Security, Identity and Compliance
- AWS Identity & Access Management (IAM) - Manage User Access and Encryption Keys
- Amazon Cognito - Identity management for your apps
- Amazon Detective - Investigate potential security issues
- Amazon GuardDuty - Managed threat detection service
- Amazon Cloud Directory - Create Flexible Cloud-native Directories
- AWS Single Sign-On - Cloud Single Sign-On (SSO) Service
- Amazon GuardDuty - Managed Threat Detection Service
- AWS Direct Connect - Dedicated Network Connection to AWS
- Amazon Inspector - Automated and continual vulnerability management for Amazon EC2 and Amazon ECR
- Automated vulnerability management for compute workloads
- Simplified one-click onboarding and integration with AWS Organizations
- Automated discovery and continual vulnerability scanning
- Integration with AWS Systems Manager Agent
- Agentless vulnerability assessments for Amazon EC2
- Suppression of findings
- Amazon Inspector risk score for findings
- Automatic closure of remediated findings
- Detailed coverage monitoring
- Integration with AWS Security Hub and Amazon EventBridge
- Integrating vulnerability mapping and generative AI powered remediation to layers in Lambda functions
- Manage software bill of materials (SBOM) exports
- Integration with developer tools
- Support for CIS Benchmark assessments
- Enhanced container security management
- Enhanced code security management
- Amazon Macie - Discover, Classify, and Protect Your Data
- Amazon Macie is a data security service that uses machine learning (ML) and pattern matching to discover and help protect your sensitive data.
- What is Amazon Macie? | Amazon Web Services - YouTube
- AWS Certificate Manager - Provision, Manage, and Deploy SSL/TLS Certificates
- AWS CloudHSM - Hardware-based Key Storage for Regulatory Compliance
- A Cloud HSM is a hardware security module (HSM) service hosted in the cloud, providing dedicated, FIPS 140-2 Level 3 validated hardware to securely generate, store, and manage cryptographic keys for customers. It combines the security of physical HSMs with the scalability and flexibility of cloud services, allowing organizations to meet strict compliance requirements and protect sensitive data without managing their own physical hardware.
- AWS Directory Service - Host and Manage Active Directory
- AWS Key Management Service - Managed Creation and Control of Encryption Keys
- AWS Organizations - Policy-based Management for Multiple AWS Accounts
- AWS Shield - DDOS Protection
- AWS WAF - Filter Malicious Web Traffic - web-application-firewall-waf
- AWS Resource Access Manager (AWS RAM) - Simple, secure service to share AWS resources
- AWS Resource Access Manager (RAM) is a service that enables you to easily and securely share AWS resources with any AWS account or within your AWS Organization. You can share AWS Transit Gateways, Subnets, AWS License Manager configurations, and Amazon Route 53 Resolver rules resources with RAM. RAM eliminates the need to create duplicate resources in multiple accounts, reducing the operational overhead of managing those resources in every single account you own. You can create resources centrally in a multi-account environment, and use RAM to share those resources across accounts in three simple steps: create a Resource Share, specify resources, and specify accounts. RAM is available to you at no additional charge.
- You can share Amazon VPCs to leverage the implicit routing within a VPC for applications that require a high degree of interconnectivity and are within the same trust boundaries. This reduces the number of VPCs that you create and manage while using separate accounts for billing and access control.
- Amazon Security Lake - Automatically centralize your security data with a few clicks
- Security Data Management - Amazon Security Lake - AWS
- Amazon Security Lake is a fully managed, purpose-built service designed to automatically collect, normalize, and centralize security-related data from various AWS accounts, Regions, services, and even third-party sources. It stores this data in Amazon S3 buckets and formats it using the Open Cybersecurity Schema Framework (OCSF), which enhances compatibility with multiple analytics tools. Security Lake eliminates the need to build custom ETL pipelines or configure cross-service log ingestion manually, significantly reducing development effort. It also integrates natively with AWS services like CloudTrail, VPC Flow Logs, GuardDuty, and AWS Config, providing a single authoritative view of security data across the organization. With built-in support for log partitioning, retention, and access management, it delivers both centralization and scalability with minimal operational overhead. The managed nature of Security Lake means there's minimal setup or custom coding, making it the lowest-effort and most scalable solution.
