Addressing Failures
Cascading Failures
A cascading failure is a failure that grows over time as a result of positive feedback.^107^ It can occur when a portion of an overall system fails, increasing the probability that other portions of the system fail. For example, a single replica for a service can fail due to overload, increasing load on remaining replicas and increasing their probability of failing, causing a domino effect that takes down all the replicas for a service.
Causes
-
Server Overload
-
Resource Exhaustion
-
CPU
-
Increased number of in-flight requests
-
Excessively long queue lengths
-
Thread starvation
-
CPU or request starvation
-
Missed RPC Deadlines
-
Reduced CPU caching benefits
-
-
Memory
-
Dying tasks
-
Increases rate of Garbage Collection (GC), resulting in increased CPU Usage
-
Reduction in cache hit rates
-
-
Threads
-
File Descriptors
-
Dependencies among resources
-
Service Unavailability
Prevention
-
Load test the server's capacity limits, and test the failure mode for overload
-
Serve degraded results
-
Instrument the server to reject requests when overloaded
-
Instrument higher-level systems to reject requests, rather than overloading servers
-
Perform capacity planning
-
Queue Management
-
Load Shedding and Graceful Degradation
Load Shedding
The idea is to ignore some requests rather than crashing a system and making it fail to serve any request.
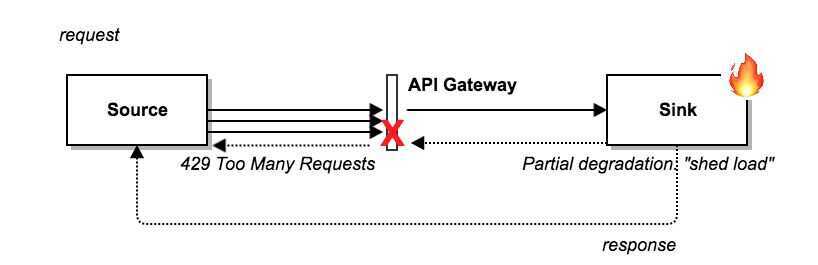
-
Retries
-
Latency and Deadlines
-
Picking a Deadline
-
Missing Deadlines
-
Deadline Propagation
-
Cancellation Propagation
-
Bimodal Latency
-
Slow Startup and Cold Caching
-
Always go Downward in the Stack
Triggering Conditions for Cascading Failures
-
Process Death
-
Process Updates
-
New Rollouts
-
Organic Growth
-
Planned Changes, Drains, or Turndowns
-
Request Profile Changes
-
Resource Limits
Testing for Cascading Failures
-
Test Until Failure and Beyond
-
Test Popular Clients
-
Test Noncritical Backends
Immediate Steps to Address Cascading Failures
-
Increase Resources
-
Stop Health Check Failures/Deaths
-
Restart Servers
-
Drop Traffic
-
Enter Degraded Modes
-
Eliminate Batch Load
-
Eliminate Bad Traffic
Reference
http://highscalability.com/blog/2018/4/25/google-addressing-cascading-failures.html