Types of Governments
turtles move slow, the government moves slower
Power is a prized possession of governments. They can let go of at least some of it and enjoy the lightness it creates in both the governed and the governing.
Monarchy
Democracy
Is Democracy Doomed? The Global Fight for Our Future | Timothy Snyder | TED - YouTube
I disapprove of what you say, but will defend to the death your right to say it.
How to Build Democracy — in an Authoritarian Country | Tessza Udvarhelyi | TED - YouTube
Democracy is not a noun but a verb, it something you do
A wicked citizen cannot do evil in a republic that is not corrupted
Dictatorship are never as strong and people are never as weak as they think they are -- Gene Sharp
Educate, agitate, organize -- Dr. B.r. Ambedkar
Why Democracy Is Mathematically Impossible - YouTube
Indian Democracy
- After Modi's great victory in the 2019 election, what is your message for Modi followers? - Quora
- Is India becoming a DICTATORSHIP? | Chandigarh Elections | Farmers Protest | Dhruv Rathee - YouTube
- Is Modi a dictator? | Dhruv Rathee vs The World - YouTube
- किसको चाहिए डिक्टेटर? कद्दू समझ रखा है? | Who wants Dictatorship in India?? - YouTube
Links
- The Age of The Strongman: How the Cult of the Leader Threatens Democracy around the World eBook : Rachman, Gideon
- How Dictatorships Work: Power, Personalization, and Collapse, Geddes, Barbara, Wright, Joseph, Frantz, Erica
- How to Be a Dictator: The Cult of Personality in the Twentieth Century : Dikötter, Frank
- Illegitimate Authority: Facing the Challenges of Our Time
- Dictatorland: The Men Who Stole Africa
- Myth of the Strong Leader
- The Origins of Totalitarian Democracy
- The Origins of Totalitarianism (Penguin Modern Classics)
Oligarchy
a small group of people having control of a country or organization.
Authoritarianism
the enforcement or advocacy of strict obedience to authority at the expense of personal freedom.
Totalitarianism
a system of government that is centralized and dictatorial and requires complete subservience to the state.
Meritocracy
Populism
a political approach that strives to appeal to ordinary people who feel that their concerns are disregarded by established elite groups.
Federalism
Federalism is the mixed or compound mode of government, combining a general government (the central or "federal" government) with regional governments (provincial, state, cantonal, territorial or other sub-unit governments) in a single political system.
Federalism can thus be defined as a form of government in which there is a division of powers between two levels of government of equal status.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Federalism
Egalitarian
believing in or based on the principle that all people are equal and deserve equal rights and opportunities.
Socialism
a political and economic theory of social organization which advocates that the means of production, distribution, and exchange should be owned or regulated by the community as a whole.
Capitalism
an economic and political system in which a country's trade and industry are controlled by private owners for profit, rather than by the state.
Feudalism
the dominant social system in medieval Europe, in which the nobility held lands from the Crown in exchange for military service, and vassals were in turn tenants of the nobles, while the peasants (villeins or serfs) were obliged to live on their lord's land and give him homage, labour, and a share of the produce, notionally in exchange for military protection.
Imperialism
A policy of extending a country's power and influence through colonization, use of military force, or other means.
Imperialism is the highest form of capitalism
Sectarianism
Excessive attachment to a particular sect or party, especially in religion.
Secularism
The principle of separation of the state from religious institutions.
Secular is the state of being unrelated or neutral in regards to religion.
