Design Patterns
Design Patterns of Microservices
- Aggregator
- API Gateway
- Chained or Chain of Responsibility
- Asynchronous Messaging
- Database or Shared Data
- Event Sourcing
- Branch
- Command Query Responsibility Segregator
- Circuit Breaker
- Decomposition
https://www.edureka.co/blog/microservices-design-patterns
- Decomposition patterns
Functional Decomposition
Functional decomposition is a term that engineers use to describea set of steps in which they break down the overall function of a device, system, or process into its smaller parts. A function is simply a task that is performed by a device, system, or process. Decomposition is a process of breaking down.
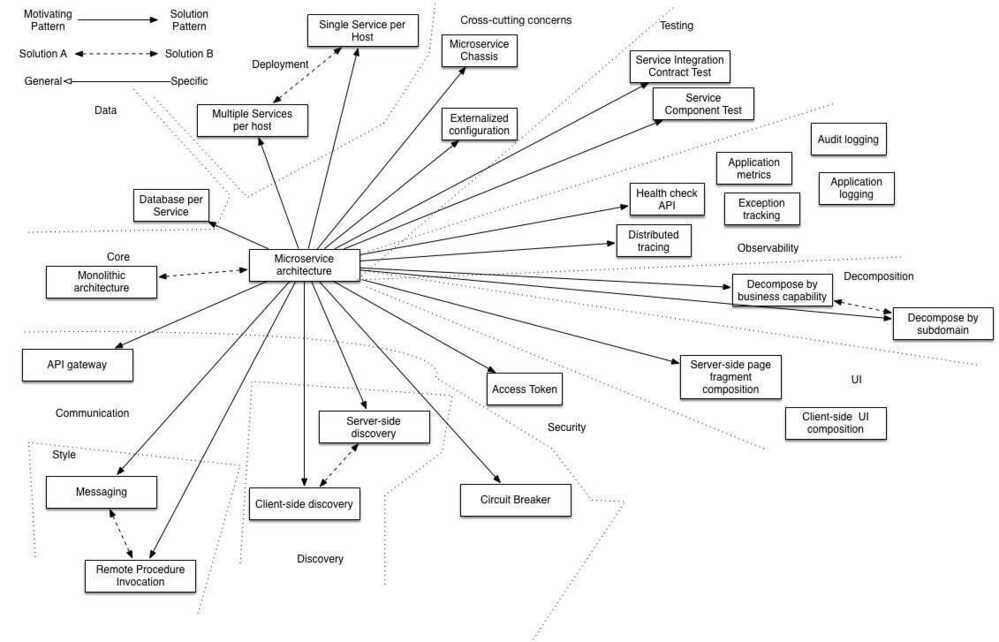
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Functional_decomposition- The Database per Service pattern describes how each service has its own database in order to ensure loose coupling.
- The API Gateway pattern defines how clients access the services in a microservice architecture.
- The Client-side Discovery and Server-side Discovery patterns are used to route requests for a client to an available service instance in a microservice architecture.
- The Messaging and Remote Procedure Invocation patterns are two different ways that services can communicate.
- The Single Service per Host and Multiple Services per Host patterns are two different deployment strategies.
- Cross-cutting concerns patterns:Microservice chassis pattern and Externalized configuration
- Testing patterns:Service Component Test and Service Integration Contract Test
- Circuit Breaker
- Access Token
- Observability patterns:
- UI patterns:
https://microservices.io/patterns/microservices.html
Catalog of patterns
| Pattern | Summary | Category |
|---|---|---|
| Ambassador | Create helper services that send network requests on behalf of a consumer service or application. | Design and Implementation Operational Excellence |
| Anti-Corruption Layer | Implement a façade or adapter layer between a modern application and a legacy system. | Design and Implementation, Operational Excellence |
| Asynchronous Request-Reply | Decouple backend processing from a frontend host, where backend processing needs to be asynchronous, but the frontend still needs a clear response. | Messaging |
| Backends for Frontends | Create separate backend services to be consumed by specific frontend applications or interfaces. | Design and Implementation |
| Bulkhead | Isolate elements of an application into pools so that if one fails, the others will continue to function. | Reliability |
| Cache-Aside | Load data on demand into a cache from a data store | Data Management, Performance Efficiency |
| Choreography | Let each service decide when and how a business operation is processed, instead of depending on a central orchestrator. | Messaging, Performance Efficiency |
| Circuit Breaker | Handle faults that might take a variable amount of time to fix when connecting to a remote service or resource. | Reliability |
| Claim Check | Split a large message into a claim check and a payload to avoid overwhelming a message bus. | Messaging |
| Compensating Transaction | Undo the work performed by a series of steps, which together define an eventually consistent operation. | Reliability |
| Competing Consumers | Enable multiple concurrent consumers to process messages received on the same messaging channel. | Messaging |
| Compute Resource Consolidation | Consolidate multiple tasks or operations into a single computational unit | Design and Implementation |
| CQRS | Segregate operations that read data from operations that update data by using separate interfaces. | Data Management, Design and Implementation, Performance Efficiency |
| Deployment Stamps | Deploy multiple independent copies of application components, including data stores. | Reliability, Performance Efficiency |
| Event Sourcing | Use an append-only store to record the full series of events that describe actions taken on data in a domain. | Data Management, Performance Efficiency |
| External Configuration Store | Move configuration information out of the application deployment package to a centralized location. | Design and Implementation, Operational Excellence |
| Federated Identity | Delegate authentication to an external identity provider. | Security |
| Gatekeeper | Protect applications and services by using a dedicated host instance that acts as a broker between clients and the application or service, validates and sanitizes requests, and passes requests and data between them. | Security |
| Gateway Aggregation | Use a gateway to aggregate multiple individual requests into a single request. | Design and Implementation, Operational Excellence |
| Gateway Offloading | Offload shared or specialized service functionality to a gateway proxy. | Design and Implementation, Operational Excellence |
| Gateway Routing | Route requests to multiple services using a single endpoint. | Design and Implementation, Operational Excellence |
