Overview
https://www.djangoproject.com/start/overview
Django is a powerful web development framework built on top of Python
Why Django - With Django, you can take Web applications from concept to launch in a matter of hours. Django takes care of much of the hassle of Web development, so you can focus on writing your app without needing to reinvent the wheel. It's free and open source.
Django Features
1. Components
- a lightweight and standalone web server for development and testing
- a form serialization and validation system that can translate between HTML forms and values suitable for storage in the database
- a template system that utilizes the concept of inheritance borrowed from object-oriented programming
- a caching framework that can use any of several cache methods
- support for middleware classes that can intervene at various stages of request processing and carry out custom functions
- an internal dispatcher system that allows components of an application to communicate events to each other via pre-defined signals
- an internationalization system, including translations of Django's own components into a variety of languages
- a serialization system that can produce and read XML and/or JSON representations of Django model instances
- a system for extending the capabilities of the template engine
- an interface to Python's built-in unit test framework
2. Bundled Applications
- an extensible authentication system
- the dynamic administrative interface
- tools for generating RSS and Atom syndication feeds
- a site's framework that allows one Django installation to run multiple websites, each with their own content and applications
- tools for generating Google Sitemaps
- built-in mitigation for cross-site request forgery, cross-site scripting, SQL injection, password cracking and other typical web attacks, most of them turned on by default
- a framework for creating GIS applications
Template namespacing
Path - polls/templates/polls/index.html
Render()
Get_object_or_404()
Namespacing URL names
Writing forms
Using F() to avoid race condition
Generic views()
TestCases using TestCase
migrations
Customizing the admin form
from django.contrib import admin
from .models import Question
class QuestionAdmin(admin.ModelAdmin):
fieldsets = [
(**None**, {'fields': ['question_text']}),
('Date information', {'fields': ['pub_date']}),
]
admin.site.register(Question, QuestionAdmin)
ChoiceInline(admin.StackedInline)
Model = Choice
Extra = 3
# StackedInline can be replaced with TabularInline for table view
Anatomy of a Dynamic Site
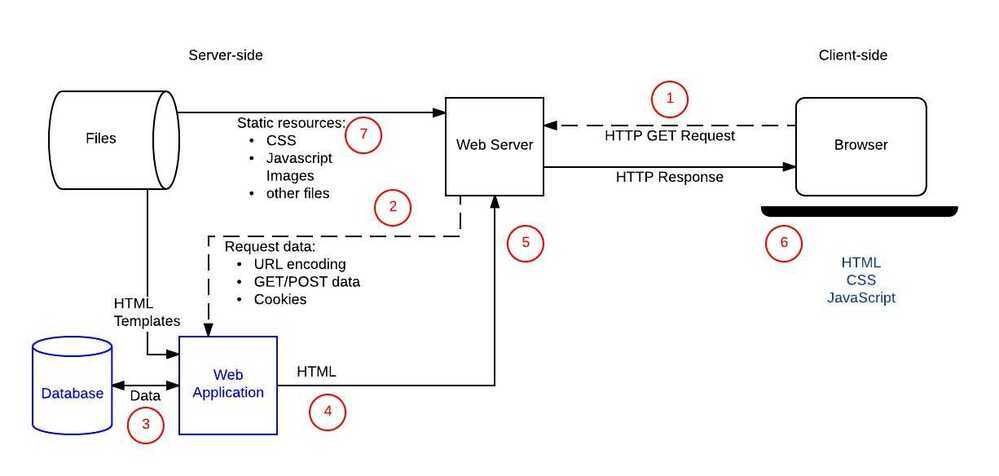
Starting a new project
This will properly initialize a new project in the same directory, without creating a recursive file path.
$ django-admin.py startproject samplesite .
Django User Model
- The username field is case-sensitive: john.doe and John.Doe are two different usernames
- The username field validates against unicode letters: joao, joão, Джон, or 約翰 are all valid username options
- The email field is not unique: More than one user can have the same email address
- A user without password cannot initiate a password reset: If you accept user creation without defining an initial random password, your user might be unable to reset and get the first password
- Swapping the default user model is very difficult after you created the initial migrations: Replacing the user model has many benefits, but you need to do it at the beginning of the project
Common Python web project's deployment stack
- Nginx: Static file serving, SSL termination, reverse proxy
- Memcached: Caching
- Celery: Background task runner
- Redis or RabbitMQ: Queue for Celery
- uWSGI: Python WSGI server
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Z5WQMSdcYv8
Django (3.0) Crash Course Tutorials | Customer Management App
- CRUD with model forms
- Inline formsets
https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/create-a-social-media-app-with-django
Interview Questions
- Explain Django’s architecture - MVT
- What is Jinja templating?
- What is serialization in Django?
- What is context in Django?
- Explain user authentication in Django
- Users
- Permissions
- Groups
- Password Hashing System
- Forms Validation
- A pluggable backend system
- What is the difference between CharField and TextField in Django?
- What is Django Rest Framework
- Explain the use of Middlewares in Django
- What are signals?
- Explain the Django Response lifecycle
Top 50 Django Interview Questions and Answers - GeeksforGeeks
30+ Django Interview Questions (2023) - InterviewBit
Releases / Changelog
Django 3.0
ASGI Support
https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/3.0/releases/3.0
https://arunrocks.com/a-guide-to-asgi-in-django-30-and-its-performance
Django 5.0
Django 5.0 release notes | Django documentation | Django
The State of Django 2025 | The PyCharm Blog
Django 6.0
Django 6.0 released | Weblog | Django
- Template Partials: modularize templates using small, named fragments for cleaner, more maintainable code.
- Background Tasks: run code outside the HTTP request-response cycle with a built-in, flexible task framework.
- Content Security Policy (CSP): easily configure and enforce browser-level security policies to protect against content injection.
- Modernized Email API: compose and send emails with Python's EmailMessage class for a cleaner, Unicode-friendly interface.