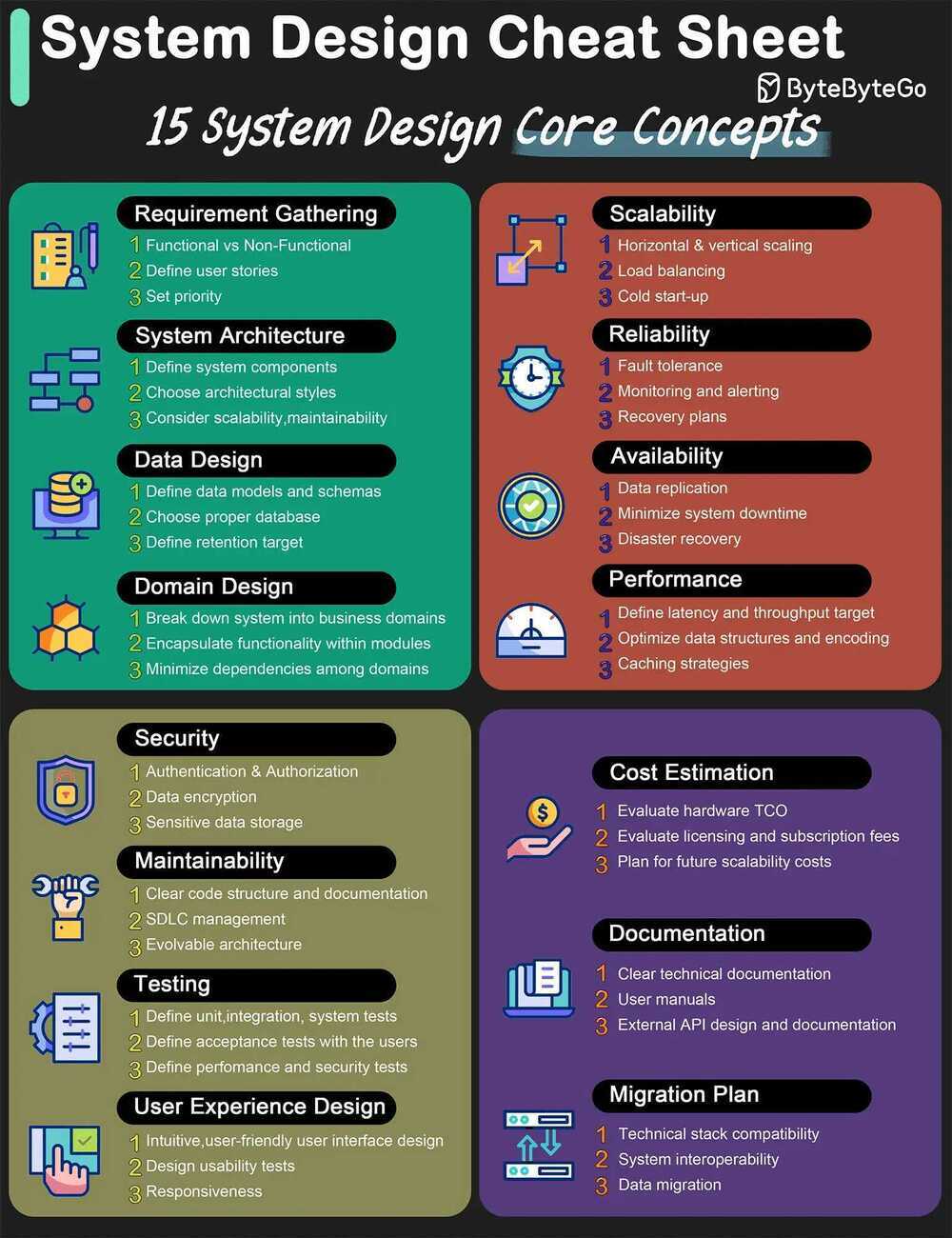
Intro
MOSCOW : Must have, Should have, Could have, Would have
Systems design is the process of defining the architecture, modules, interfaces, and data for a system to satisfy specified requirements. Systems design could be seen as the application of systems theory to product development. There is some overlap with the disciplines of systems analysis, systems architecture and systems engineering
- Inversion Of Control
- Callbacks
- Hollywood principle - Don't call me, we will call you
- Android - Used Interface for callback onSuccess of async task
- Build vs Buy vs Get for Free
- Planet Scale Systems
Answering system design interview questions
- Get domain knowledge of what are we building
- Core features - Only design 2-3 core features for a system design question
- For what scale we are building
Introduction
- Features
- Define APIs
- CAP Theorem
- Consistency
- Availability, and
- Partition Tolerance
- Latency Performance (If customer facing application, then latency matters)
- Scalability (Add more users and requests)
- Durability (Data is not lost or compromised)
- Class Diagrams
- Security & Privacy
- Cost Effective
Approaching a system design problem
Gather requirements (Functional and non-functional requirements)
- Functional
- sendMessage(messageBody)
- receiveMessage()
- Non-functional
- Scalable (handles load increases, more queues and messages)
- Highly available (services hardware/network failures)
- Highly performent (single digit latency for main operations)
- Durable (once submitted, data is not lost)
- What is the expected read-to-write ratio?
