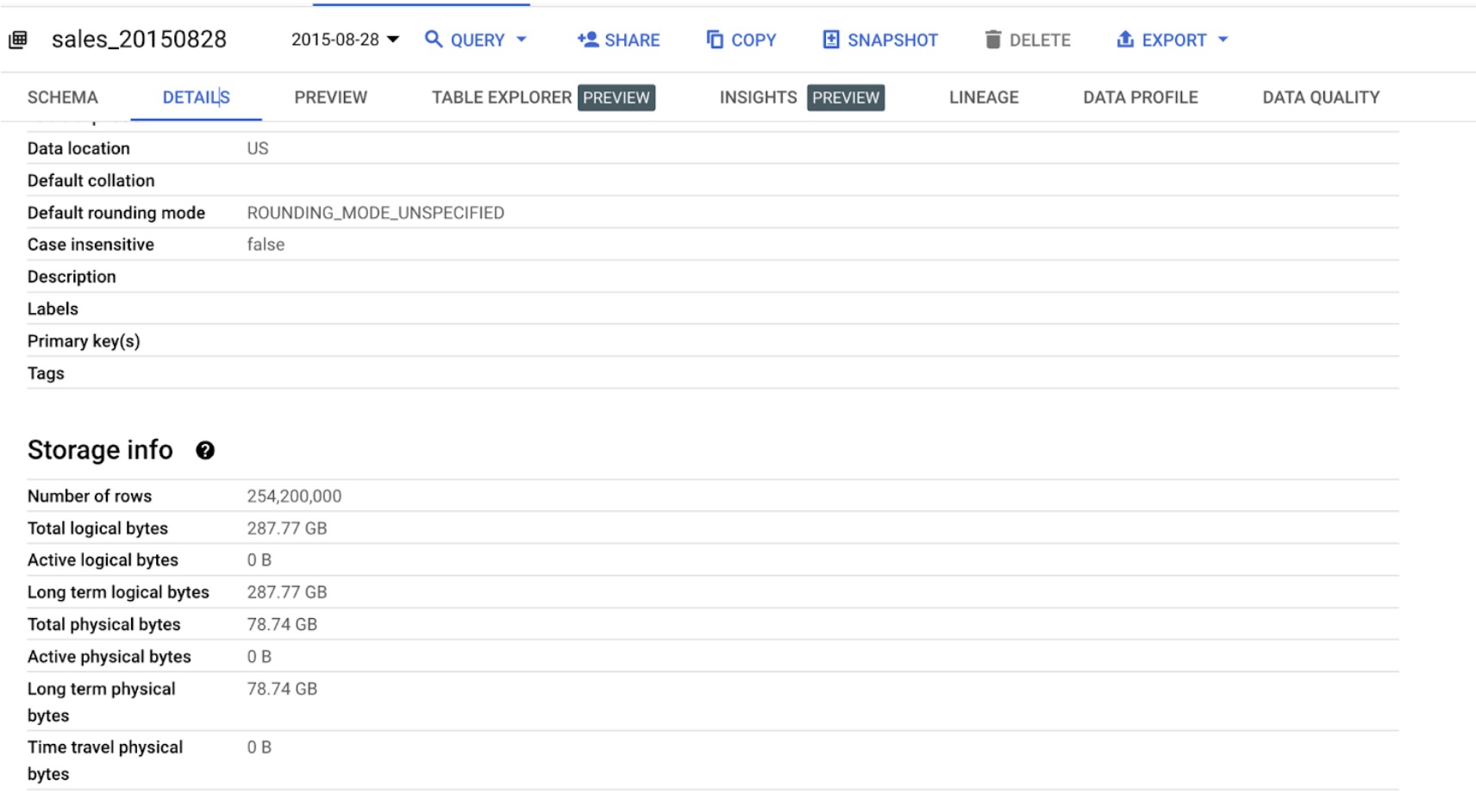
From the above snapshot and the storage cost information, we can deduce the following about the cost efficiency of physical storage over logical storage due to compression:
Logical Storage (us-multi region dataset)
- Active logical storage costs $0.02 per GiB per month.
- Long-term logical storage costs $0.01 per GiB per month.
Physical Storage (us-multi region dataset)
- Active physical storage costs $0.04 per GiB per month.
- Long-term physical storage costs $0.02 per GiB per month.
While the cost of physical storage is generally twice that of logical storage, effective compression can reduce the effective cost to as low as 1/5th of the original logical storage cost, depending on your data characteristics. This strategy can lead to significant cost savings over time.
Snapshot Data(us-multi region dataset)
- Total logical bytes: 287.77 GiB
- Total physical bytes: 78.74 GiB
Cost Comparison
Without Compression (Logical Storage)
Active logical storage cost:
- 287.77 GiB * $0.02/GiB = $5.75 per month
Long-term logical storage cost:
- 287.77 GiB * $0.01/GiB = $2.88 per month
With Compression (Physical Storage)
Active physical storage cost:
- 78.74 GiB * $0.04/GiB = $3.15 per month
Long-term physical storage cost:
- 78.74 GiB * $0.02/GiB = $1.57 per month Savings Analysis
Logical vs. Physical Storage (Active)
- Logical: $5.75 per month
- Physical: $3.15 per month
- Savings: $5.75 - $3.15 = $2.60 per month
Logical vs. Physical Storage (Long-term)
- Logical: $2.88 per month
- Physical: $1.57 per month
- Savings: $2.88 - $1.57 = $1.31 per month
Conclusion
Due to compression, storing data physically is more cost-effective:
- For active storage, you save $2.60 per month.
