AWS Redshift
- OLAP
- Columnar data storage structure
- Fully managed data warehouse service
- Its datasets range from 100s of gigabytes to a petabyte
- Based on industry-standard PostgreSQL and ParAccel's Massive Parallel Processing technology, leveraging its distributed architecture, columnar storage, and column compression to execute exploratory queries
- Due to being based off of PostgreSQL, Redshift allows clients to make connections and execute DDL and DML SQL statements using JDBC or ODBC
- Very efficient, targeted data compression encoding schemes
- Redshift spectrum which basically allows the customers to use the computing power of Redshift cluster on data stored in S3 by creating external tables.
The initial process to create a data warehouse is to launch a set of compute resources callednodes, which are organized into groups calledcluster. After that you can process your queries.
History
In July 2011, Amazon invested in ParAccel, a software company that developed a shared-nothing architecture relational database system for analytics and business intelligence. In exchange for its investment, Amazon acquired license rights to ParAccel's database system which would form the foundation of Amazon's own data warehouse solution: Amazon Redshift. After subsequent development by Amazon and integration with AWS, Amazon Redshift was officially announced at the AWS re:invent 2012 conference and, after a limited preview, was released to the general public in February 2013.
Rewrote whole storage engine for columnar, MPP
Compression
Dictionary EncodingDelta EncodingRun-Length EncodingNaïve (Page-Level)Bit Packing / Mostly Encoding
Redshift allows for the columns to be compressed, reducing data size and storing more data within each disk block. This allows for reduced disk I/O and improves query performance. Column compression will be automatically applied when loading data into Redshift using the COPY command but can also be selected manually.
Redshift allows for the following possible compression options.
Raw
Raw encoding stores the data as-is. None of the values are compressed. By default, no compression is applied to values of columns defined as the sort key and values of BOOLEAN, REAL, or DOUBLEdatatypes.
Byte-Dictionary
For each 1 MB block on disk, a dictionary a created which maps the first 256 unique column values to a single byte. In the original data, those values are replaced with the corresponding single byte. If there are more than 256 unique column data values in a block, any unique data values beyond the first 256 are stored raw. This encoding is primarily suited for columns containing a limited number of character values and does not support BOOLEAN data types.
Delta
For each 1MB block on disk, data is stored as the difference relative to the previous value in series. Redshift supports two delta variations, DELTA (supports SMALLINT, INT, BIGINT, DATE, TIMESTAMP, DECIMAL) which stores difference as 1-byte values and DELTA32K (INT, BIGINT, DATE, TIMESTAMP, DECIMAL) which stores the difference as 2-byte values. Any difference greater than the delta representable is stored raw along with a 1 byte flag.
Mostly
This encoding utilizes packing to reduce storage. In the event that the value cannot be compressed, the original raw value is stored. MOSTLY8 supports SMALLINT, INT, BIGINT, and DECIMAL. MOSTLY16 supports INT, BIGINT, and DECIMAL. MOSTLY32 supports BIGINT and DECIMAL.
Runlength
For each 1MB block on disk, consecutive values are replaced with a corresponding token that indicates the number of repetitions and the value repeated. A separate dictionary of unique values is also created for each 1MB block. Runlength is supported for all datatypes.
Naive Block-level
Under this encoding, each block is compressed with a standard compression algorithm. Particular choices include LZO and ZTSD. For all columns other than the sort key or with types BOOLEAN, REAL, or DOUBLE, LZO is the default compression.- Compress ratio: 2 to 4 times less
- By default COPY automatically analyzes and compresses data on first load into an empty table
- ANALYZE COMPRESSION is a built-in command that will find the optimal compression for each column on an existing table
- Compression can return raw if there are very less number of rows in a column or data is very sparse (i.e. column has a lot of NULL)
- Changing column encoding requires a table rebuild
- SELECT "column", type, encoding FROM pg_table_def WHERE tablename = 'deep dive';

Concurrency Control
Multi-version Concurrency Control (MVCC)
Although not explicitly stated, Redshift utilizes Multi Version Concurrency Control. In particular, transactions capture a snapshot of the latest committed version of the data at the time a SELECT query, a DML statement, ALTER TABLE statement, CREATE TABLE statement, DROP TABLE statement, or TRUNCATE TABLE statement is executed. Redshift prevents write-write conflicts from happening by forcing a transaction to obtain a table-level write lock and only allowing a transaction to release all its write locks when the transaction either commits or aborts. Furthermore, a VACUUM operation is required in order to remove all records marked for deletion and also perform any resorting operations that may or may not be required.
However, Redshift does not offer deadlock prevention or deadlock detection. As such, Redshift warns users to schedule transaction operations in a way that would prevent any deadlocks from arising in the first place, such as by updating tables in the same order or taking locks in the same order.