- How many concurrent requests should we expect?
- What's the average expected response time?
- What's the limit of the data we allow users to provide?
- How many customers
- RPS / Traffic
- Who are the users
Establish the Scope
- Do we want to discuss the end-to-end experience or just the API?
- What clients do we want to support (mobile, web, etc)?
- Do we require authentication? Analytics? Integrating with existing systems?
High level design
- Cloud - CDN / LoadBalancers / Servers / Queues
- Database layer
- Scalability
Low level design
- DS + Algo
- API
- Data model
- Database schema
- Optimizations
- Edge cases
- Viral Videos
- High number of followers
Others
- Security
- Reliability
- Replication
- Tradeoffs
https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/systems-design-for-interviews
https://hackernoon.com/anatomy-of-a-system-design-interview-4cb57d75a53f
https://towardsdatascience.com/the-complete-guide-to-the-system-design-interview-ba118f48bdfc
System Design Introduction For Interview. - YouTube
- Ask good questions
- What features to work on
- How much to scale
- Don't use Buzzwords
- Clear and organized thinking
- Drive discussions (80% you talk, 20% interviewer talk)
Scaling
- Vertical Scaling / Scale up (Add more CPU, RAM, Storage to an existing host)
- Horizontal Scaling / Scale out (Keep one host small and add another host)
Vertical Scaling is expensive and have a limit whereas Horizontal Scaling is cheap. But we have to take care of distributed systems problem in Horizontal Scaling and not in Vertical Scaling.
Data Centers / Rack / Hosts
Consider latency between cross racks, cross hosts
CPU / Memory / HardDrive / Network Bandwidth
All of the above are limited resources. How to improve limitations while scaling
Random vs Sequential read/writes on disk
Always sequential read is far faster than random read/write on a disk.
CDNs and Edge
CDN - Content Delivery Network
Edge - You do processing close to the end user. It has dedicated network from the edge to all the way to the data center so your request could be routed over this dedicated network instead of going over the general internet.
Virtual machines and containers
Virtual Machines - are a way of giving you an OS on top of a shared resource such that you feel like you are the exclusive owner of that hardware while in reality that hardware is shared between different isolated operating system. Containers - is a way of running your applications and its dependencies in an isolated environment.
Publisher - Subscriber or Queue
- Queuing is a point-to-point communication model - a pool of consumers may read from a server and each message is delivered to one of them - it allows you to divide up the processing of data over multiple consumer instances and scale your processing.
- Publish-subscribe is a broadcast communication model - a message is broadcast to all the consumers.
Thin clients, Thick clients, Dumb clients, Smart client
Kafka clients tend to be "thick" and have a lot of complexity. That is, they do a lot because the broker is designed to be simple. That's my guess as to why there are so few native client libraries up to par with the Java client. NATS Streaming clients, on the other hand, are relatively "thin" because the server does more. We end up just pushing the complexity around based on our design decisions, but one can argue that the smart client and dumb server is a more scalable approach.
Availability
| Nines | Percent | Downtime/Year | σ Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 99.99% | 52.596 minutes | 4σ |
| 5 | 99.999% | 5.2596 minutes | - |
| 6 | 99.9999% | 31.5576 seconds | 5σ |
| 7 | 99.99999% | 3.15576 seconds | - |
| 8 | 99.999999% | 315.6 milliseconds | 6σ |
5 9s (99.999%) or higher scenario with a recovery time under one minute - Reliability Pillar
ADR - Architecture Design Record
Architects are often writing the ADRs (Architecture Decision Record), those are documents that are helping anyone in the company to understand why a decision was made describing the context, the options available, the chosen one and finally the consequences generated by this decision.- An architecture decision record(ADR) is a document that captures an important architectural decision made along with its context and consequences.
- An architecture decision(AD) is a software design choice that addresses a significant requirement.