- For long-term storage, you save $1.31 per month.
The compression reduces the physical storage size, thus lowering the overall cost despite the higher per-GiB rate for physical storage.
Implementation Steps
Non-programmatic Approach
Step1: Apply Physical Billing model at a Dataset level
Click on Edit Details
Click on Advanced Options and select the storage and time travel window
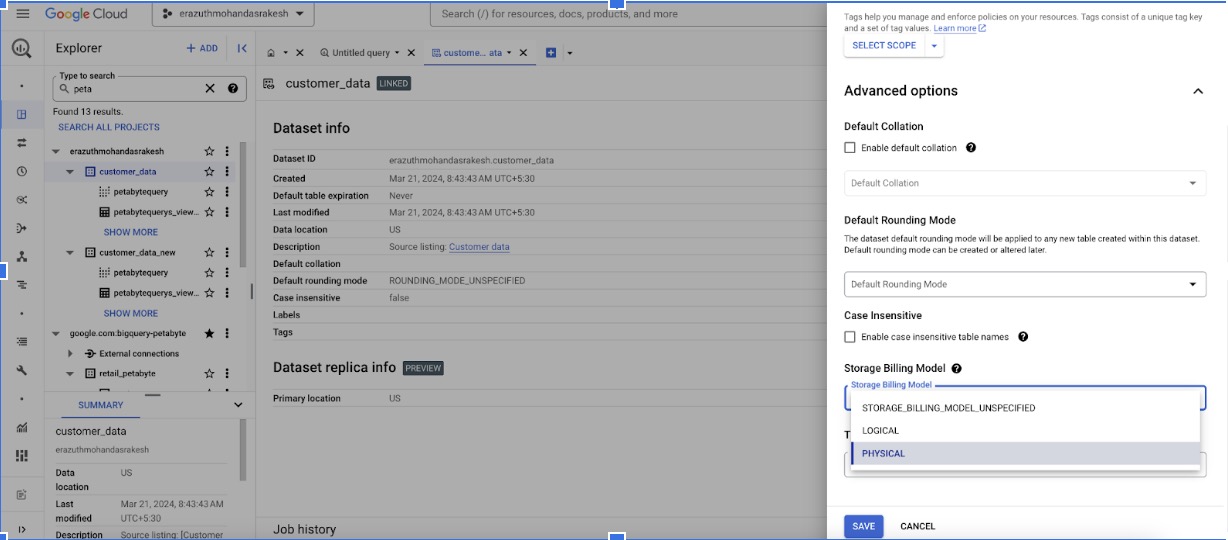
Identifying tables with the type of storage across Organization Steps
WITH storage_data AS (
SELECT
project_id,
project_number,
table_catalog,
table_schema,
table_name,
total_logical_bytes,
active_logical_bytes,
long_term_logical_bytes,
current_physical_bytes,
total_physical_bytes,
active_physical_bytes,
long_term_physical_bytes
FROM
`region-asia-south1`.INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLE_STORAGE
-- `region-asia-south1`.INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLE_STORAGE_BY_ORGANIZATION
),
compression_ratios AS (
SELECT
project_id,
table_catalog,
table_schema,
table_name,
total_logical_bytes,
active_logical_bytes,
long_term_logical_bytes,
current_physical_bytes,
total_physical_bytes,
active_physical_bytes,
long_term_physical_bytes,
SAFE_DIVIDE(total_logical_bytes, total_physical_bytes) AS total_logical_to_physical_ratio,
SAFE_DIVIDE(active_logical_bytes, active_physical_bytes) AS active_logical_to_physical_ratio,
SAFE_DIVIDE(long_term_logical_bytes, long_term_physical_bytes) AS long_term_logical_to_physical_ratio
FROM
storage_data
),
costs AS (
SELECT
project_id,
table_catalog,
table_schema,
table_name,
total_logical_bytes,
active_logical_bytes,
long_term_logical_bytes,
current_physical_bytes,
total_physical_bytes,
active_physical_bytes,
long_term_physical_bytes,
total_logical_to_physical_ratio,
active_logical_to_physical_ratio,
long_term_logical_to_physical_ratio,
GREATEST(0, SAFE_DIVIDE(active_logical_bytes, 1024 * 1024 * 1024) - 10) * 0.02 AS active_logical_cost,
GREATEST(0, SAFE_DIVIDE(long_term_logical_bytes, 1024 * 1024 * 1024) - 10) * 0.01 AS long_term_logical_cost,
GREATEST(0, SAFE_DIVIDE(active_physical_bytes, 1024 * 1024 * 1024) - 10) * 0.04 AS active_physical_cost,
GREATEST(0, SAFE_DIVIDE(long_term_physical_bytes, 1024 * 1024 * 1024) - 10) * 0.02 AS long_term_physical_cost
FROM
compression_ratios
)
SELECT
project_id,
table_catalog,
table_schema,
table_name,
total_logical_bytes,
active_logical_bytes,
long_term_logical_bytes,
current_physical_bytes,
total_physical_bytes,
active_physical_bytes,
long_term_physical_bytes,
total_logical_to_physical_ratio,
active_logical_to_physical_ratio,
long_term_logical_to_physical_ratio,
active_logical_cost,
long_term_logical_cost,
active_physical_cost,
long_term_physical_cost
FROM
costs
ORDER BY
project_id, table_catalog, table_schema, table_name;
Programmatically change all the dataset whose cost is reduced due to compressed storage
from google.cloud import bigquery
import subprocess
import pandas as pd
# Initialize BigQuery client
client = bigquery.Client()
# Define your query to find datasets with high logical storage
query = """
SELECT
project_id,
dataset_id,
SUM(total_logical_bytes) AS total_logical_bytes_sum,
SUM(total_physical_bytes) AS total_physical_bytes_sum
FROM
`region-asia-south1`.INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLE_STORAGE
-- `region-asia-south1`.INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLE_STORAGE_BY_ORGANIZATION
GROUP BY
project_id, dataset_id
HAVING
SUM(total_logical_bytes) > 2 * SUM(total_physical_bytes)
"""
# Run the query
query_job = client.query(query)
results = query_job.result()