Communism
Communism (from Latin communis, 'common, universal') is a philosophical, social, political, economic ideology and movement whose ultimate goal is the establishment of a communist society, namely a socioeconomic order structured upon the ideas of common ownership of the means of production and the absence of social classes, money and the state. - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Communism
Orwellian
"Orwellian" is an adjective describing a situation, idea, or societal condition that George Orwell identified as being destructive to the welfare of a free and open society. It denotes an attitude and a brutal policy of draconian control by propaganda, surveillance, disinformation, denial of truth (doublethink), and manipulation of the past, including the "unperson" - a person whose past existence is expunged from the public record and memory, practiced by modern repressive governments. Often, this includes the circumstances depicted in his novels, particularly Nineteen Eighty-Four but political doublespeak is criticized throughout his work, such as in Politics and the English Language.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Orwellian
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nineteen_Eighty-Four
Gerontocracy
a state, society, or group governed by old people
Plutocracy
government by the wealthy
an elite or ruling class whose power derives from their wealth
Paedocracy
Rule by children
Elite Theory
In philosophy, political science and sociology, elite theory is a theory of the State that seeks to describe and explain power relationships in contemporary society. The theory posits that a small minority, consisting of members of the economic elite and policy-planning networks, holds the most power-and that this power is independent of democratic elections.
Rhine Captalism
Social market economy - Wikipedia
Don't Underestimate The German Economy | Economics Explained - YouTube
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Government
