SDLC Methodologies
- Agile: Flexible, Fast, And Short Collaborative Sprint Projects
- Scrum: Quick And Continuous Development Projects
- Kanban: Visualize Task Progress For Agile Teams
- Lean: Projects That Do More With Less
- Waterfall: Large-Scale, End-Goal Focused, And Fixed Projects
- Hybrid: Flexible And Fast-Paced Projects With Structured Plans
Project Methodology
Project methodology is a system of principles, techniques, and procedures that project managers use to guide their work. Different methodologies can have different structures, deliverables, workflows, and software requirements. Here are some examples of project management methodologies:
Scrum
A popular Agile framework that uses short, regular work cycles called sprints to deliver products quickly and with high quality. Scrum teams self-organize and use meetings, tools, and roles to learn from experience and adapt to change.
Kanban
A lean project management framework that uses a visual board to show the status of each project component and who is working on it. Kanban helps teams manage workflow and communicate in real time.
Agile
An approach that breaks projects into phases and emphasizes continuous improvement and collaboration. Teams follow a cycle of planning, executing, and evaluating.
Critical path method
A technique that helps identify the longest sequence of activities that must be completed on time to finish a project. The method involves creating a detailed schedule that includes all activities, milestones, and dependencies.
Lean
Lean was created in the Japanese manufacturing industry to improve quality control and remove redundancies that may increase the price or value for customers down the line.
Known as the three M's, Lean methodology defines three types of project waste: muda, mura, and muri.
- Muda is about getting rid of the waste or anything that doesn't add value.
- Mura streamlines processes, so if one aspect of the project takes too long, for instance, then something further down the task list will have to be completed faster.
- Muri is about removing blockers, such as too many stakeholder meetings.
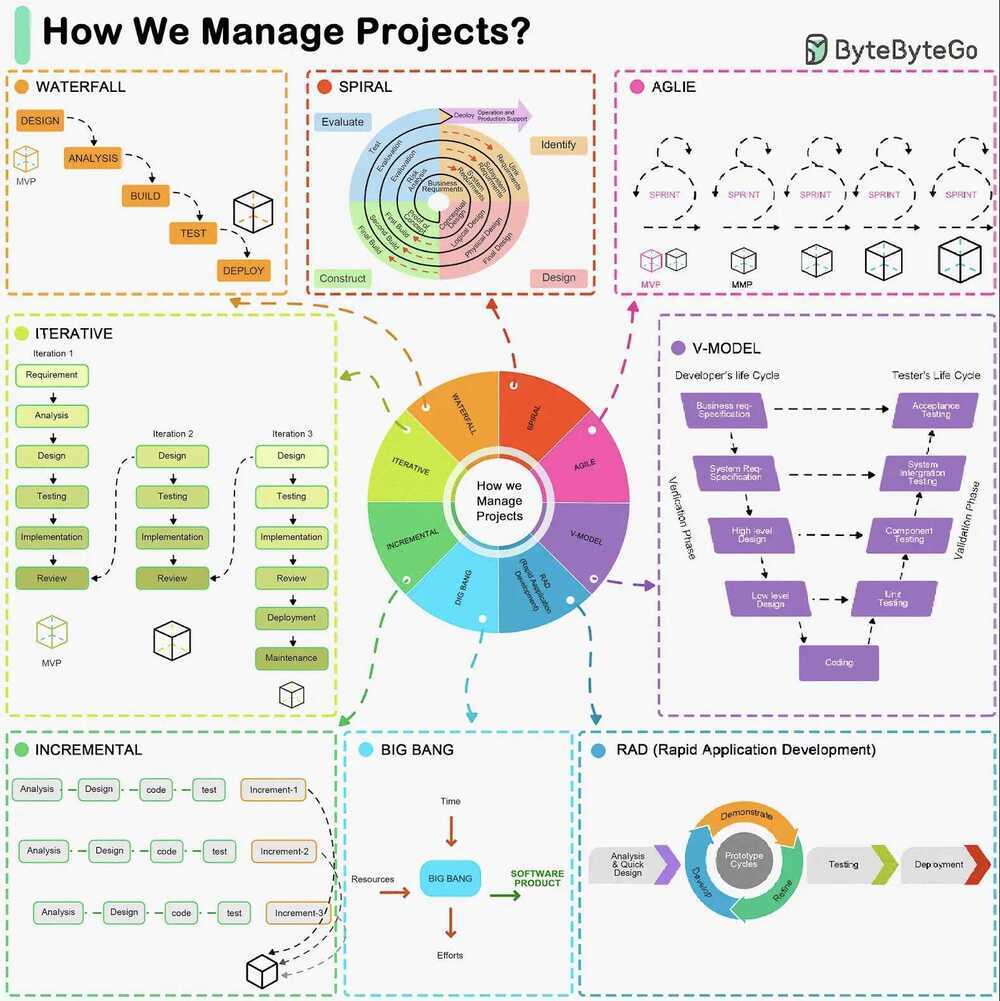
SDLC
The Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a framework that outlines the process of developing software in a systematic way. Here are some of the most common ones:
1 - Waterfall Model
- A linear and sequential approach.
- Divides the project into distinct phases: Requirements, Design, Implementation, Verification, and Maintenance.
2 - Agile Model
- Development is done in small, manageable increments called sprints.
- Common Agile methodologies include Scrum, Kanban, and Extreme Programming (XP).
3 - V-Model (Validation and Verification Model)
- An extension of the Waterfall model.
- Each development phase is associated with a testing phase, forming a V shape.
4 - Iterative Model
- Focuses on building a system incrementally.
- Each iteration builds upon the previous one until the final product is achieved.
5 - Spiral Model
- Combines iterative development with systematic aspects of the Waterfall model.
- Each cycle involves planning, risk analysis, engineering, and evaluation.
6 - Big Bang Model
- All coding is done with minimal planning, and the entire software is integrated and tested at once.
7 - RAD Model (Rapid Application Development)
- Emphasizes rapid prototyping and quick feedback.
- Focuses on quick development and delivery.
8 - Incremental Model
- The product is designed, implemented, and tested incrementally until the product is finished.