AWS Glue Concepts
AWS Glue is a fully managed ETL (extract, transform, load) service that allows you to easily move data between different data sources and targets. The key components are:
- Data Catalog: A metadata store containing table definitions, job definitions, and other control information for your ETL workflows.
- Crawlers: Programs that connect to data sources, infer data schemas, and create metadata table definitions in the Data Catalog.
- ETL Jobs: The business logic to extract data from sources, transform it using Apache Spark scripts, and load it into targets.
- Triggers: Mechanisms to initiate job runs based on schedules or events.
The typical workflow involves:
- Define data sources and targets in the Data Catalog.
- Use Crawlers to populate the Data Catalog with table metadata from data sources.
- Define ETL jobs with transformation scripts to move and process data.
- Run jobs on-demand or based on triggers.
- Monitor job performance using dashboards.
The following diagram shows the architecture of an AWS Glue environment.
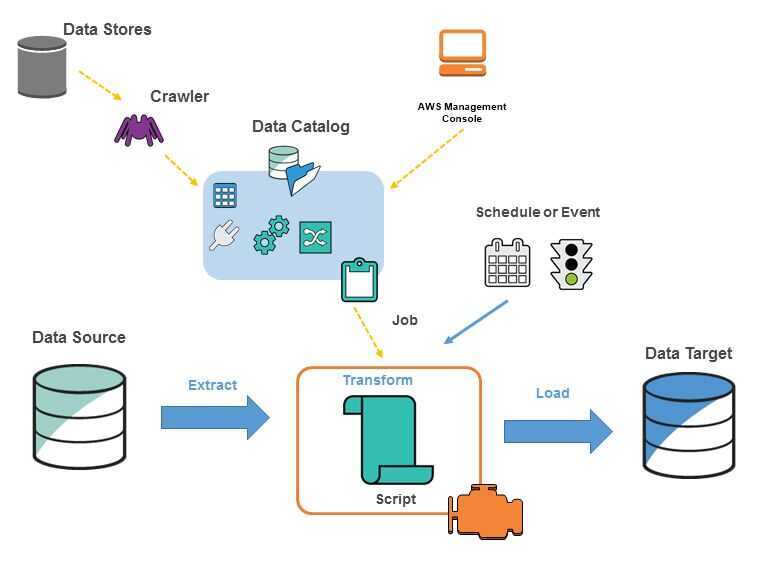
You define jobs in AWS Glue to accomplish the work that's required to extract, transform, and load (ETL) data from a data source to a data target. You typically perform the following actions:
- You define a crawler to populate your AWS Glue Data Catalog with metadata table definitions. You point your crawler at a data store, and the crawler creates table definitions in the Data Catalog. In addition to table definitions, the AWS Glue Data Catalog contains other metadata that is required to define ETL jobs. You use this metadata when you define a job to transform your data.
- AWS Glue can generate a script to transform your data. Or, you can provide the script in the AWS Glue console or API.
- You can run your job on demand, or you can set it up to start when a specified trigger occurs. The trigger can be a time-based schedule or an event. When your job runs, a script extracts data from your data source, transforms the data, and loads it to your data target. The script runs in an Apache Spark environment in AWS Glue.
Important
- Tables and databases in AWS Glue are objects in the AWS Glue Data Catalog. They contain metadata; they don't contain data from a data store.
Text-based data, such as CSVs, must be encoded inUTF-8for AWS Glue to process it successfully.
AWS Glue Terminology
AWS Glue Data Catalog
The persistent metadata store in AWS Glue. Each AWS account has one AWS Glue Data Catalog. It contains table definitions, job definitions, and other control information to manage your AWS Glue environment.
Classifier
Determines the schema of your data. AWS Glue provides classifiers for common file types, such as CSV, JSON, AVRO, XML, and others. It also provides classifiers for common relational database management systems using a JDBC connection. You can write your own classifier by using a grok pattern or by specifying a row tag in an XML document.
Connection
Contains the properties that are required to connect to your data store.
Crawler
A program that connects to a data store (source or target), progresses through a prioritized list of classifiers to determine the schema for your data, and then creates metadata in the AWS Glue Data Catalog.
Database
A set of associated table definitions organized into a logical group in AWS Glue.
Data store, data source, data target
A data store is a repository for persistently storing your data. Examples include Amazon S3 buckets and relational databases. Adata sourceis a data store that is used as input to a process or transform. Adata targetis a data store that a process or transform writes to.
Development endpoint
An environment that you can use to develop and test your AWS Glue scripts.
Dynamic Frame
A distributed table that supports nested data such as structures and arrays. Each record is self-describing, designed for schema flexibility with semi-structured data. Each record contains both data and the schema that describes that data. You can use both dynamic frames and Apache Spark dataframes in your ETL scripts, and convert between them. Dynamic frames provide a set of advanced transformations for data cleaning and ETL.
Job
The business logic that is required to perform ETL work. It is composed of a transformation script, data sources, and data targets. Job runs are initiated by triggers that can be scheduled or triggered by events.
Notebook server
A web-based environment that you can use to run your PySpark statements. For more information, see Apache Zeppelin. You can set up a notebook server on a development endpoint to run PySpark statements with AWS Glue extensions.
Script
Code that extracts data from sources, transforms it, and loads it into targets. AWS Glue generates PySpark or Scala scripts. PySpark is a Python dialect for ETL programming.
Table
The metadata definition that represents your data. Whether your data is in an Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) file, an Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) table, or another set of data, a table defines the schema of your data. A table in the AWS Glue Data Catalog consists of the names of columns, data type definitions, and other metadata about a base dataset. The schema of your data is represented in your AWS Glue table definition. The actual data remains in its original data store, whether it be in a file or a relational database table. AWS Glue catalogs your files and relational database tables in the AWS Glue Data Catalog. They are used as sources and targets when you create an ETL job.
Transform
The code logic that is used to manipulate your data into a different format.
Trigger
Initiates an ETL job. Triggers can be defined based on a scheduled time or an event.