Slots
- A BigQuery slot is a virtual compute unit used by BigQuery to execute SQL queries or other job types. During the execution of a query, BigQuery automatically determines how many slots are used by the query. The number of slots used depends on the amount of data being processed, the complexity of the query, and the number of slots available.
- Fair scheduling in BigQuery
- Idle slots
Understand slots | BigQuery | Google Cloud
Utilizing Slots and Autoscaling
BigQuery offers a slot-based pricing model where you can reserve slots (compute capacity) to run queries. This can be more cost-effective than on-demand pricing, especially for workloads with consistent or predictable query patterns.
Steps to Implement
1. Determine Slot Requirements
- Analyze your current query workload to understand the number of slots required to process queries efficiently. Start with an estimate based on historical usage or query patterns.
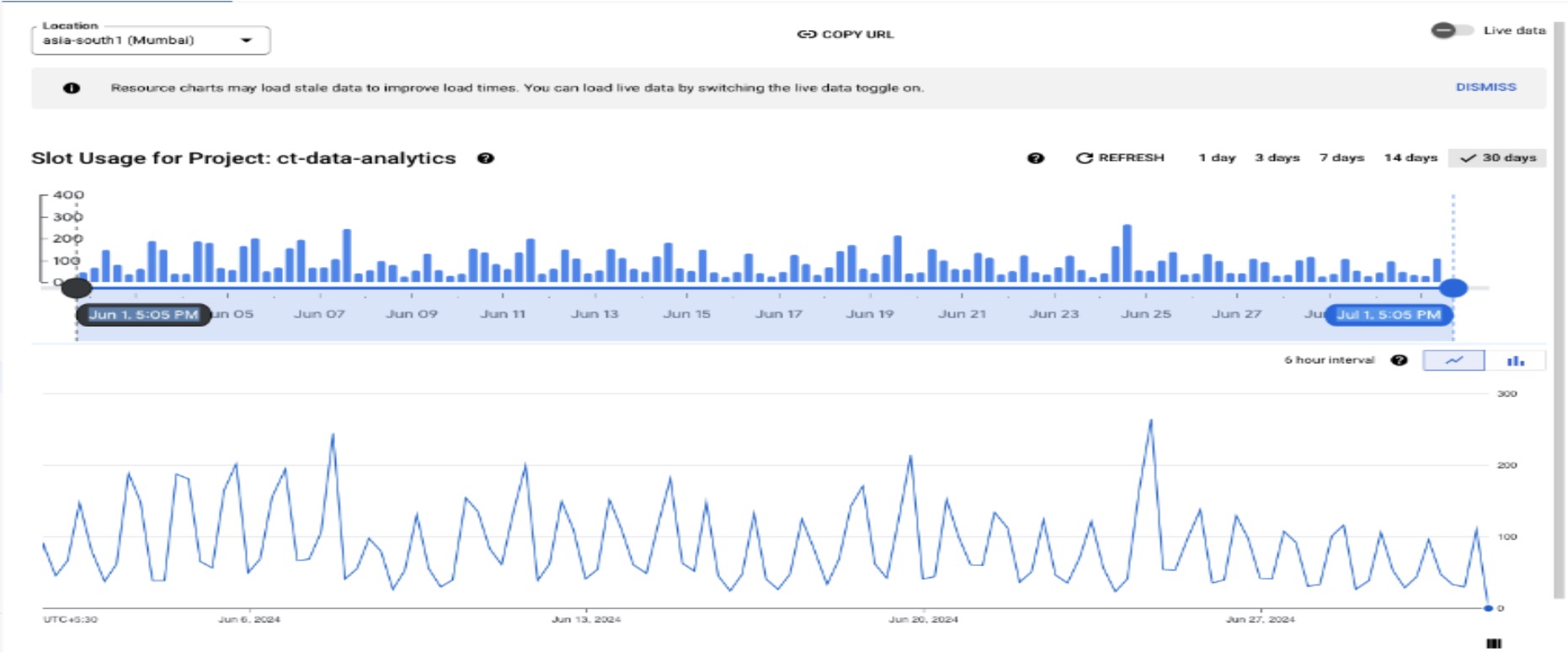
