Architecture
- Dremel - The execution engine
- Colossus - Distributed Storage
- Borg - Compute
- Jupiter - The Network
- BigQuery - The Service
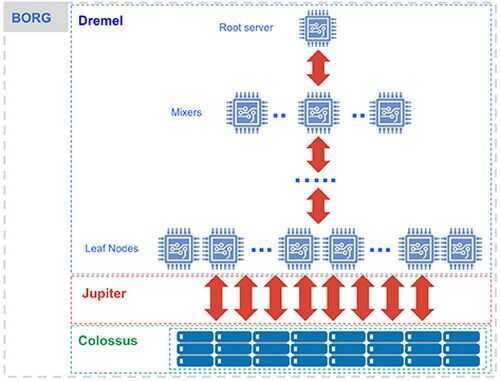
Separation of Compute and State
Separation of compute and state refers to the ability to maintain intermediate state between processing stages in a high-performance component separate from either the compute cluster or storage.
- Less state in compute means compute becomes more ephemeral and scalable. It's easier to re-parallelize processing intra-stage and interstage, and easier to recover from a lost node.
- Processing is more streamlined; processing stages don't conflict within the same compute nodes, resulting in resource contention and bottlenecks.
- It's easier for the processing engine to re-partition workloads between stages.
- Your processing engine can take advantage of pipelined execution. In other words, it doesn't have to wait for Stage N to finish before starting Stage N+1.
- The processing engine can implement dynamic work repartitioning (the ability to re-parallelize work due to slow workers or data skew).
- Keeping less state in processing nodes makes workloads more resilient to individual node issues.
- The service can utilize available resources much more efficiently across compute as well as shuffle.
https://cloud.google.com/blog/products/gcp/bigquery-under-the-hood