General
Domain Specific Languages (DSLs)
A domain-specific language (DSL) is a computer language specialised to a particular application domain. This is in contrast to a general-purpose language (GPL), which is broadly applicable across domains. There are a wide variety of DSLs, ranging from widely used languages for common domains, such as HTML for web pages, down to languages used by only one or a few pieces of software, such as MUSH soft code. DSLs can be further subdivided by the kind of language, and include domain-specific markup languages, domain-specific modeling languages (more generally, specification languages), and domain-specific programming languages. Special-purpose computer languages have always existed in the computer age, but the term "domain-specific language" has become more popular due to the rise of domain-specific modeling. Simpler DSLs, particularly ones used by a single application, are sometimes informally called mini-languages.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Domain-specific_language
Channels
Channels are data-race safe communication primitives. The operations set is trivial: atomic write/read. The main purpose is to keep the code free from data races and easy to maintain.
In the most popular channel implementation libraries, there are two varieties (or modes) of channels available
1. Buffered
Global data flow is async. Tasks are processed independently with some probability of data flow delays, missing data, and logic/events collision.
2. Unbuffered
Global data flow is strictly synchronous, even if there are several independent processors.
The difference between them is that buffered channels can be pulled with the data, even without a coroutine waiting for it. Unbuffered channels, on the contrary, can't be written into until some other coroutine is expecting some data from it.
Python vs C++
https://realpython.com/python-vs-cpp
Performance node php java go
https://www.toptal.com/back-end/server-side-io-performance-node-php-java-go
Benchmarks
https://benchmarksgame-team.pages.debian.net/benchmarksgame/index.html
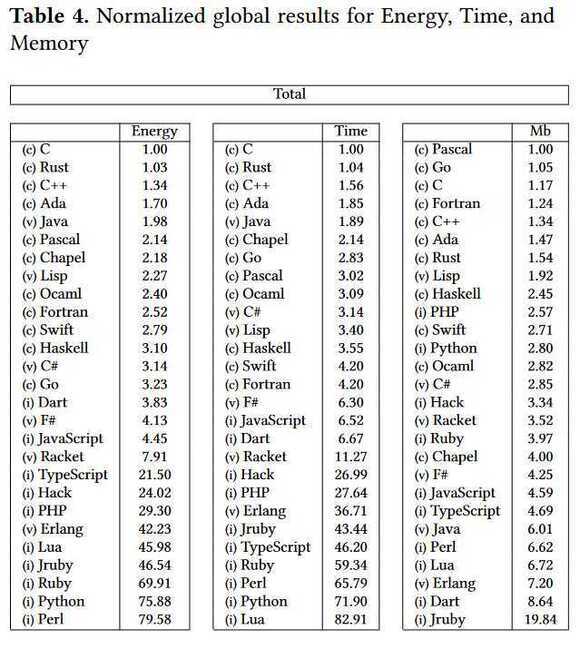
Which Programming Languages Use the Least Electricity? - The New Stack
Selecting a language
- Time
- Skill
- Available resources