AWS Startup Security Baseline (AWS SSB) - AWS Prescriptive Guidance
Amazon Cognito - Identity Management for your Apps
Amazon Cognito is an identity platform for web and mobile apps. It’s a user directory, an authentication server, and an authorization service for OAuth 2.0 access tokens and AWS credentials. With Amazon Cognito, you can authenticate and authorize users from the built-in user directory, from your enterprise directory, and from consumer identity providers like Google and Facebook.
User Pools
Create a user pool when you want to authenticate and authorize users to your app or API. User pools are a user directory with both self-service and administrator-driven user creation, management, and authentication. Your user pool can be an independent directory and OIDC identity provider (IdP), and an intermediate service provider (SP) to third-party providers of workforce and customer identities. You can provide single sign-on (SSO) in your app for your organization's workforce identities in SAML 2.0 and OIDC IdPs with user pools. You can also provide SSO in your app for your organization's customer identities in the public OAuth 2.0 identity stores Amazon, Google, Apple and Facebook.
Identity Pools
Set up an Amazon Cognito identity pool when you want to authorize authenticated or anonymous users to access your AWS resources. An identity pool issues AWS credentials for your app to serve resources to users. You can authenticate users with a trusted identity provider, like a user pool or a SAML 2.0 service. It can also optionally issue credentials for guest users. Identity pools use both role-based and attribute-based access control to manage your users’ authorization to access your AWS resources.
Identity pools don’t require integration with a user pool. An identity pool can accept authenticated claims directly from both workforce and consumer identity providers.
An Amazon Cognito user pool and identity pool used together
- Your app user signs in through a user pool and receives OAuth 2.0 tokens.
- Your app exchanges a user pool token with an identity pool for temporary AWS credentials that you can use with AWS APIs and the AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI).
- Your app assigns the credentials session to your user, and delivers authorized access to AWS services like Amazon S3 and Amazon DynamoDB.
Others
Application Load Balancer can be used to securely authenticate users for accessing your applications. This enables you to offload the work of authenticating users to your load balancer so that your applications can focus on their business logic. You can use Cognito User Pools to authenticate users through well-known social IdPs, such as Amazon, Facebook, or Google, through the user pools supported by Amazon Cognito or through corporate identities, using SAML, LDAP, or Microsoft AD, through the user pools supported by Amazon Cognito. You configure user authentication by creating an authenticate action for one or more listener rules.
You cannot directly integrate Cognito User Pools with CloudFront distribution as you have to create a separate AWS Lambda@Edge function to accomplish the authentication via Cognito User Pools.
Links
- AWS Cognito Course – Authentication and Authorization - YouTube
- What is Amazon Cognito? - Amazon Cognito
Security Groups
- Cluster security group - It is designed to allow all traffic from the control plane and managed node groups to flow freely between each other
- Node security group - It is designed to allow traffic between worker nodes, or allowing a service like rds, redshift
Cryptography & PKI
- AWS Cryptographic Services Overview
- AWS PKI Services Overview
- AWS CloudHSM
- AWS Crypto Tools
- AWS Certificate Manager
- AWS Certificate Manager Private Certificate Authority
AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS)
AWS Key Management Service (KMS) makes it easy for you to create and manage cryptographic keys and control their use across a wide range of AWS services and in your applications. AWS KMS is a secure and resilient service that uses hardware security modules that have been validated under FIPS 140-2, or are in the process of being validated, to protect your keys. AWS KMS is integrated with AWS CloudTrail to provide you with logs of all key usage to help meet your regulatory and compliance needs.
Multi Region Keys
AWS KMS supports multi-Region keys, which are AWS KMS keys in different AWS Regions that can be used interchangeably – as though you had the same key in multiple Regions. Each set of related multi-Region keys has the same key material and key ID, so you can encrypt data in one AWS Region and decrypt it in a different AWS Region without re-encrypting or making a cross-Region call to AWS KMS.
AWS services that integrate with AWS KMS for encryption at rest or digital signatures currently treat multi-Region keys as though they were single-Region keys. They might re-wrap or re-encrypt data moved between Regions. For example, Amazon S3 cross-region replication decrypts and re-encrypts data under a KMS key in the destination Region, even when replicating objects protected by a multi-Region key.
Multi-Region keys are not global. You create a multi-Region primary key and then replicate it into Regions that you select within an AWS partition. Then you manage the multi-Region key in each Region independently. Neither AWS nor AWS KMS ever automatically creates or replicates multi-Region keys into any Region on your behalf. AWS managed keys, the KMS keys that AWS services create in your account for you, are always single-Region keys.