- An architecture decision log(ADL) is the collection of all ADRs created and maintained for a particular project (or organization).
- An architecturally-significant requirement(ASR) is a requirement that has a measurable effect on a software system's architecture.
- All these are within the topic of architecture knowledge management(AKM).
https://github.com/joelparkerhenderson/architecture-decision-record
https://cognitect.com/blog/2011/11/15/documenting-architecture-decisions
Scale Cube
The scale cube is a technology model that indicates three methods (or approaches) by which technology platforms may be scaled to meet increasing levels of demand upon the system in question. The three approaches defined by the model include scaling through replication or cloning (the "X axis"), scaling through segmentation along service boundaries or dissimilar components (the "Y axis") and segmentation or partitioning along similar components (the "Z axis").
3 Dimensions to Scaling
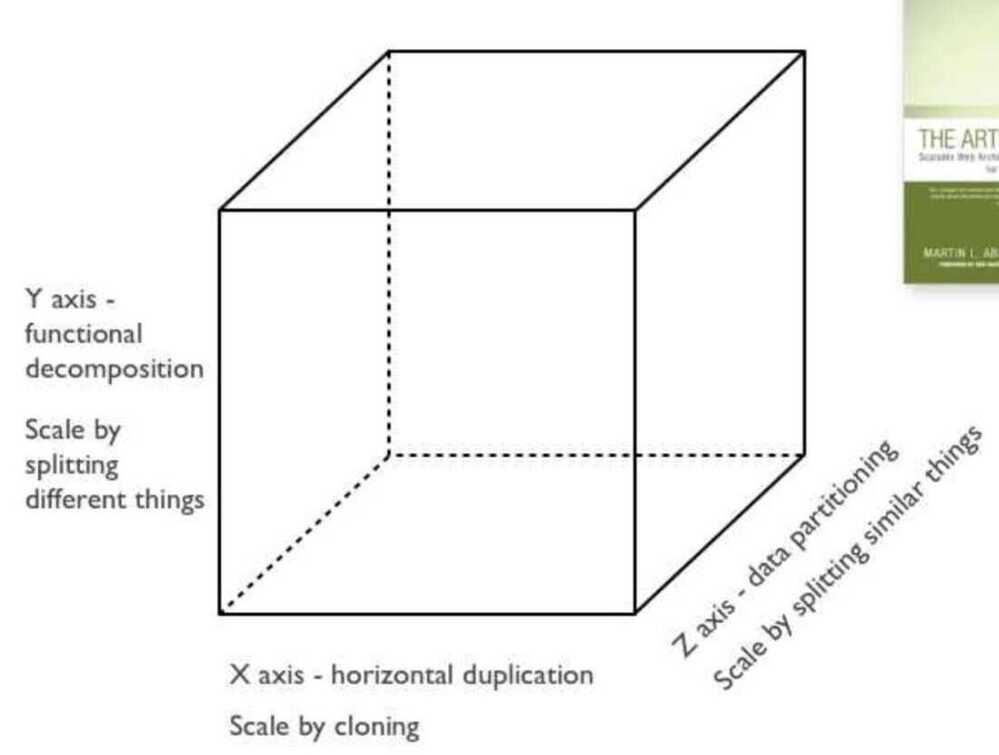
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Scale_cube
https://microservices.io/articles/scalecube.html
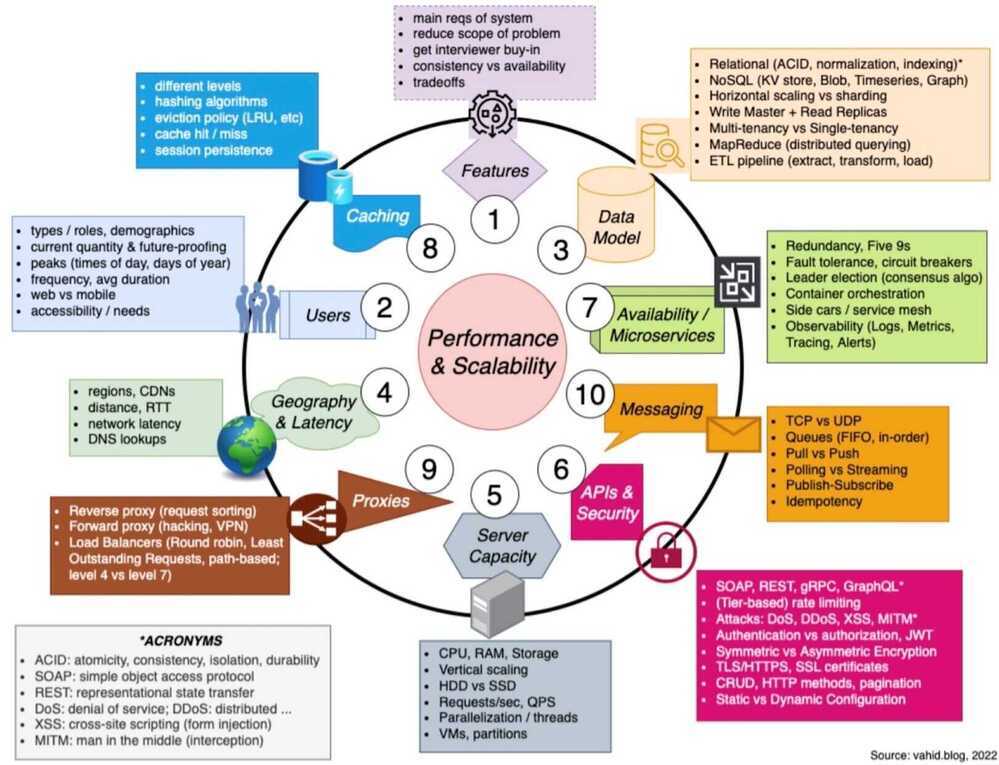
LLD (Low Level Design)
https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLAC2AM9O1C5KioUMeH9qIjbAV_RMmX8rd
