GCP BigQuery / Big Query
Architecture
- Dremel - The execution engine
- Colossus - Distributed Storage
- Borg - Compute
- Jupiter - The Network
- BigQuery - The Service
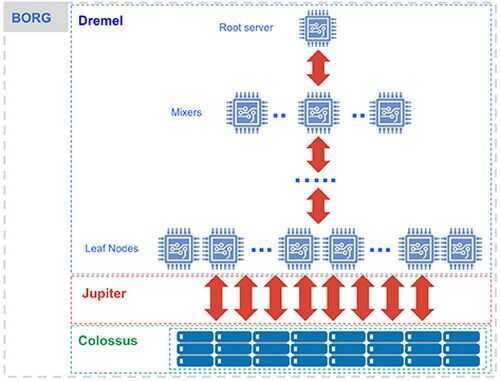
Separation of Compute and State
Separation of compute and state refers to the ability to maintain intermediate state between processing stages in a high-performance component separate from either the compute cluster or storage.
- Less state in compute means compute becomes more ephemeral and scalable. It's easier to re-parallelize processing intra-stage and interstage, and easier to recover from a lost node.
- Processing is more streamlined; processing stages don't conflict within the same compute nodes, resulting in resource contention and bottlenecks.
- It's easier for the processing engine to re-partition workloads between stages.
- Your processing engine can take advantage of pipelined execution. In other words, it doesn't have to wait for Stage N to finish before starting Stage N+1.
- The processing engine can implement dynamic work repartitioning (the ability to re-parallelize work due to slow workers or data skew).
- Keeping less state in processing nodes makes workloads more resilient to individual node issues.
- The service can utilize available resources much more efficiently across compute as well as shuffle.
https://cloud.google.com/blog/products/gcp/bigquery-under-the-hood
Commands
from google.cloud import bigquery
client = bigquery.Client()
dataset_ref = client.dataset("hacker_news", project="bigquery-public-data")
dataset_ref = client.dataset("chicago_crime", project="bigquery-public-data")
dataset = client.get_dataset(dataset_ref)
-- standardSQL
SELECT
departure_airport,
arrival_airport,
COUNT(1) AS num_flights
FROM
`bigquery-samples.airline_ontime_data.flights`
GROUP BY
departure_airport,
arrival_airport
ORDER BY
num_flights DESC
LIMIT
10
-- standardSQL
SELECT
departure_delay,
COUNT(1) AS num_flights,
APPROX_QUANTILES(arrival_delay, 5) AS arrival_delay_quantiles
FROM
`bigquery-samples.airline_ontime_data.flights`
GROUP BY
departure_delay
HAVING
num_flights > 100
ORDER BY
departure_delay ASC
Google Cloud Dataflow
- Dataflow is a unified programming model and a managed service for developing and executing a wide range of data processing patterns including ETL, batch computation, and continuous computation.
- The Dataflow model combines batch and stream processing so developers don't have to make tradeoffs between correctness, cost, and processing time.
Pricing
Queries (on-demand) - $6.25 per TiB - The first 1 TiB per month is free.
Pricing | BigQuery: Cloud Data Warehouse | Google Cloud
Others
BigQueryshould not be used if you expect OLTP behavior or performance.
References
https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/training-data-analyst
php - Speed of inserting to BigQuery - should this be batched in background? - Stack Overflow