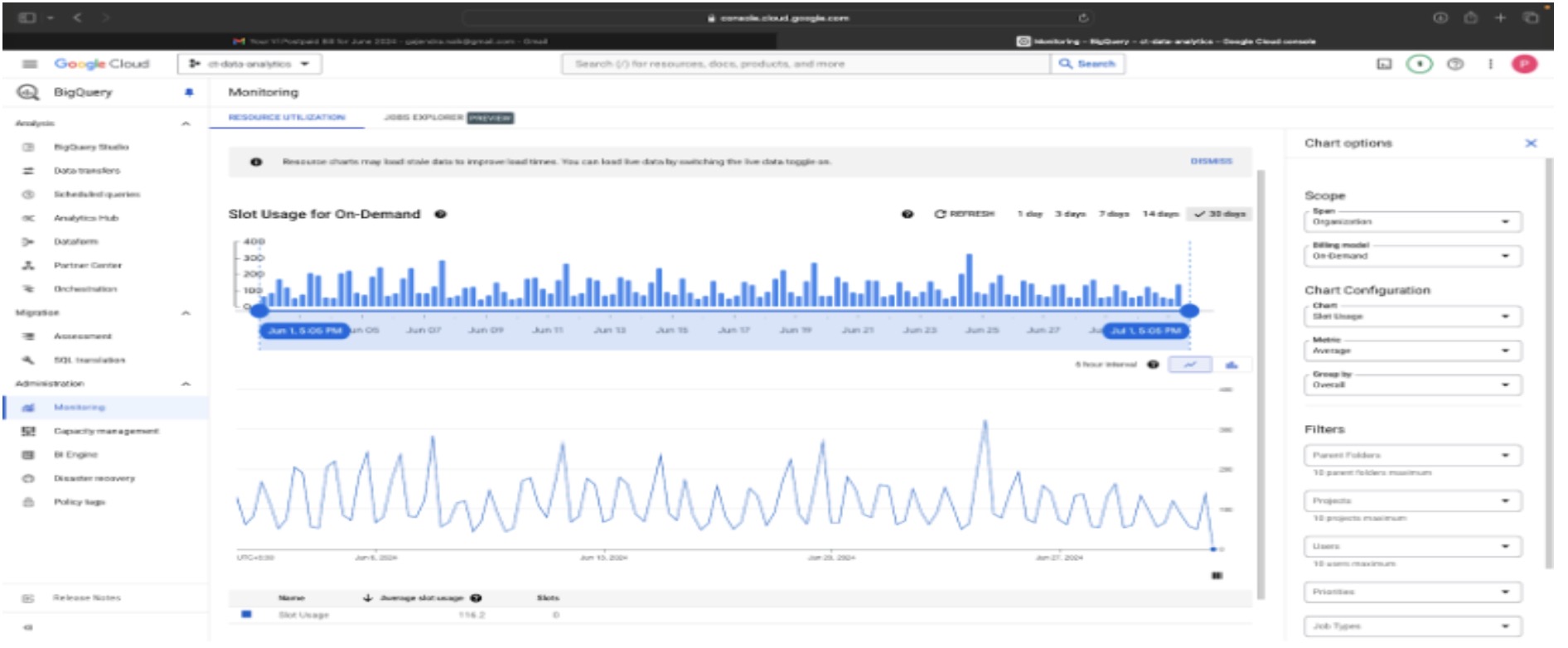
- Based on the previous pattern of usage, we have observed that the slots that you are on average using is around 100 slots and a max of 300 slots autoscaling
2. Reserve Slots
- Based on your analysis, purchase a reservation for a specific number of slots. The slot monitoring chart shows a baseline of 100 slots running 24/7, with an increased capacity of 300 slots as needed. It is assumed that all 300 slots will be used for at least 6 hours a day, even though the chart indicates less than 6 hours of usage. You will be charged for the reserved slots for the entire month, while autoscaling charges will be based solely on usage.
Note: BigQuery allows you to reserve slots in increments of 100.
Implementation Method
- Purchase a reservation for 100 slots. This will cover your baseline needs 24/7 and 300 slots with 25% utilization a day (6 hours of usage of all 300 slots) provide a significant cost reduction compared to on-demand pricing.