When building a full-stack feature, start where the data is
Exposing some data from the database?
Start with the backend. Build the API first and then consume it in the front end
Is it coming from a user input?
Start with the front end. Build the form and then build an API to publish it to
This helps as you no longer have to make assumptions about
- the format of the data,
- the data types of each field, or
- what data is even available
Links
System Design Blueprint: The Ultimate Guide | by Love Sharma | Apr, 2023 | Dev Genius
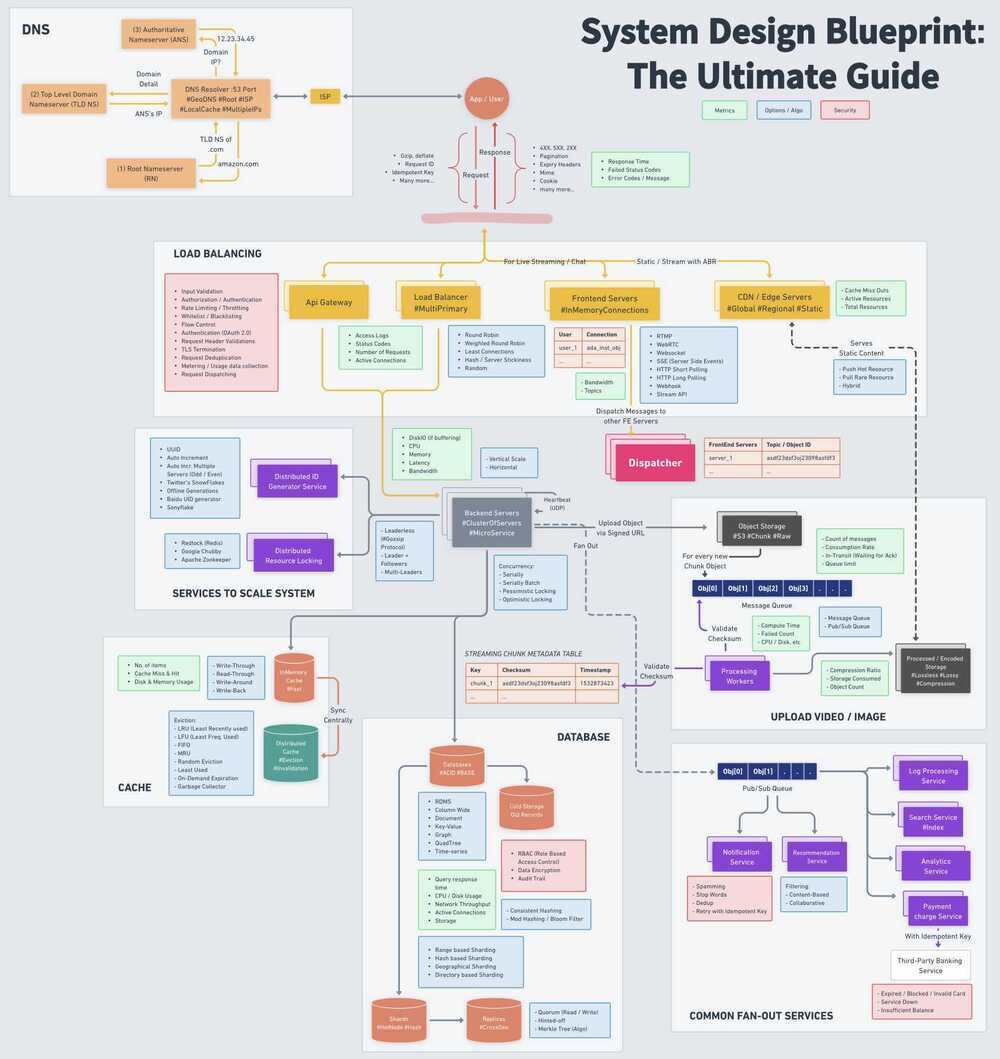
- System Designs - YouTube
- System Design Master Template: How to Answer Any System Design Interview Question. | by Arslan Ahmad | Level Up Coding
- Mastering the Art of Caching for System Design Interviews: A Complete Guide | by Arslan Ahmad | Level Up Coding
- How to Use Consistent Hashing in a System Design Interview? | by Arslan Ahmad | InterviewNoodle
- System Design Interview Basics: CAP vs. PACELC | by Arslan Ahmad | InterviewNoodle
- System Design Interviews: A Step-By-Step Guide | by Arslan Ahmad | InterviewNoodle
- System Design Interview Question: Designing a URL Shortening Service | by Arslan Ahmad | InterviewNoodle
