NLTK
NLTK -- the Natural Language Toolkit -- is a suite of open source Python modules, data sets, and tutorials supporting research and development in Natural Language Processing.
NLTK supports classification, tokenization, stemming (lemmatization better than stemming), tagging, parsing, and semantic reasoning functionalities.
Library highlights
- Lexical analysis: Word and text tokenizer
- n-gram and collocations
- Part-of-speech tagger
- Tree model and Textchunker for capturing
- Named-entity recognition
Commands
import nltk
nltk.download()
from nltk.book import *
text1
len(text6)
texts()
sents()
The sents() function divides the text up into its sentences, where each sentence is a list of words
text1.concordance("monstrous") #A concordance view shows us every occurrence of a given word, together with some context
text2.similar("monstrous")
text2.common_contexts(["monstrous", "very"])
text4.dispersion_plot(["citizens", "democracy", "freedom", "duties", "America"])
text6.dispersion_plot(["Arthur", "Holy", "Grail"])
text6.generate()
text6.count("Grail")
text6.count("grail")
fdist1 = FreqDist(text1)
fdist1.most_common(50)
fdist1.plot(50, cumulative=True)
cfd = nltk.ConditionalFreqDist(
... (genre, word)
... for genre in brown.categories()
... for word in brown.words(categories=genre))
genres = ['news', 'religion', 'hobbies', 'science_fiction', 'romance', 'humor']
modals = ['can', 'could', 'may', 'might', 'must', 'will']
cfd.tabulate(conditions=genres, samples=modals)
NLTK's Frequency Distributionss
| Example | Description |
|---|---|
| fdist = FreqDist(samples) | create a frequency distribution containing the given samples |
| fdist[sample] += 1 | increment the count for this sample |
| fdist['monstrous'] | count of the number of times a given sample occurred |
| fdist.freq('monstrous') | frequency of a given sample |
| fdist.N() | total number of samples |
| fdist.most_common(n) | the n most common samples and their frequencies |
| for sample in fdist: | iterate over the samples |
| fdist.max() | sample with the greatest count |
| fdist.tabulate() | tabulate the frequency distribution |
| fdist.plot() | graphical plot of the frequency distribution |
| fdist.plot(cumulative=True) | cumulative plot of the frequency distribution |
fdist1 |= fdist2 | update fdist1 with counts from fdist2 |
fdist1 < fdist2 | test if samples in fdist1 occur less frequently than in fdist2 |
Corpus
nltk.chat.chatbots()
nltk.corpus.gutenberg.fileids()
emma = nltk.Text(nltk.corpus.gutenberg.words('austen-emma.txt'))
len(gutenberg.raw('austen-emma.txt'))
The raw() function gives us the contents of the file without any linguistic processing.
from nltk.corpus import webtext
webtext.fileids()
from nltk.corpus import nps_chat
nps_chat.posts('10-19-20s_706posts.xml')
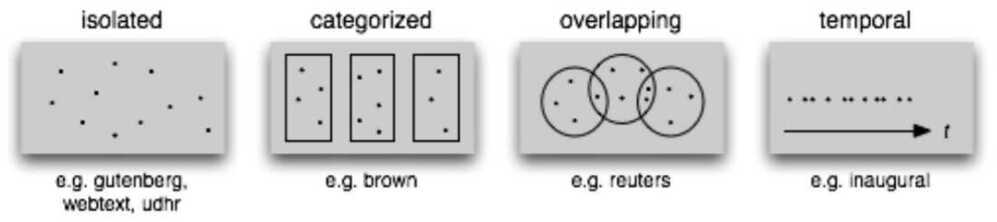
The Brown Corpus is a convenient resource for studying systematic differences between genres, a kind of linguistic inquiry known as stylistics.
first million-word electronic corpus of English
from nltk.corpus import brown
brown.categories()
brown.words(categories='news')
brown.words(fileids=['cg22'])
brown.sents(categories=['news', 'editorial', 'reviews'])
from nltk.corpus import reuters
reuters.fileids()
reuters.categories()
reuters.categories(['training/9865', 'training/9880'])
from nltk.corpus import inaugural
inaugural.fileids()
cfd = nltk.ConditionalFreqDist(
... (target, fileid[:4])
... for fileid in inaugural.fileids()
... for w in inaugural.words(fileid)
... for target in ['america', 'citizen']
... if w.lower().startswith(target))
cfd.plot()
nltk.corpus.indian.words('hindi.pos')
nltk.corpus.cess_esp.words()
nltk.corpus.floresta.words()
nltk.corpus.udhr.fileids() #univeral declaration of human rights in 300 languages
| Example | Description |
|---|---|
| fileids() | the files of the corpus |
| fileids([categories]) | the files of the corpus corresponding to these categories |
| categories() | the categories of the corpus |
| categories([fileids]) | the categories of the corpus corresponding to these files |
| raw() | the raw content of the corpus |
| raw(fileids=[f1,f2,f3]) | the raw content of the specified files |
| raw(categories=[c1,c2]) | the raw content of the specified categories |
| words() | the words of the whole corpus |
| words(fileids=[f1,f2,f3]) | the words of the specified fileids |
| words(categories=[c1,c2]) | the words of the specified categories |
| sents() | the sentences of the whole corpus |
| sents(fileids=[f1,f2,f3]) | the sentences of the specified fileids |
| sents(categories=[c1,c2]) | the sentences of the specified categories |
| abspath(fileid) | the location of the given file on disk |
| encoding(fileid) | the encoding of the file (if known) |
| open(fileid) | open a stream for reading the given corpus file |
| root | if the path to the root of locally installed corpus |
| readme() | if the path to the root of locally installed corpus the contents of the README file of the corpus |
Others
python - indian-namematch 1.3.0
https://pypi.org/project/indian-namematch
https://towardsdatascience.com/surprisingly-effective-way-to-name-matching-in-python-1a67328e670e