Crash Course World History
Crash Course World History 1
1. The Agriculture Revolution
- 15000 years ago
- Controllable food supply
2. Indus Valley Revolution
Civilization
- Surplus production
- City
- Specilized labour
- Trade
- Shared values (generally in the form of religion)
- Social stratification
- Centralized government
- Writing
Indus valley civilization
- flood plains of indus valley in today's pakistan
- around 3000 BCE
- Trading with mesopotamian civilization around 3500 BCE
- Harappa
- Mohenjadaro
- Have drainage systems
- The great bath
- Traded cotton cloth with mesopotamia
- No signs of warfare and no weapons
- Around 1750 BCE declined
- conquest (by carcauses)
- Environmental disaster
- Earthquake
3. Mesopotamia
- writing
- taxes
- Meso (between) + potamia (river) (tigres and euphrates rivers)
- The epic of Gilgamesh
- Writing giving by mesopotamia - Quinea form
- Hameorabi - Kingdom of babylon
- Neo-Assyrian empire (911 BCE - 612 BCE)
4. Ancient Egypt (3400 BCE - 525 BCE)
- Nile river shaped the egypt
- All the egypt was located on the sides of nile river
- It provided transport and twice a year flooding with rich nutrients for agriculture
- Dynasties
- Old kingdom (2649 BCE - 2152 BCE)
- Middle kingdom (2040 BCE - 1640 BCE)
- New kingdom (1550 BCE - 1070 BCE)
- In between there were intermediate kingdoms
- Great pyramid for pharoah kufu
- Heiroglyphics (sacred writing) and demotic script (recording contracts and agreements)
- King Tut
5. The Persians & Greeks
Greeks gave music, democracy, idealization
Realism - The view that the subject matter of politics is political power, not matter of principle
Non-rhetorical question - Did the right side win the persian wars?
Persians - Monarchy (one-man rule)
- life under persians pretty good (lot more stable and successful empires than democracies in history)
Greeks / Athenians - Democracy
- Government corrupt
- Life of women and slaves were very bad
Real questions of history -
- What's the point of being alive
- How should we organize ourselves
- What should we seek from this life
6. Buddha and Ashoka
- The Vedas (Indus valley civilization)
- The caste system
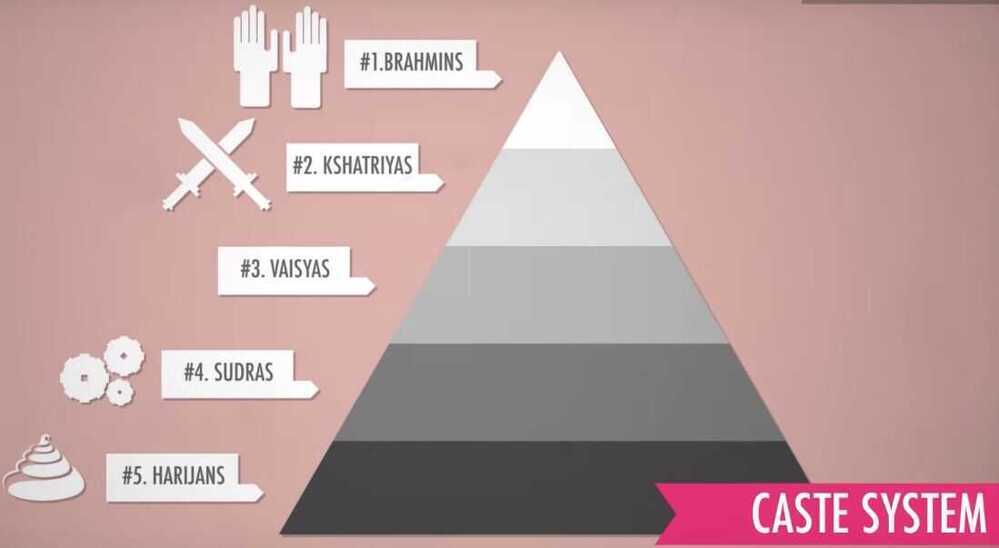
Dharma - One's role in life and society primarily by birth and by caste
Bhagavada Gita is a 700-verse Hindu scripture in Sanskrit that is part of the Hindu epicMahabharata(chapters 23--40 of the 6th book of Mahabharata).