- System Design Interviews: What distinguishes you from others? | by Arslan Ahmad | InterviewNoodle
- The Complete Guide to Ace the System Design Interview in 2023 | by Arslan Ahmad | CodeX | Medium
- Top 7 Facebook System Design Interview Questions and Answers (2023) | by Arslan Ahmad | CodeX | Medium
- System Design Tutorial: 3 Must-Know Distributed Systems Concepts | by Arslan Ahmad | Geek Culture | Medium
- Brief History of Scaling Uber
- Behind AWS S3’s Massive Scale
- Software Architecture Patterns - ByteByteGo Newsletter
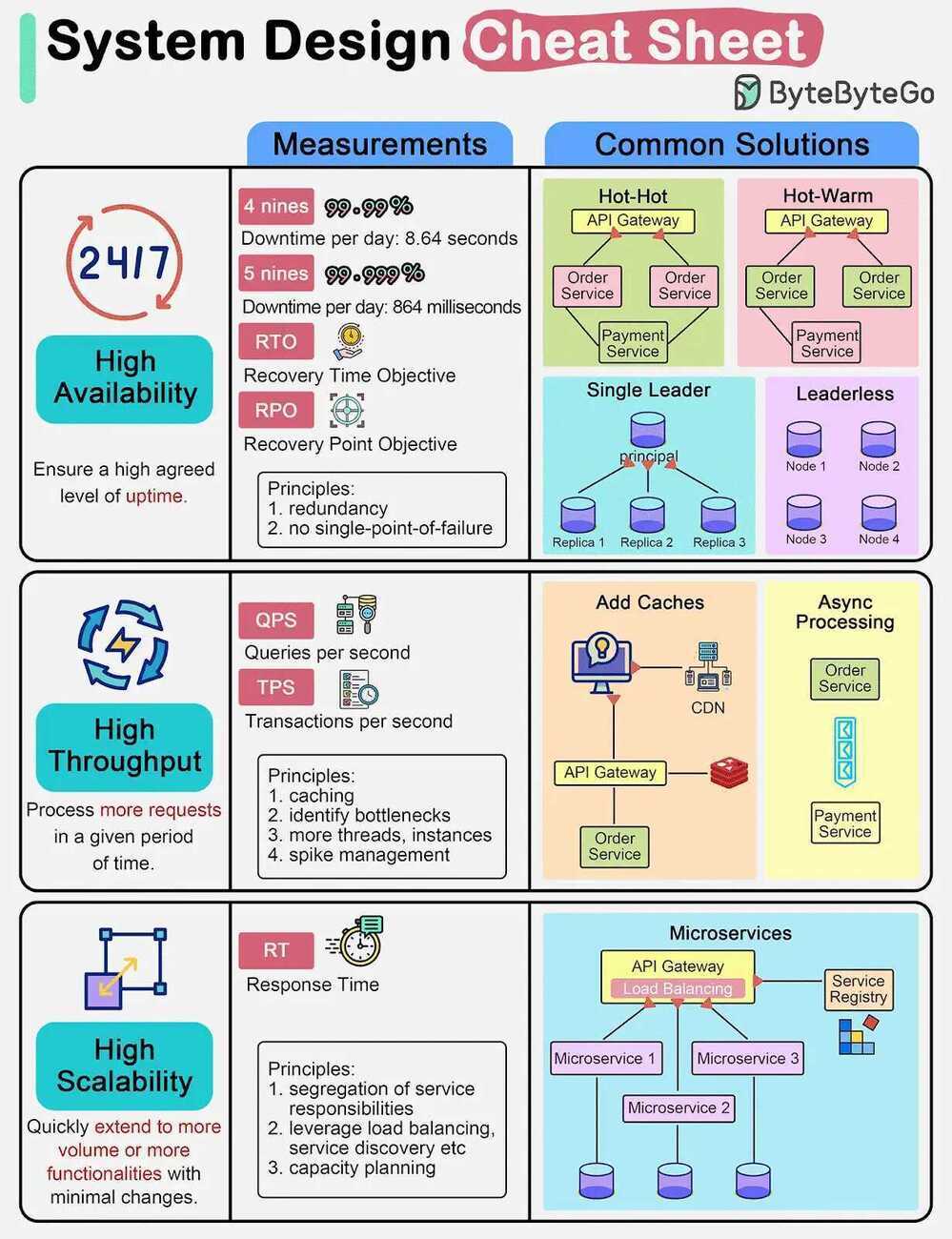
- Latency vs Throughput: https://lnkd.in/gSBsmijw
- CAP Theorem: https://lnkd.in/gV7NunUD
- ACID Transactions: https://lnkd.in/gpQMxV9u
- Consistent Hashing: https://lnkd.in/gaCVWBJM
- Rate Limiting: https://lnkd.in/gjkrHkGu
- Microservices Architecture: https://lnkd.in/gy3kRzep
- API Design: https://lnkd.in/ghcbQySg
- Strong vs Eventual Consistency: https://lnkd.in/g2ACr56Q
- Synchronous vs asynchronous communications: https://lnkd.in/gYZ8Acth
- REST vs RPC: https://lnkd.in/gs7htCMG
- Batch Processing vs Stream Processing: https://lnkd.in/gBKHzqAe
- Fault Tolerance: https://lnkd.in/ggzdZVhM
- Consensus Algorithms: https://lnkd.in/gUcVEhUx
- Gossip Protocol: https://lnkd.in/gvkckQGY
- Serverless Architecture: https://lnkd.in/g3EYA3nz