- Enable autoscaling to automatically increase slot allocation up to 300 during peak usage times. This flexibility ensures your queries run smoothly without overspending on unnecessary capacity
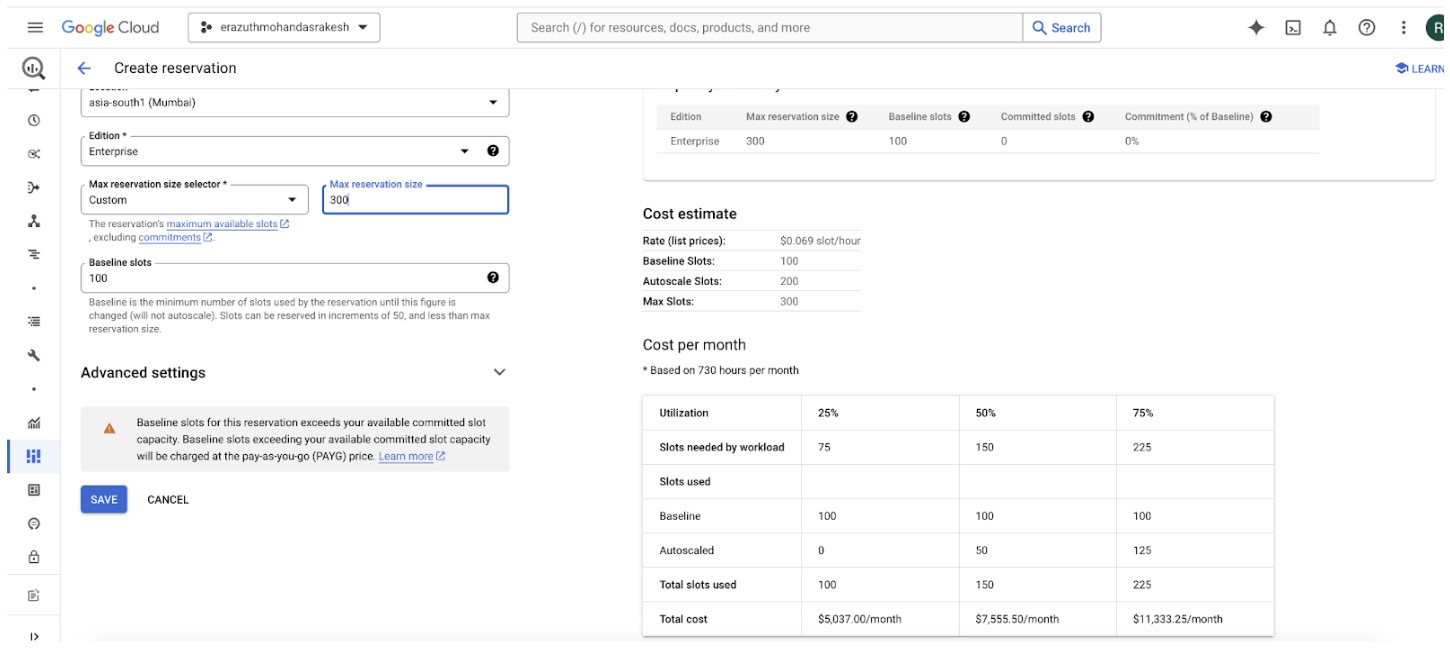
Select the maximum reservation and baseline slots. Additionally, you can view the estimated cost when combining baseline and autoscaling. Below