Architecture and Key Components
The diagram below shows the Flink components as well as the Flink runtime flow. The program code or SQL query is composed into an operator graph which is then submitted by the client to a job manager. The job manager breaks the job into operators which execute as tasks on nodes that are running task managers. These tasks process streaming data and interact with various data sources, such as the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) and Apache Kafka.
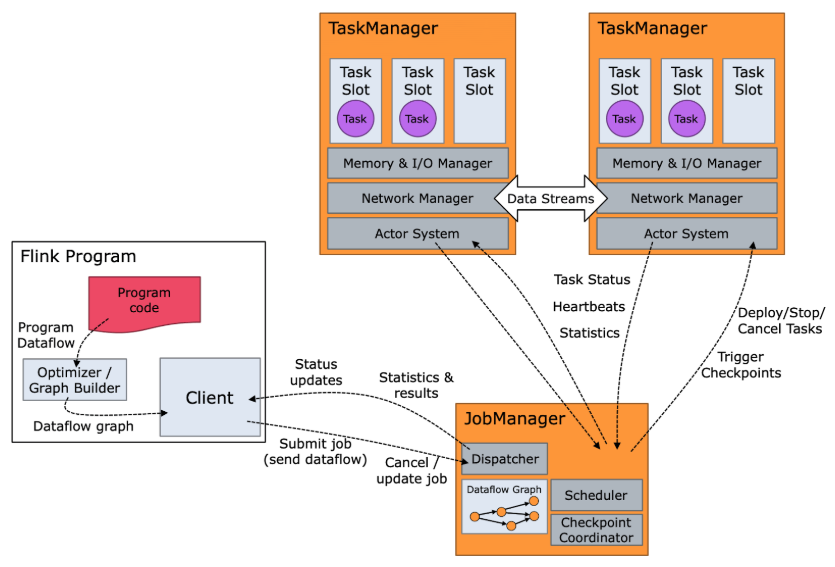
The figure below shows the building blocks of every Flink cluster. There is always somewhere a client running. It takes the code of the Flink applications, transforms it into a JobGraph and submits it to the JobManager.
The JobManager distributes the work onto the TaskManagers, where the actual operators (such as sources, transformations and sinks) are running.
When deploying Flink, there are often multiple options available for each building block. We have listed them in the table below the figure.

Flink Components
| Component | Purpose | Implementations |
|---|---|---|
| Flink Client | Compiles batch or streaming applications into a dataflow graph, which it then submits to the JobManager. | - Command Line Interface - REST Endpoint - SQL Client - Python REPL |
| JobManager | JobManager is the name of the central work coordination component of Flink. It has implementations for different resource providers, which differ on high-availability, resource allocation behavior and supported job submission modes. JobManager modes for job submissions: - Application Mode: runs the cluster exclusively for one application. The job's main method (or client) gets executed on the JobManager. Calling execute/executeAsync multiple times in an application is supported.- Per-Job Mode: runs the cluster exclusively for one job. The job's main method (or client) runs only prior to the cluster creation. - Session Mode: one JobManager instance manages multiple jobs sharing the same cluster of TaskManagers | - Standalone (this is the barebone mode that requires just JVMs to be launched. Deployment with Docker, Docker Swarm / Compose, non-native Kubernetes and other models is possible through manual setup in this mode) - Kubernetes - YARN |
| TaskManager | TaskManagers are the services actually performing the work of a Flink job. |
External Components (all optional)
| Component | Purpose | Implementations |
|---|---|---|
| High Availability Service Provider | Flink's JobManager can be run in high availability mode which allows Flink to recover from JobManager faults. In order to failover faster, multiple standby JobManagers can be started to act as backups. | - Zookeeper - Kubernetes HA |
| File Storage and Persistency | For checkpointing (recovery mechanism for streaming jobs) Flink relies on external file storage systems | See FileSystems page. |
| Resource Provider | Flink can be deployed through different Resource Provider Frameworks, such as Kubernetes or YARN. | See JobManager implementations above. |
| Metrics Storage | Flink components report internal metrics and Flink jobs can report additional, job specific metrics as well. | See Metrics Reporter page. |
| Application-level data sources and sinks | While application-level data sources and sinks are not technically part of the deployment of Flink cluster components, they should be considered when planning a new Flink production deployment. Colocating frequently used data with Flink can have significant performance benefits | For example: - Apache Kafka - Amazon S3 - Elasticsearch - Apache Cassandra See Connectors page. |
Workflow
Apache Flink is extensively used for stream processing. In a simple Flink application, you define —
- One or more sources from where the data will be ingested.
- A series of operations on the data —Both Stateful and stateless computations
- Degree of parallelism for the operations to speed up the computation
- One or more sinks to send the output of the computation
Here are a few of the important aspects that need to be understood to be able to start understanding how Flink manages and executed the application —
- In a Flink program, you define the data source/s, specify the operations on the input data, define the flow of data between the operators, and egress it to one or more sinks.
- Flink has its optimizer that optimizes the application from the execution efficiency perspective.
- Flink application will be converted into a “Dataflow graph” and will be submitted to the Flink cluster for execution.