Data Model
Redshift is a relational database even though it is built upon PostgreSQL. Particular reasons are that Redshift does not support many features considered to be part of the "object-relational" definition, such as but not limited to inheritance and definition of custom structured types.
Foreign Keys
Redshift supports the concept of foreign keys but does not actually enforce the foreign key constraint. Redshift utilizes foreign keys as pieces of information during the query planning and optimization stage. However, Redshift does not spend computational resources to ensure that the constraint holds, instead relying on the application where the data originated from to ensure that the foreign key constraint is satisfied.
Indexes
Redshift does not support indexes. As such, Redshift does not suffer any computational overhead from the creation, maintenance, or concurrent use of index data structures.
Isolation Levels
Redshift only supports serializable isolation, which provides each transaction with the illusion that they are the only transaction operating on a table at a given time (utilizing table-level locks) and ensures that the end-result is equivalent to some serial execution of the transactions. In the event that a transaction executes an operation which would violate serializability, the violating transaction would be aborted and rolled back.
Joins
Nested Loop JoinHash JoinSort-Merge JoinBroadcast JoinShuffle Join
The query planner and optimizer picks the best join and distributed joining algorithm possible. The three join algorithms utilized by Redshift are nested join, hash join which is used for inner and left/right outer joins, and merge join which is used for inner and outer joins. Redshift only uses merge join if the join column is both the distribution and sort key and if the percentage of unsorted data in the two tables is less than 20%.
In the event that the query planner needs to move data around, Redshift will either perform a redistribution (shuffle) or broadcast one side of the join to all other nodes. If redistribution is needed, Redshift may move table data between slices of a single node or between nodes, utilizing the distribution key if the distribution key is part of the join.
Logging
Redshift provides logging for both audit purposes and also for all operations executed by transactions on the system. In particular, Redshift logs the rawSQLstatements that are executed by users and transactions in the system. Furthermore, with the auditing functionality built-in to Redshift, administrators can also track all the SQL statements executed by a specific user.
Query Compilation
The query execution plan is generated at the leader node of a particular Redshift cluster. The leader (coordinator) node is responsible for evaluating all the possible execution plans and cost effectiveness of each plan. The leader node rewrites the query, generates compiled C++ code, and sends the compiled binaries to the compute nodes for execution.
Query Execution
Redshift utilizes the materialized query processing model, where each processing step emits the entire result at a time. The leader node is responsible for coordinating query execution with the compute nodes and stitching together the results of all the compute nodes into a final result that is returned to the user.
To improve performance, Redshift utilizes late materialization where row reconstruction, utilizing the value's block position, is delayed until later steps in the process. Furthermore, Redshift utilizes zone map optimization for its sequential scan, storing a min and max value in the header of each disk block to allow the executor to determine which blocks can be skipped.
Query Interface
Redshift supports a majority of the standard DDL statements to create and define tables and DML statements to manipulate the data stored within the database. Furthermore, Redshift supports scalar User-Defined Functions that can be constructed either via a SQL SELECT clause or a Python program.
In addition, there are certain functions that can only be executed on the leader node, primarily functions to query the database schema. Furthermore, Redshift implements various extensions to SQL, such as aggregate functions, string functions, and JSON functions although careful care must be taken to the many PostgreSQL features that became unsupported in Redshift.
In 2019, Amazon announced that Redshift Spectrum supports their own SQL dialect called PartiQL.
Storage Architecture
Redshift uses disk storage. In the distributed system, all the data is stored at the compute node layer. Based on the particular distribution style elected for a particular table, the leader node will either duplicate the data across all the compute nodes or partition the data across all the compute nodes. Furthermore, each compute node will partition its data across its CPU slices in order to achieve maximum parallel computation. To tolerate node or slice failures, data is also duplicated at other nodes in the system.
Storage Model
Decomposition Storage Model (Columnar)
Redshift utilizes columnar storage as opposed to row storage. Instead of storing the entire row record together, Redshift stores the values of each table column together. This allows Redshift to pack data together and apply compression in order to minimize disk I/O during query execution. A row can be stitched together by utilizing the offset of a specific value.
Storage Organization
On tables without a sort key specified and that remains unsorted, Redshift preserves the order in which the records were originally inserted in. In the unsorted scenario, Redshift stores data in 1MB blocks on disk where new records are simply appended to the end.
On tables with a sort key specified, Redshift stores the "sorted" portion of the data in sorted blocks on disk. Adding new data to the table except for the special case listed below will result in the data being appended to the "unsorted" portion that will only be merged into the "sorted" potion upon aVACUUM. In addition, Redshift provides that theCOPYcommand will automatically sort the incoming data.
In the event that the following conditions are met, adding data to a table will preserve the sortedness of the data and not require an additionalVACUUMoperation to sort the table.