You cannot convert an existing single-Region key to a multi-Region key. This design ensures that all data protected with existing single-Region keys maintain the same data residency and data sovereignty properties.
Supported KMS key types
You can create the following types of multi-Region KMS keys:
- Symmetric encryption KMS keys
- Asymmetric KMS keys
- HMAC KMS keys
- KMS keys with imported key material
You cannot create multi-Region keys in a custom key store.
Multi-Region keys in AWS KMS - AWS Key Management Service
AWS Shared Responsibility Model
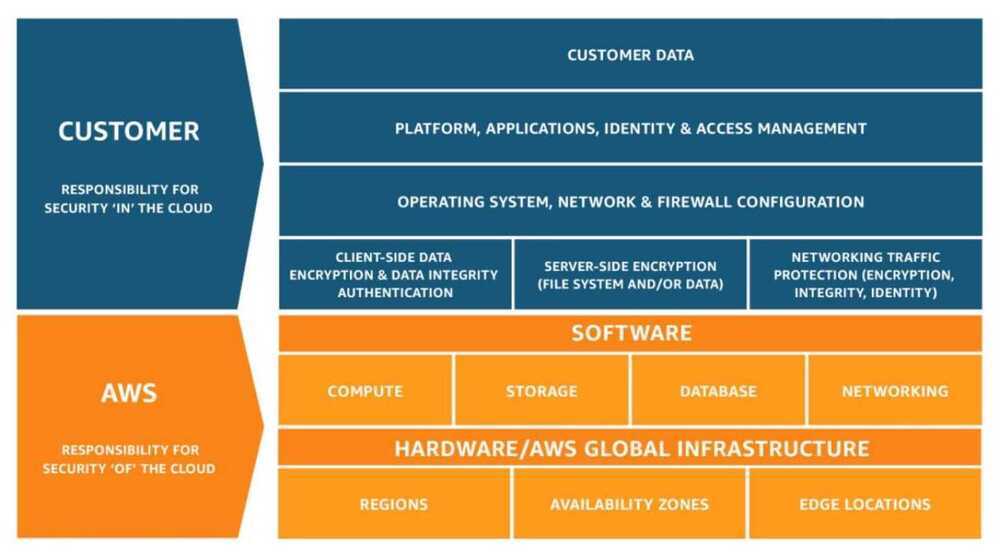
Shared responsibility model - Amazon Web Services: Risk and Compliance
AWS Shield
AWS Shield Standard is automatically enabled for all AWS customers at no additional cost and protects against common DDoS attacks on your AWS services like ELB, CloudFront, and Route 53. However, for enhanced protection against more sophisticated attacks, you must explicitly enable and configure AWS Shield Advanced for specific AWS resources.
AWS Shield is a managed Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) protection service that provides two tiers of protection: AWS Shield Standard is automatically included for all AWS customers at no extra cost, offering protection against common network and transport layer DDoS events. AWS Shield Advanced provides more sophisticated and customized protection against large and complex attacks, includes access to the AWS Shield Response Team for expert guidance, and offers cost protection for excess data transfer during a DDoS attack.
AWS Shield Standard and AWS Shield Advanced provide protections against Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks for AWS resources at the network and transport layers (layer 3 and 4) and the application layer (layer 7).
Classes of attacks that Shield detects
- Network volumetric attacks (layer 3) – This is a sub category of infrastructure layer attack vectors. These vectors attempt to saturate the capacity of the targeted network or resource, to deny service to legitimate users.
- Network protocol attacks (layer 4) – This is a sub category of infrastructure layer attack vectors. These vectors abuse a protocol to deny service to the targeted resource. A common example of a network protocol attack is a TCP SYN flood, which can exhaust connection state on resources like servers, load balancers, or firewalls. A network protocol attack can also be volumetric. For example, a larger TCP SYN flood may intend to saturate the capacity of a network while also exhausting the state of the targeted resource or intermediate resources.
- Application layer attacks (layer 7) – This category of attack vector attempts to deny service to legitimate users by flooding an application with queries that are valid for the target, such as web request floods.
AWS Shield Advanced
AWS Shield Advanced is a managed service that helps you protect your application against external threats, like DDoS attacks, volumetric bots, and vulnerability exploitation attempts. For higher levels of protection against attacks, you can subscribe to AWS Shield Advanced.
