Load Balancer Features
Service discovery
Service discovery is the process by which a load balancer determines the set of available backends. The methods are quite varied and some examples include:
- Static configuration file.
- DNS.
- Zookeeper, Etcd, Consul, etc.
- Envoy's universal data plane API.
- Client-side discovery pattern
- Server-side discovery pattern
- Service Registry
- etcd
- zookeeper
- consul
- Service registry pattern
- self-registration pattern
- third-party registration pattern
- DNS based Service Discovery (DNS-SD)
https://www.nginx.com/blog/service-discovery-in-a-microservices-architecture
https://iximiuz.com/en/posts/service-discovery-in-kubernetes
Health checking
Health checking is the process by which the load balancer determines if the backend is available to serve traffic. Health checking generally falls into two categories:
Active
The load balancer sends a ping on a regular interval (e.g., an HTTP request to a /healthcheck endpoint) to the backend and uses this to gauge health
Passive
The load balancer detects health status from the primary data flow. e.g., an L4 load balancer might decide a backend is unhealthy if there have been three connection errors in a row. An L7 load balancer might decide a backend is unhealthy if there have been three HTTP 503 response codes in a row
Others
- Deep Health Checks
- Shallow Health Checks
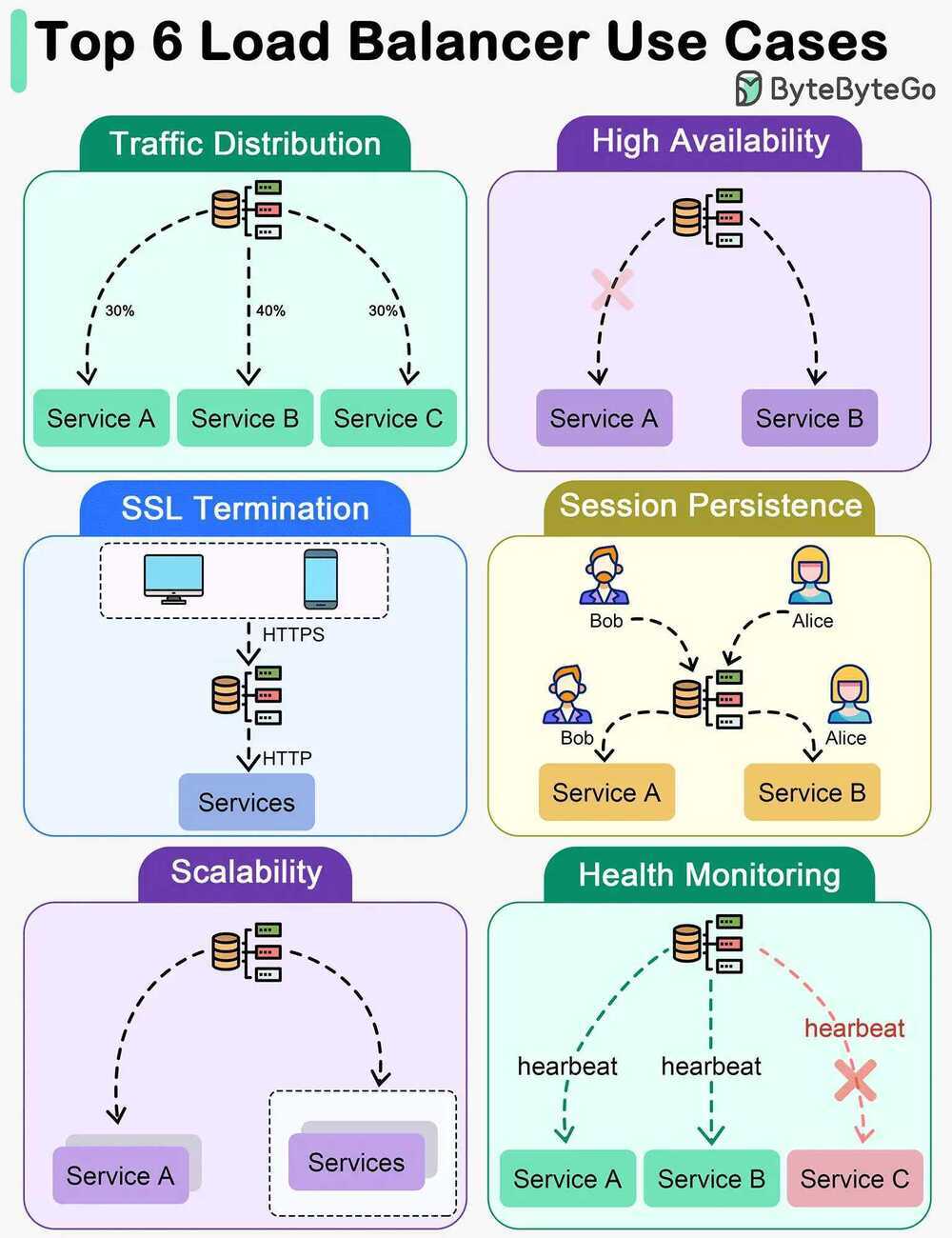
Use Cases
Traffic Distribution
Load balancers evenly distribute incoming traffic among multiple servers, preventing any single server from becoming overwhelmed. This helps maintain optimal performance, scalability, and reliability of applications or websites.
High Availability
Load balancers enhance system availability by rerouting traffic away from failed or unhealthy servers to healthy ones. This ensures uninterrupted service even if certain servers experience issues.
SSL Termination
Load balancers can offload SSL/TLS encryption and decryption tasks from backend servers, reducing their workload and improving overall performance.
Session Persistence
For applications that require maintaining a user's session on a specific server, load balancers can ensure that subsequent requests from a user are sent to the same server.
Scalability
Load balancers facilitate horizontal scaling by effectively managing increased traffic. Additional servers can be easily added to the pool, and the load balancer will distribute traffic across all servers.
Health Monitoring
Load balancers continuously monitor the health and performance of servers, removing failed or unhealthy servers from the pool to maintain optimal performance.