- The sort column is NOT NULLand there is only 1 sort column
- Using COPY into an empty table or the table is 100% sorted
- The data can be appended in sort-order to the end of any existing data
Stored Procedures
Stored procedures, from PostgreSQL, are not supported.
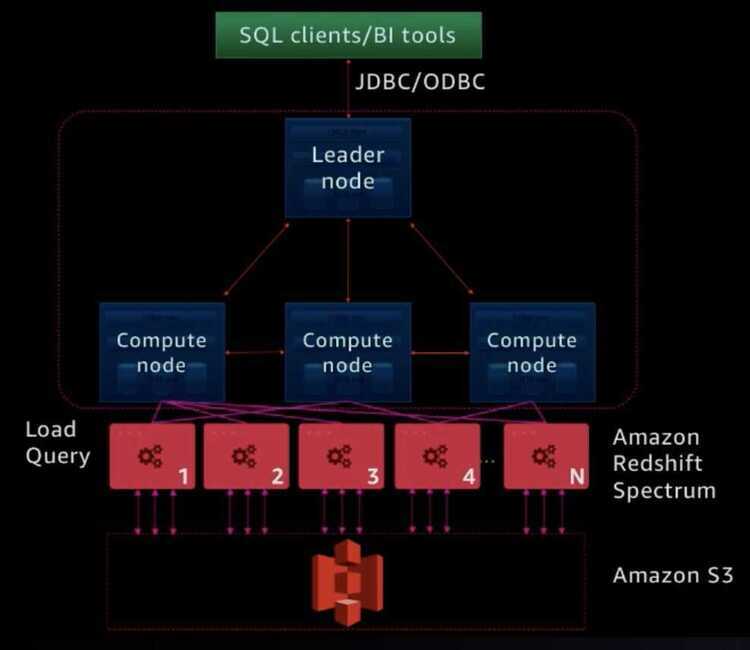
System Architecture
Redshift clusters take a two-tiered architecture approach. The leader node serves the role as the coordinator and handles accepting client query requests, generating the query plan, dispatching query fragments to compute nodes, and coalescing results from compute nodes.
The compute nodes utilize a shared-nothing architecture, with each node having dedicated CPU, memory, and disk storage. The leader node determines the data each node stores and will only dispatch a query fragment to a node if the query requires data from that node. For performance reasons, each compute node assigns a portion of memory and disk to each CPU slice for parallel processing.
To ensure data availability during disk or node failure, Redshift utilizes synchronous replication to save redundant copies of the data on other nodes in the system. To provide further durability, Redshift provides complete automated backups to S3 which can then later be used to restore the entire database or a particular table to a cluster.
Leader Node
- SQL endpoint
- Stores metadata
- Coordinates parallel SQL processing
Compute Nodes
- Local, columnar storage
- Executes query in parallel
- Load, unload, backup, restore
Amazon Redshift Spectrum Nodes
- Execute queries directly again Amazon S3
Views
Redshift supports virtual views. The contents of the view are not directly materialized and the query defining the view is rerun every time the view is being used in another query. DELETE or UPDATE statements cannot be used against the view.
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/redshift/latest/dg/c_high_level_system_architecture.html
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/redshift/latest/dg/c_challenges_achieving_high_performance_queries.html
Table Locks
Amazon Redshift uses table-level locks
Amazon Redshift has three lock modes:
- AccessExclusiveLock: Acquired primarily during DDL operations, such as ALTER TABLE, DROP, or TRUNCATE. AccessExclusiveLock blocks all other locking attempts.
- AccessShareLock: Acquired during UNLOAD, SELECT, UPDATE, or DELETE operations. AccessShareLock blocks only AccessExclusiveLock attempts. AccessShareLock doesn't block other sessions that are trying to read or write on the table.
- ShareRowExclusiveLock: Acquired during COPY, INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE operations. ShareRowExclusiveLock blocks AccessExclusiveLock and otherShareRowExclusiveLock attempts, but doesn't block AccessShareLock attempts.
When a query or transaction acquires a lock on a table, the lock remains for the duration of the query or transaction. Other queries or transactions that are waiting to acquire the same lock are blocked.
https://aws.amazon.com/premiumsupport/knowledge-center/prevent-locks-blocking-queries-redshift
It is worth mentioning that Merge join(typically the fastest join ; for inner joins and outer joins) is used when joining tables where the join columns are both distribution keysandsort keys, and when less than 20 percent of the joining tables are unsorted.The merge join is not used for full joins.
https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/big-data/whats-new-in-amazon-redshift-2021-a-year-in-review
- Query Editor V2 with charts and jupyter notebooks
What’s new in Amazon Redshift - 2022, a year in review | Amazon Web Services