Compilers
LLVM - The LLVM compiler infrastructure project is a "collection of modular and reusable compiler and toolchain technologies" used to develop compiler front ends and back ends.
LLVM is written in C++ and is designed for compile-time, link-time, run-time, and "idle-time" optimization of programs written in arbitrary programming languages.
- LLVM Intermediate Representation (IR)
- LLVM debugger
- LLVM representation of the C++ standard library
Computer voting can never be safe - Medium
- Trusting trust attack
Occurs when an attacker attempts to disseminate a compiler executable that produces corrupted executables, at least one of those produced corrupted executables is a corrupted compiler, and the attacker attempts to make this situation self-perpetuating.- Diverse double-compiling
Using 4 compilers of different languages and sources to check each other's work
References
- I'm a Computer Scientist. Here's why you should never trust a Computer (Especially when it comes to voting) - Medium blog by Ryan North
- Fully Countering Trusting Trust through Diverse Double-Compiling by David A. Wheeler (MS, George Mason University)
Compiled vs Interpreted Language
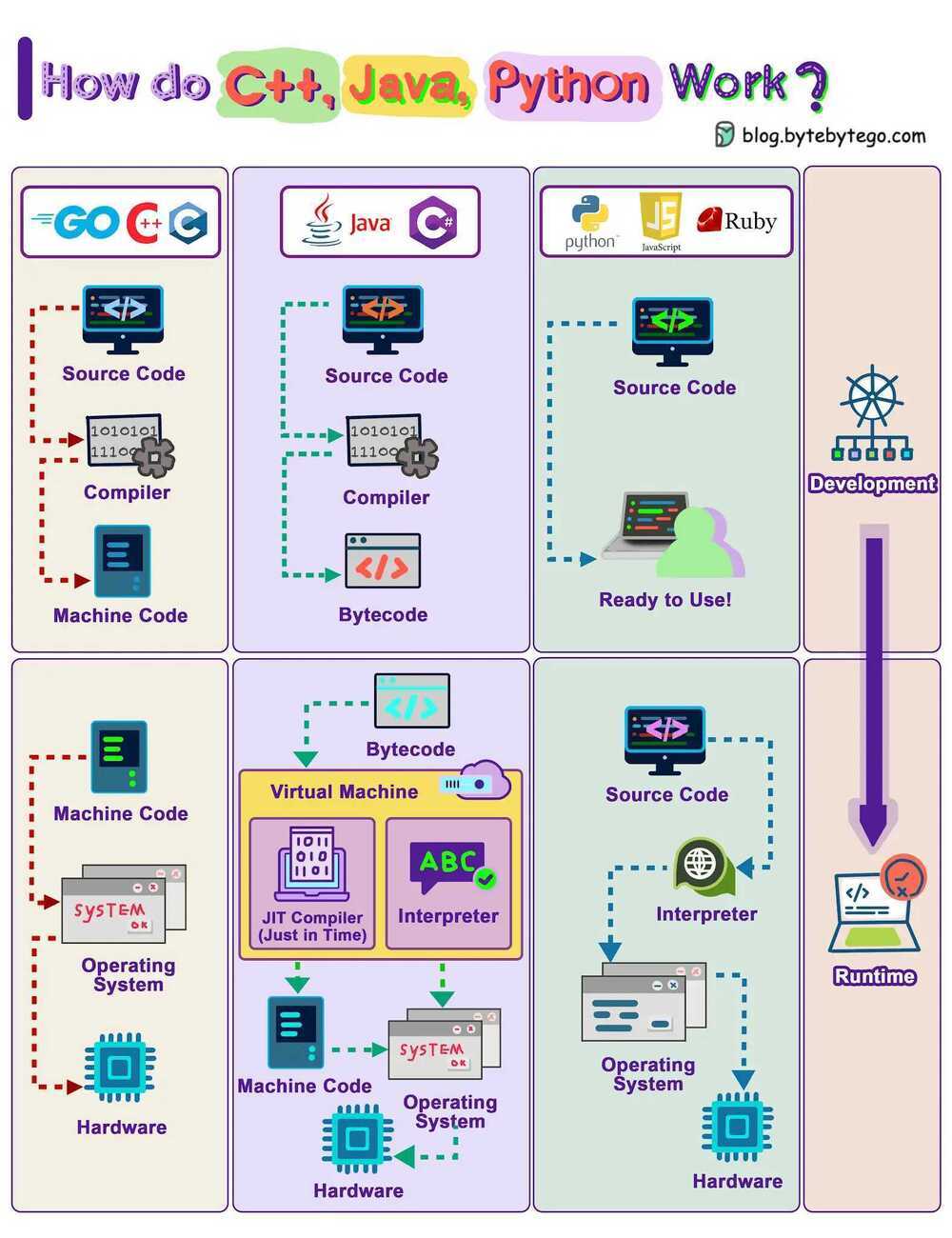
Compiler
- Lexers (Tokenization)
- AST (Abstract Syntax Tree)
PEG Parsers (Parsing Expression Grammer)
In computer science, aparsing expression grammar, orPEG, is a type of analyticformal grammar, i.e. it describes a formal language in terms of a set of rules for recognizing strings in the language. The formalism was introduced by Bryan Ford in 2004and is closely related to the family of top-down parsing languages introduced in the early 1970s. Syntactically, PEGs also look similar to context-free grammars(CFGs), but they have a different interpretation: the choice operator selects the first match in PEG, while it is ambiguous in CFG. This is closer to how string recognition tends to be done in practice, e.g. by a recursive descent parser. Unlike CFGs, PEGs cannot be ambiguous; if a string parses, it has exactly one valid parse tree. It is conjectured that there exist context-free languages that cannot be recognized by a PEG, but this is not yet proven.PEGs are well-suited to parsing computer languages (and artificial human languages such as Lojban), but not natural languages where the performance of PEG algorithms is comparable to general CFG algorithms such as the Earley algorithm.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parsing_expression_grammar
https://medium.com/@gvanrossum_83706/peg-parsing-series-de5d41b2ed60
Compilation JIT vs AOT
Just-In-time (JIT) compilation is the process of translating code written in a programming language to machine code at runtime (during a program or application's execution). At runtime, certain dynamic information is available, such as type identification. A JIT compiler monitors to detect functions or loops of code that are run multiple times. These pieces of code are then compiled. If they're quite commonly executed, JIT will optimize them and also store the optimized, compiled code for execution. Browsers use JIT compilation to run JavaScript
Ahead-Of-Time (AOT) compilation is the process of translating code written in a programming language to machine code before execution (as opposed to at runtime). Doing so reduces runtime overhead and compiles all files together rather than separately
Some benefits of AOT:
- Better security because evaluation is already done.
- Templates and styles are inlined with JS so fewer asynchronous calls.
- Small download size, because the compiler need not to be download as the app is precompiled.
- AOT also enables tree shaking.
https://github.com/jamiebuilds/the-super-tiny-compiler/blob/master/the-super-tiny-compiler.js
https://www.toptal.com/scala/writing-an-interpreter