is a sample cost breakdown for autoscaling usage at 25%, 50%, and 100% in a day.
- Baseline Slots: 100 slots (running 24/7)
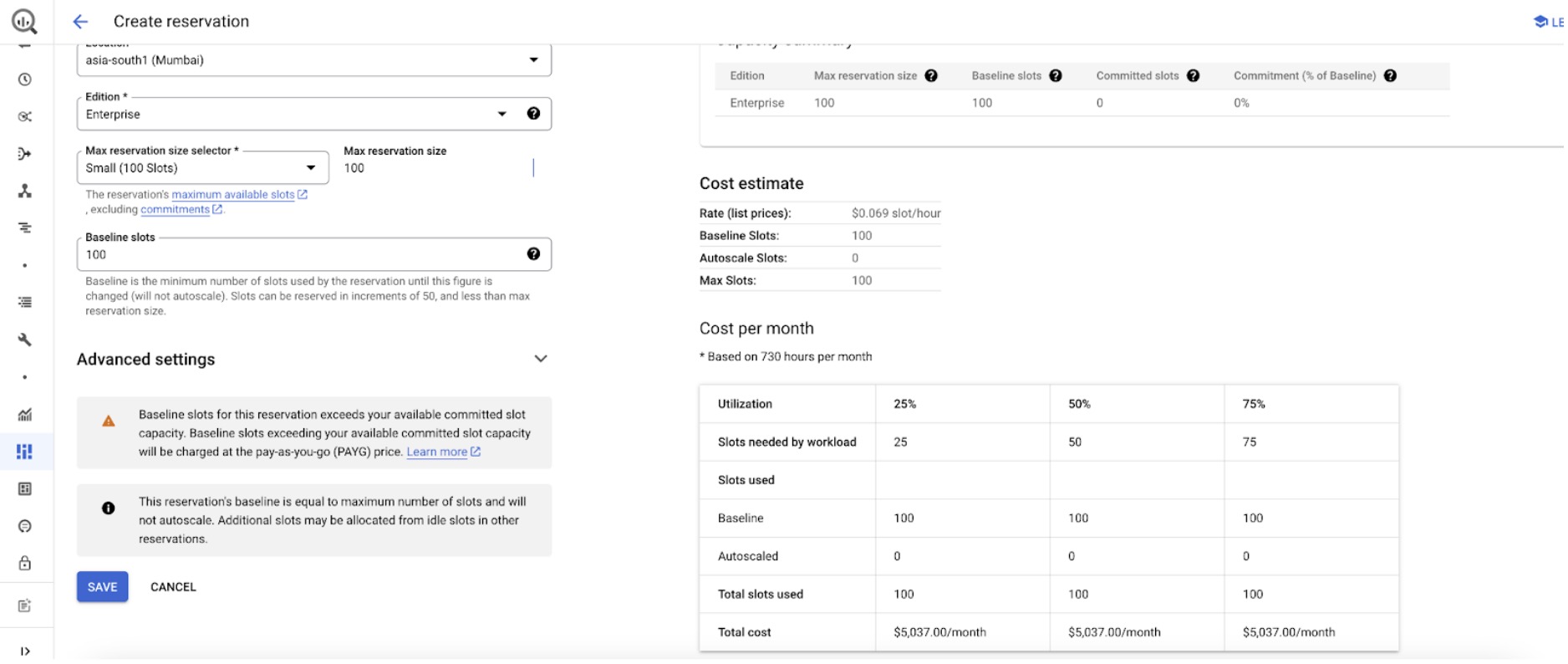
- Maximum Reservation Slots: 300 slots (used for increased capacity)
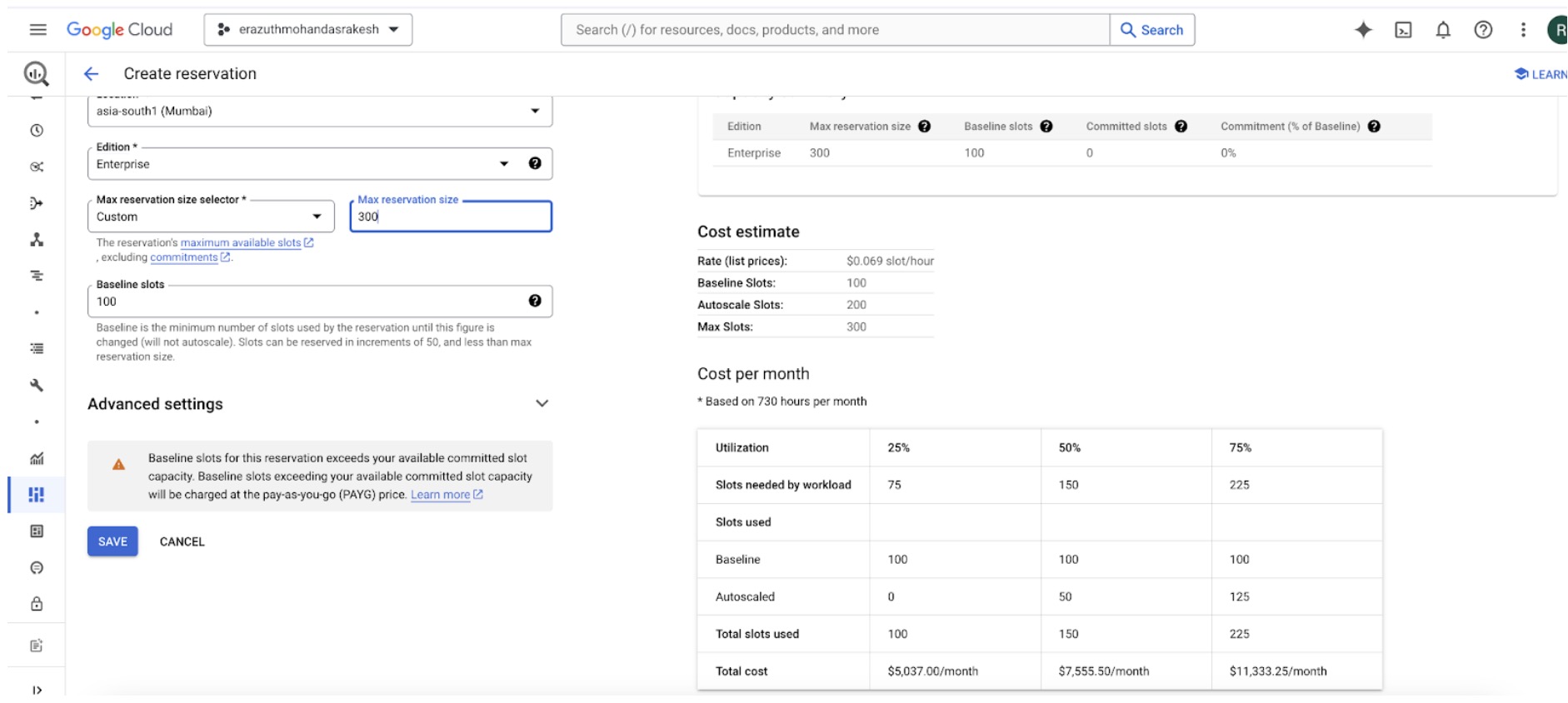
Estimated Cost Breakdown
- Baseline Cost: Cost for 100 slots running continuously for the entire month.