- Full presidential republics
- Semi-presidential republics
- Republics with an executive president elected by or nominated by the legislature that may or may not be subject to parliamentary confidence
- Parliamentary republics
- Parliamentary constitutional monarchies
- Parliamentary semi-constitutional monarchies which have a separate head of government but where royalty holds significant executive and/or legislative power
- Absolute monarchies
- One-party states
- Countries where constitutional provisions for government have been suspended (e.g. military dictatorships)
- Countries which do not fit any of the above systems (e.g. provisional governments/unclear political situations)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parliamentary_system
Permanent Revolution
Permanent revolution is the strategy of a revolutionary class pursuing its own interests independently and without compromise or alliance with opposing sections of society. As a term within Marxist theory, it was first coined by Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels as early as 1850, but since then it has been used to refer to different concepts by different theorists, most notably Leon Trotsky.
Permanent revolution - Wikipedia
Liberalism
Every Liberalism Term Explained in 5 Minutes - YouTube
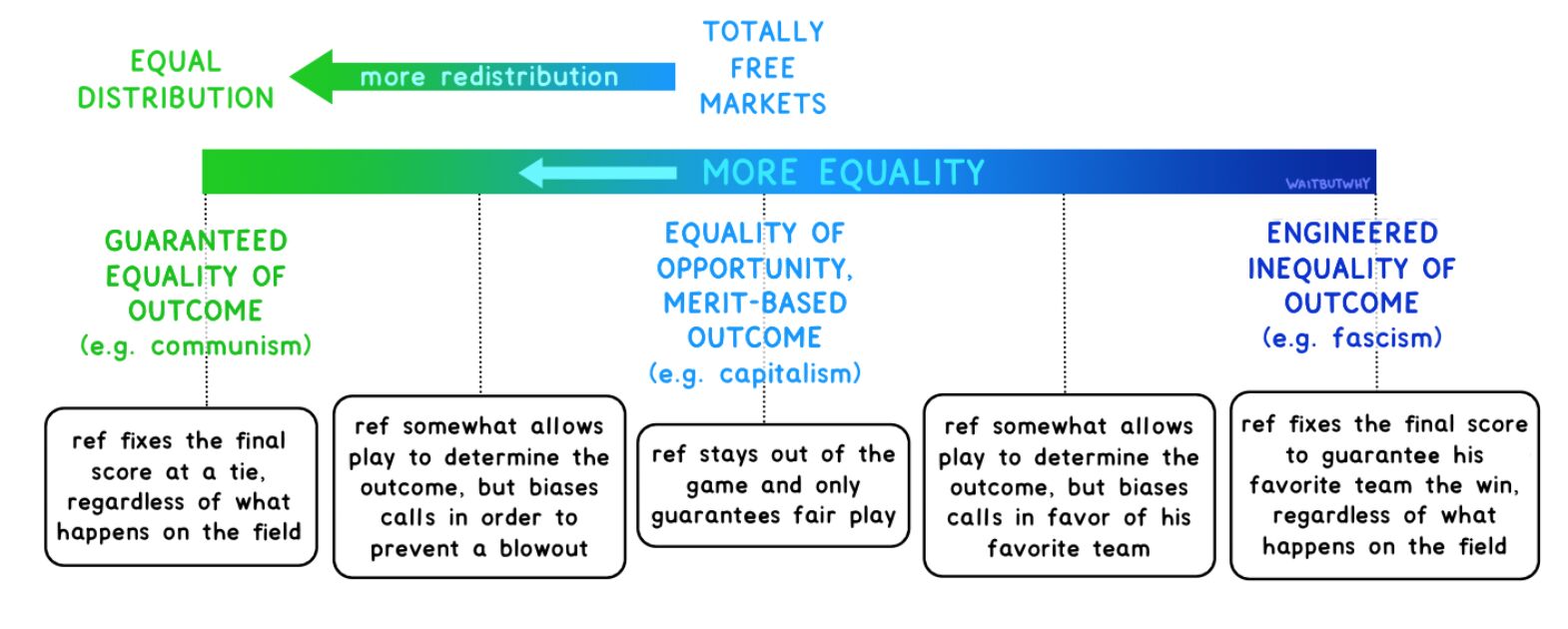
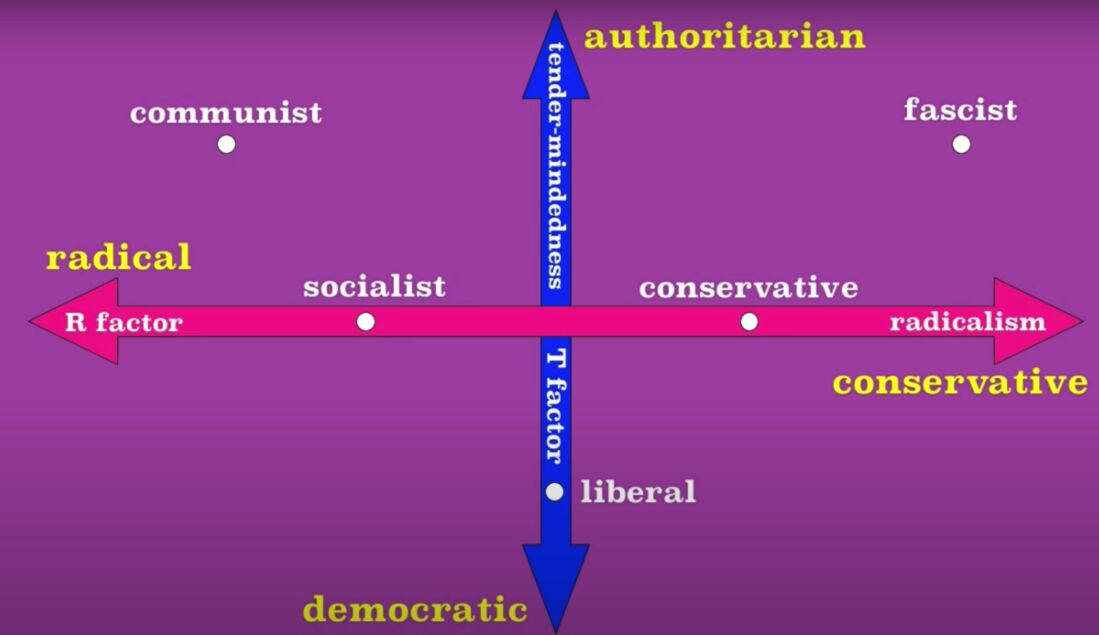
The Political Spectrums - Left wing vs right wing, centrism (Crap)
Left (Liberal)
- Liberty - Freedom to do everything which injures no one else
- Equality (egalitarianism)
The idea of fairness for all humans
- Progress
- Internationalism
- Reform
Right (Conservative)
- Authority
- Hierarchy
- Tradition
- Nationalism
- Reaction


https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8SOQduoLgRw
Bipartisan
Of or involving the agreement or cooperation of two political parties that usually oppose each other's policies.
"the reforms received considerable bipartisan approval"