When you subscribe to Shield Advanced and add protection to your resources, Shield Advanced provides expanded DDoS attack protection for those resources. The protections that you receive from Shield Advanced can vary depending on your architecture and configuration choices. Use the information in this guide to build and protect resilient applications using Shield Advanced, and to escalate when you need expert help.
If your organization has multiple AWS accounts, then you can subscribe multiple AWS Accounts to AWS Shield Advanced by individually enabling it on each account using the AWS Management Console or API. You will pay the monthly fee once as long as the AWS accounts are all under a single consolidated billing, and you own all the AWS accounts and resources in those accounts.
AWS Firewall manager
AWS Firewall Manager is a security management service which allows you to centrally configure and manage firewall rules across your accounts and applications in AWS Organizations. As new applications are created, Firewall Manager makes it easy to bring new applications and resources into compliance by enforcing a common set of security rules. Now you have a single service to build firewall rules, create security policies, and enforce them in a consistent, hierarchical manner across your entire infrastructure.
Using AWS Firewall Manager, you can centrally configure
- AWS WAF rules
- AWS Shield Advanced protection
- Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) security groups
- AWS Network Firewalls
- Amazon Route 53 Resolver DNS Firewall rules,
across accounts and resources in your organization. It does not support Network ACLs as of today.
FAQs | AWS Firewall Manager | Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Amazon GuardDuty
Amazon GuardDuty combines ML and integrated threat intelligence from AWS and leading third parties to help protect your AWS accounts, workloads, and data from threats.
Amazon GuardDuty continuously monitors for malicious or unauthorized behavior to help protect your AWS resources, including your AWS accounts and access keys. Amazon GuardDuty identifies any unusual or unauthorized activity, like cryptocurrency mining or infrastructure deployments in a region that has never been used. Powered by threat intelligence and machine learning, GuardDuty is continuously evolving to help you protect your AWS environment.
The cryptocurrency finding expands the service’s ability to detect Amazon EC2 instances querying IP addresses associated with the cryptocurrency-related activity. The finding type is: CryptoCurrency:EC2/BitcoinTool.B, CryptoCurrency:EC2/BitcoinTool.B!DNS.
This finding informs you that the listed Amazon EC2 instance in your AWS environment is querying a domain name that is associated with Bitcoin or other cryptocurrency-related activity. Bitcoin is a worldwide cryptocurrency and digital payment system that can be exchanged for other currencies, products, and services. Bitcoin is a reward for bitcoin mining and is highly sought after by threat actors.
If you use the Amazon EC2 instance to mine or manage cryptocurrency, or this instance is otherwise involved in blockchain activity, this finding could represent expected activity for your environment. If this is the case in your AWS environment, AWS recommends that you set up a suppression rule for this finding.
Amazon GuardDuty is a threat detection service that continuously monitors for malicious activity and unauthorized behavior to protect your AWS accounts, workloads, and data stored in Amazon S3. With the cloud, the collection and aggregation of account and network activities is simplified, but it can be time-consuming for security teams to continuously analyze event log data for potential threats. With GuardDuty, you now have an intelligent and cost-effective option for continuous threat detection in AWS. The service uses machine learning, anomaly detection, and integrated threat intelligence to identify and prioritize potential threats.
Amazon GuardDuty analyzes tens of billions of events across multiple AWS data sources, such as AWS Cloud Trail events, Amazon VPC Flow Logs, and DNS logs.
With a few clicks in the AWS Management Console, GuardDuty can be enabled with no software or hardware to deploy or maintain. By integrating with Amazon EventBridge Events, GuardDuty alerts are actionable, easy to aggregate across multiple accounts, and straightforward to push into existing event management and workflow systems.
GuardDuty foundational data sources
- AWS CloudTrail management event logs: These logs provide a record of actions taken by users, roles, or AWS services in your AWS account, offering insights into control plane activity.
- Amazon VPC Flow Logs: These logs capture information about the IP traffic going to and from network interfaces in your Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), providing visibility into network activity.
- DNS logs: GuardDuty monitors DNS query logs to identify communication with known malicious domains and detect anomalous DNS activity.
GuardDuty foundational data sources - Amazon GuardDuty
Others
Open-source SAST tools such as Semgrep, Bandit, or KICS can help you find vulnerabilities and compliance issues in your code.
GitHub - ossf/scorecard: OpenSSF Scorecard - Security health metrics for Open Source
Security Checks Simplified: How to Implement Best Practices with Ease - YouTube