| Geodes | Deploy backend services into a set of geographical nodes, each of which can service any client request in any region. | Reliability, Operational Excellence |
| Health Endpoint Monitoring | Implement functional checks in an application that external tools can access through exposed endpoints at regular intervals. | Reliability, Operational Excellence |
| Index Table | Create indexes over the fields in data stores that are frequently referenced by queries. | Data Management, Performance Efficiency |
| Leader Election | Coordinate the actions performed by a collection of collaborating task instances in a distributed application by electing one instance as the leader that assumes responsibility for managing the other instances. | Design and Implementation, Reliability |
| Materialized View | Generate prepopulated views over the data in one or more data stores when the data isn't ideally formatted for required query operations. | Data Management, Operational Excellence |
| Pipes and Filters | Break down a task that performs complex processing into a series of separate elements that can be reused. | Design and Implementation, Messaging |
| Priority Queue | Prioritize requests sent to services so that requests with a higher priority are received and processed more quickly than those with a lower priority. | Messaging, Performance Efficiency |
| Publisher/Subscriber | Enable an application to announce events to multiple interested consumers asynchronously, without coupling the senders to the receivers. | Messaging |
| Queue-Based Load Leveling | Use a queue that acts as a buffer between a task and a service that it invokes in order to smooth intermittent heavy loads. | Reliability, Messaging, Resiliency, Performance Efficiency |
| Retry | Enable an application to handle anticipated, temporary failures when it tries to connect to a service or network resource by transparently retrying an operation that's previously failed. | Reliability |
| Scheduler Agent Supervisor | Coordinate a set of actions across a distributed set of services and other remote resources. | Messaging, Reliability |
| Sequential Convoy | Process a set of related messages in a defined order, without blocking processing of other groups of messages. | Messaging |
| Sharding | Divide a data store into a set of horizontal partitions or shards. | Data Management, Performance Efficiency |
| Sidecar | Deploy components of an application into a separate process or container to provide isolation and encapsulation. | Design and Implementation, Operational Excellence |
| Static Content Hosting | Deploy static content to a cloud-based storage service that can deliver them directly to the client. | Design and Implementation, Data Management, Performance Efficiency |
| Strangler Fig | Incrementally migrate a legacy system by gradually replacing specific pieces of functionality with new applications and services. | Design and Implementation, Operational Excellence |
| Throttling | Control the consumption of resources used by an instance of an application, an individual tenant, or an entire service. | Reliability, Performance Efficiency |
| Valet Key | Use a token or key that provides clients with restricted direct access to a specific resource or service. | Data Management, Security |
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/architecture/patterns
Enterprise Application Architecture
- Domain Logic Patterns: Transaction Script, Domain Model, Table Module, Service Layer.
- Data Source Architectural Patterns: Table Data Gateway, Row Data Gateway, Active Record, Data Mapper.
- Object-Relational Behavioral Patterns: Unit of Work, Identity Map, Lazy Load
- Object-Relational Structural Patterns: Identity Field, Foreign Key Mapping, Association Table Mapping, Dependent Mapping, Embedded Value, Serialized LOB, Single Table Inheritance, Class Table Inheritance, Concrete Table Inheritance, Inheritance Mappers.
- Object-Relational Metadata Mapping Patterns: Metadata Mapping, Query Object, Repository.
- Web Presentation Patterns: Model View Controller, Page Controller, Front Controller, Template View, Transform View, Two-Step View, Application Controller.
- Distribution Patterns: Remote Facade, Data Transfer Object
- Offline Concurrency Patterns: Optimistic Offline Lock, Pessimistic Offline Lock, Coarse Grained Lock, Implicit Lock.
- Session State Patterns: Client Session State, Server Session State, Database Session State.
- Base Patterns: Gateway, Mapper, Layer Supertype, Separated Interface, Registry, Value Object, Money, Special Case, Plugin, Service Stub, Record Set
https://martinfowler.com/eaaCatalog/index.html
Self Contained System (SCS)
The Self-contained System (SCS) approach is an architecture that focuses on a separation of the functionality into many independent systems, making the complete logical system a collaboration of many smaller software systems. This avoids the problem of large monoliths that grow constantly and eventually become unmaintainable.