- Autoscaling Costs (based on usage percentages):
- 25% Usage: Cost for using up to 300 slots for 25% of the day.
- 50% Usage: Cost for using up to 300 slots for 50% of the day.
- 100% Usage: Cost for using up to 300 slots for the entire day.
Sample Calculations
- Baseline Cost: Fixed monthly cost for 100 slots.
- Autoscaling 25% Usage Cost: Cost for 300 slots running for 6 hours per day.
- Autoscaling 50% Usage Cost: Cost for 300 slots running for 12 hours per day.
- Autoscaling 100% Usage Cost: Cost for 300 slots running for 24 hours per day.
By comparing these estimates, you can better understand the cost implications of different levels of autoscaling usage.
3. Monitor and Adjust
- Regularly monitor your query performance and adjust the number of reserved slots and autoscaling settings based on actual usage patterns. This ensures that you are optimizing costs while maintaining performance.
Slot Autoscaling
When you create autoscaling reservations, consider the following:
- BigQuery scales reservations almost instantly until it has reached the number of slots needed to execute the jobs, or it reaches the maximum number of slots available to the reservation. Slots always autoscale to a multiple of 50.
- Scaling up is based on actual usage, and is rounded up to the nearest 50 slot increment.
- Your autoscaled slots are charged at capacity compute pricing for your associated edition while scaling up. You are charged for the number of scaled slots, not the number of slots used. This charge applies even if the job that causes BigQuery to scale up fails. For this reason, don't use the jobs information schema to match the billing. Instead, see Monitor autoscaling with information schema.
- While the number of slots always scales by multiples of 50, it may scale more than 50 slots within one step. For example, if your workload requires an additional 450 slots, BigQuery can attempt to scale by 450 slots at once to meet the capacity requirement.
- BigQuery scales down when the jobs associated with the reservation no longer need the capacity (subject to a 1 minute minimum).
Any autoscaled capacity is retained for at least 60 seconds. This 60-second period is called the scale-down window. Any new peak in capacity resets the scale-down window, treating the entire capacity level as a new grant. However, if 60 seconds or more have passed since the last capacity increase and there is less demand, the system reduces the capacity without resetting the scale-down window, enabling consecutive decreases without an imposed delay.
For example, if your initial workload capacity scales to 100 slots, the peak is retained for at least 60 seconds. If, during that scale-down window, your workload scales to a new peak of 200 slots, a new scale-down window begins for 60 seconds. If there is no new peak during this scale-down window, your workload begins to scale down at the end of the 60 seconds.
Consider the following detailed example: At 12:00:00, your initial capacity scales to 100 slots and the usage lasts for one second. That peak is retained for at least 60 seconds, beginning at 12:00:00. After the 60 seconds have elapsed (at 12:01:01), if the new usage is 50 slots, BigQuery scales down to 50 slots. If, at 12:01:02, the new usage is 0 slots, BigQuery again scales down immediately to 0 slots. After the scale-down window has ended, BigQuery can scale down multiple times consecutively without requiring a new scale-down window.