Samsara, Moksha and Karma
Samsara - Cycle of re-birth, re-incarnation
Moksha - free from the cycle of re-birth
Karma - The doer of good becomes good, the doer of evil becomes evil. One becomes virtuous by virtuous action, bad by bad action
5. Buddhism - 6th century BCE - Siddhartha Gautam - achieved Nirvana
Four noble truths
- All life is suffering
- The source of suffering is desire
- To stop suffering, you must get rid of desire
- Follow the 8 folds paths
- Right view
- Right intention
- Right speech
- Right action
- Right livelihood
- Right effort
- Right mindfulness
- Right concentration
Snakes & Ladders invented in India
7. Ashoka from Mauryan dynasty
- United twice
- Mauryan Dynasty (321 - 185 BCE)
- Gupta Dyansty (320 - 550 CE)
- Got into Buddhism after his army destroyed the Kingdom of Kalinga
- Build stupas
Hinduism is highly flexible because God can take many forms
7. 2000 years of Chinese history! The Mandate of Heaven and Confucius
- Central government and core of bureaucrats that execute the wishes of that government (150 BCE to 1911 CE)
- Shang dynasty (1600 - 1029 BCE)
- Zhou dynasty (1029 - 771 BCE)
- The warring states period (475 BCE - 221 BCE)
- Qin dynasty (221 - 206 BCE)
- Han dynasty (206 BCE - 220 CE)
- The three kingdoms period (220 - 280 CE)
- Sui dynasty (581 - 618 CE)
- Tang dynasty (618 - 907 CE)
- Song dynasty (960 - 1271 CE)
- Yuan dynasty (1271 - 1368 CE)
- Red turban rebellion (1351 - 1368 CE)
- Ming dynasty (1368 - 1644 CE) (built the great wall)
- Qing dynasty (1644 - 1911 CE)
8. Alexander the Great and the Situation .. the Great?
- Alexander of Macedon (356 BCE - 323 BCE)
- Destroyed the Persian empire
- After his death the empire broke down into 3 empires called the Hallenistic kingdoms - Antigonids, Seleucids and Ptolemies
9. The silk road and ancient trade
- Network of roads
Others
- The Roman Empire. Or Republic. Or... Which was it?
- Christianity from Judaism to Constantine
- Fall of the Roman Empire...in the 15th Century
- Islam, the Quran, and the Five Pillars all without a flamewar
- The Dark Ages...How Dark were they really?
- The Crusades - Pilgrimage or Holy War?
- Mansa Musa and Islam in Africa
- Wait for it... The Mongols
- Int'l Commerce, Snorkeling Camels, and The Indian Ocean Trade
- Venice and the Ottomon Empire
- Russia, the Kievan Rus, and the Mongols
- Columbus, de Gama, and Zheng He!
- The Renaissance: Was it a Thing?
- The Columbian Exchange
- The Atlantic Slave Trade
- The Spanish Empire, Silver, & Runaway Inflation
- The Seven Years War
- The Amazing Life and Strange Death of Captain Cook
- Tea, Taxes, and The American Revolution
- The French Revolution
- Haitian Revolutions
- Latin American Revolutions
- Coal, Steam, and The Industrial Revolution
- Capitalism and Socialism
- Samurai, Daimyo, Matthew Perry, and Nationalism
- Imperialism
- Archdukes, Cynicism, and World War I
- Communists, Nationalists, and China's Revolutions
- World War II
- USA vs USSR Fight! The Cold War
- Decolonization and Nationalism Triumphant
- Globalization I - The Upside
- Globalization II - Good or Bad?
Crash Course World History 2
- Rethinking Civilization
- Money & Debt
- Disease
- War & Human Nature
- War and Civilization
- Climate Change, Chaos, and the Little Ice Age
- Little Ice Age - 13th to 19th Century
- Humans and Energy
- Drought and Famine
- How World War I started
- Who started World War I
- The End of Civilization (In the Bronze Age)
- The Rise of the West and Historical Methodology
- Asian Responses to Imperialism
- The Railorad journey and the Industrial Revolution
- Population, Sustainability and Malthus
- Islam and Politics
- The Mughal Empire and Historical Reputation
- Luther and the Protestant Reformation
- Charles V and the Holy Roman Empire
- World War II, A War for Resources
- Congo and Africa's World War
- Water and Classical Civilizations
- Conflict in Israel and Palestine
- The Vikings
- War and Nation Building in Latin America
- Iran's Revolutions
- Japan in the Heian Period and Cultural History
- Nonviolence and Peace Movements
- Capitalism and the Dutch East India Company
- Democracy, Authoritarian Capitalism, and China