- Service Discovery: https://lnkd.in/gt84khQG
- Disaster Recovery: https://lnkd.in/grpEFGfD
- Distributed Tracing: https://lnkd.in/ga5FJuH2
- Horizontal vs Vertical Scaling: https://lnkd.in/eQc9FRjf
- Content Delivery Network (CDN): https://lnkd.in/e7reQ4VF
- Domain Name System (DNS): https://lnkd.in/es8Fp7Q5
- Caching: https://lnkd.in/eZkyjptm
- Distributed Caching: https://lnkd.in/e4AHNSeT
- Load Balancing: https://lnkd.in/eWdwhGap
- SQL vs NoSQL: https://lnkd.in/es6vJwit
- Database Index: https://lnkd.in/ebKcznNJ
- Consistency Patterns: https://lnkd.in/eTZ5dHQx
- HeartBeat: https://lnkd.in/eRBRtfk9
- Circuit Breaker: https://lnkd.in/eStETWQA
- Idempotency: https://lnkd.in/eSYjuq-b
- Database Scaling: https://lnkd.in/egFC33Zk
- Data Replication: https://lnkd.in/ehZjnuWx
- Data Redundancy: https://lnkd.in/eUCxcXr2
- Database Sharding: https://lnkd.in/eF_2KNKT
- Microservices Guidelines: https://lnkd.in/ea8hcbqp
- Failover: https://lnkd.in/eftew-CE
- Proxy Server: https://lnkd.in/eVCYxMZQ
- Message Queues: https://lnkd.in/eVeVWT3a
- WebSockets: https://lnkd.in/eA4zYkjF
- Bloom Filters: https://lnkd.in/eG3xPV-x
- API Gateway: https://lnkd.in/e-zCR3ft
- Distributed Locking: https://lnkd.in/eXsuuthN
- Checksum: https://lnkd.in/ed4j8cfk