Using reservations with baseline and autoscaling slots
In addition to specifying the maximum reservation size, you can optionally specify a baseline number of slots per reservation. The baseline is the minimum number of slots that will always be allocated to the reservation, and you will always be charged for them. Autoscaling slots are only added after all of the baseline slots (and idle slots if applicable) are consumed. You can share idle baseline slots in one reservation with other reservations that need capacity.
You can increase the number of baseline slots in a reservation every few minutes. If you want to decrease your baseline slots, you are limited to once an hour if you have recently changed your baseline slot capacity and your baseline slots exceed your committed slots. Otherwise, you can decrease your baseline slots every few minutes.
Reservations use and add slots in the following priority:
- Baseline slots.
- Idle slot sharing (if enabled). Reservations can only share idle baseline or committed slots from other reservations that were created with the same edition and the same region.
- Autoscale slots.
Introduction to slots autoscaling | BigQuery | Google Cloud
Cost Impact
- Commitments, which let you purchase slot capacity.
- Reservations (optional), which give you the ability to partition your capacity.
- Assignments, which gives you the ability to assign projects, folders, or your entire organization to Reservations.
Cost flexibility for your data warehouse | Google Cloud Blog
- Predictable Costs: Slot reservations provide predictable costs compared to on-demand pricing, where costs can fluctuate based on usage.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: Autoscaling ensures efficient use of compute resources, scaling up when needed and scaling down during idle times, which helps in cost optimization.
Flex Slots
Flex Slots, a new way to purchase BigQuery slots for short durations, as little as 60 seconds at a time. A slot is the unit of BigQuery analytics capacity. Flex Slots let you quickly respond to rapid demand for analytics and prepare for business events such as retail holidays and app launches. Flex Slots are rolling out to all BigQuery Reservations customers in the coming days!
Flex Slots give BigQuery Reservations users immense flexibility without sacrificing cost predictability or control.
- Flex Slots are priced at $0.04 per slot per hour, and are available in increments of 100 slots.
- It usually takes just a few minutes to deploy Flex Slots in BigQuery Reservations.
- Once deployed, you can cancel after just 60 seconds, and you will only be billed for the seconds Flex Slots are deployed.
Scale cloud data warehouse up and down quickly | Google Cloud Blog
Summary
Implementing slot-based pricing with autoscaling in BigQuery can help reduce analysis costs significantly while ensuring that you have the necessary compute resources to handle your workload efficiently. By optimizing your slot reservations based on actual usage patterns and workload characteristics, you can achieve cost predictability and operational efficiency in your BigQuery data analysis tasks.
Slots and Slot Time Consumed
- Slots are virtual CPUs used by BigQuery to execute your Queries and BigQuery allocates these resources based on Query complexity.
- Slot time consumed refers to the amount of time your query actively uses these resources to execute.
- When BigQuery processes a query job, it transforms the SQL statement into an execution plan. This plan is divided into a sequence of query stages, each consisting of finer-grained execution steps. BigQuery utilizes a distributed parallel architecture to execute these queries.
Bytes Shuffled
- BigQuery uses a distributed, multi-node architecture to execute queries so Bytes shuffled refers to the amount of data that was moved between these nodes during query execution.
- In queries involving complex joins, data will be distributed across nodes or shuffled to perform the required operations.
- Data shuffling is a resource-intensive process and one of the key factors that impact query performance, so reducing the data shuffled is a priority.
Some practises to reduce Bytes shuffled
- Use Sub-queries effectively — Subqueries can reduce shuffling by selecting a smaller subset of data but overusing the same(nested subqueries) is not recommended.
- Partitioned Tables
- If you are just exploring the table use the preview option rather than using a SELECT * statement (Applying Limit wouldn’t make a difference).
- Avoid using the
SELECT *statement and query only the columns you need or use theSELECT * EXCEPTto exclude columns.
Slot time consumed and Bytes Shuffled | by KS Haarish Dharan | DevOps.dev
Slot Time Consumed
In a course of Google, there is an example where a query shows 13 "elapsed time" seconds and 50 minutes of "slot time consumed". They says:
Hey, across all of our workers, we did essentially 50 minutes of work massively in parallel, 50 minutes so that your query could be returned back in 13 seconds. Best of all for you, you don't need to worry about spinning up those workers, moving data in-between them, making sure they're sharing all their results between their aggregations. All you care about is writing the SQL, finding the insights, and then running that query in a very fast turnaround. But there is abstracted from you a lot of distributed parallel processing that's happening.
Links
Purchase and manage slot commitments | BigQuery | Google Cloud