Let’s try to understand that what will the Job consist of that is submitted to the Flink cluster. It is not that complicated. It is a directed graph that consists of Nodes (nothing but the Operators or Tasks) and edges (defines inputs/outputs and relationship between nodes). So, Flink cluster should be able to provide some way to accept & execute the tasks the way it is submitted as part of the Job. Consider this as our first requirement from the Flink Cluster.
Flink supports distributed processing and horizontal scaling. So, Flink cluster should be able to support distributed processing and horizontal scaling. Consider this as our second requirement from the Flink Cluster.
Considering the about requirements from the Flink cluster, it has two types of components —
- Job manager — Accepts the task (Can be one or more)
- Task manager — Executes the tasks (Can be one or more)

Let’s talk about the Job manager first. Here is the list of responsibilities of the Job manager-
- Its primary function is to accept the task from the Client and manage the execution of the job graph. A Flink cluster can be used for the execution of more than one Job Graph.
- It also manages the cluster of Task managers.
- Fault tolerance
Considering the above responsibilities, Job manager has the following sub-components —
- Dispatcher — Provide an interface to submit a Job graph and starts a new Job master for each submitted job.
- Job master — Responsible for managing the execution of the single job graph.
- Resource manager / Task scheduler— For managing the Task managers and assigning the tasks to the task managers for execution.
- Checkpoint coordinator — To enable fault tolerance.

The responsibility of the task manager is to provide the resources for the execution of the tasks in the Flink Job. There might be multiple nodes as Task manager in the Flink cluster. Task manager nodes are also called “Worker nodes”. The smallest unit of resource scheduling in a Task Manager is a “Task Slot”. A Task manager can have one or more Task Slots. Task Scheduler in the Job Manager, schedules the task of a Flink Job using the Task slot.
Task manager also contains the components that are responsible for memory management among the Task slots. Since the tasks of a Flink Job can be distributed to multiple task managers hence there has to be a network manager to coordinate and communicate data flow among the Task manager nodes.
Task manager sends the Task status, Heartbeats, and various statistics to the Job Manager periodically for it to manage the cluster effectively.

Putting it all together
- Flink application has one or more sources (data source), a series of operations, and one or more sinks.
- Flink application is represented as a Job graph, where the nodes are the operators and links determine the input and output, to and from various operators.
- Flink Job is submitted as a Dataflow graph (Job graph)to the Job Manager.
- Task manager has one or more Task slots that provide an execution environment to the tasks.
- Job manager schedules the tasks from the Job graph to one more Task slots in the Task managers.
- Multiple tasks can be submitted to a Job Manager which creates a Job master for each of the submitted jobs.
- Job master also takes the responsibility of providing the Fault tolerance abilities using the checkpoint coordinator.

Understanding Apache Flink architecture and its components | by Harshit Sharma | Medium