# Function to change storage type
def change_storage_type(project_id, dataset_id, billing_model):
# Construct the curl command
curl_command = f"""
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer $(gcloud auth print-access-token)" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-L -X PUT \
https://bigquery.googleapis.com/bigquery/v2/projects/{project_id}/datasets/{dataset_id} \
-d '{{"datasetReference": {{"projectId": "{project_id}", "datasetId": "{dataset_id}"}}, "storageBillingModel": "{billing_model}"}}'
"""
# Execute the curl command
result = subprocess.run(curl_command, shell=True, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE, text=True)
if result.returncode == 0:
return True, result.stdout
else:
return False, result.stderr
# List to store results
data = []
# Process each dataset that meets the criteria
for row in results:
project_id = row['project_id']
dataset_id = row['dataset_id']
logical_bytes = row['total_logical_bytes']
physical_bytes = row['total_physical_bytes']
print(f"Changing storage type for {project_id}.{dataset_id}")
# Change the storage type to physical storage (or the desired billing model)
success, message = change_storage_type(project_id, dataset_id, "PHYSICAL_STORAGE")
# Store the result
data.append({
'project_id': project_id,
'dataset_id': dataset_id,
'total_logical_bytes': logical_bytes,
'total_physical_bytes': physical_bytes,
'success': success,
'message': message
})
# Convert the results to a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Display the DataFrame
print(df)
import ace_tools as tools
tools.display_dataframe_to_user(name="Storage Type Update Results", dataframe=df)
Auto Deleting Tables that are not frequently used in a project with table Prefix ’bqc’: This script is designed to automatically delete tables in a Google BigQuery dataset that are prefixed with "bqc" and have not been modified for a specified number of hours.
Why?
- This script would be useful in environments where there are many temporary or ephemeral tables that are not needed after a certain period.
- It helps in managing and cleaning up the dataset by removing old or unused tables, potentially reducing costs and improving manageability.
from google.cloud import bigquery
# Create a BigQuery client
client = bigquery.Client()
# Define your dataset and filter criteria
dataset_id = 'erazuthmohandasrakesh-emr.Banking'
prefix = '_bqc_'
hours_threshold = 8760 <--- change this to
# Construct the SQL query to list tables matching the criteria
query = f"""
SELECT
*
FROM (
SELECT
*,
TIMESTAMP_DIFF(CURRENT_TIMESTAMP(), creation_time_dt, HOUR) AS hours_since_creation,
TIMESTAMP_DIFF(CURRENT_TIMESTAMP(), last_modified_time_dt, HOUR) AS hours_since_last_modification,
FROM (
SELECT
project_id AS table_catalog,
dataset_id AS table_schema,
table_id AS table_name,
*,
TIMESTAMP_MILLIS(creation_time) AS creation_time_dt,
TIMESTAMP_MILLIS(last_modified_time) AS last_modified_time_dt,
ROUND(SAFE_DIVIDE(size_bytes, POW(1000, 2)), 1) AS size_mb,
ROUND(SAFE_DIVIDE(size_bytes, POW(1000, 3)), 2) AS size_gb,
CASE
WHEN type = 1 THEN 'native table'
WHEN type = 2 THEN 'view'
WHEN type = 3 THEN 'external table'
ELSE
'unknown'
END
AS type
FROM
{dataset_id}.__TABLES__
WHERE
project_id IS NOT NULL
AND table_id LIKE '{prefix}%'))
WHERE
hours_since_last_modification>={hours_threshold}
"""
# Execute the query and drop the matching tables
query_job = client.query(query)
for row in query_job:
table_id = row['table_id']
client.query(f"DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `{dataset_id}.{table_id}`").result()