Kong
Kong is a cloud-native, fast, scalable, and distributed Microservice Abstraction Layer (also known as an API Gateway, API Middleware or in some cases Service Mesh). Made available as an open-source project in 2015, its core values are high performance and extensibility.
If you are building for web, mobile or IoT (Internet of Things) you will likely end up needing common functionality to run your actual software. Kong can help by acting as a gateway (or a sidecar) for microservices requests while providing load balancing, logging, authentication, rate-limiting, transformations, and more through plugins.
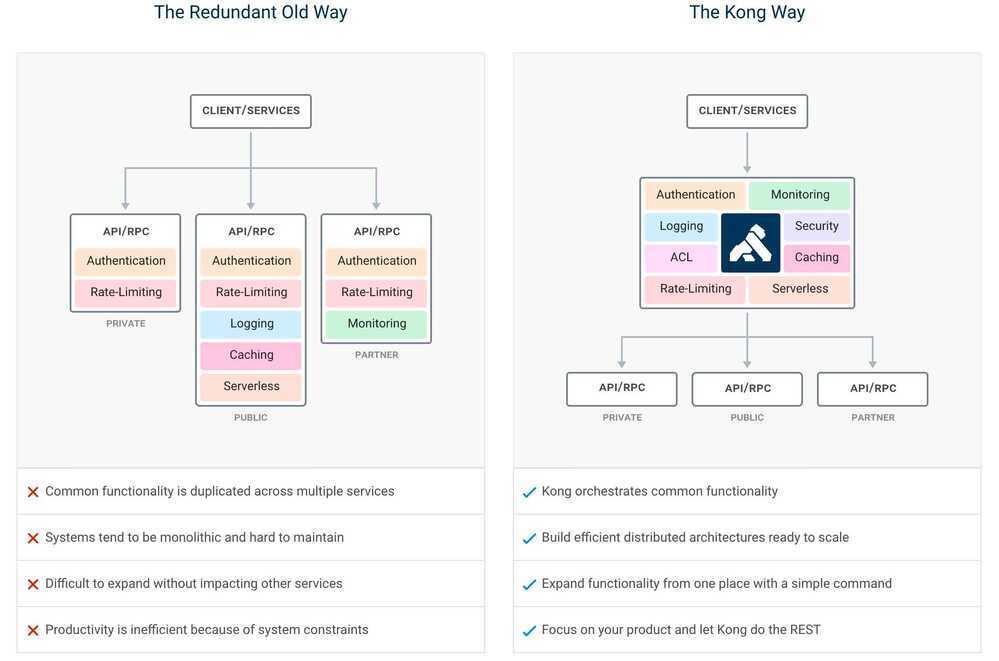
Features
- Cloud-Native: Platform agnostic, Kong can run from bare metal to Kubernetes.
- Dynamic Load Balancing: Load balance traffic across multiple upstream services.
- Hash-based Load Balancing: Load balance with consistent hashing/sticky sessions.
- Circuit-Breaker: Intelligent tracking of unhealthy upstream services.
- **Health Checks:**Active and passive monitoring of your upstream services.
- Service Discovery: Resolve SRV records in third-party DNS resolvers like Consul.
- Serverless: Invoke and secure AWS Lambda or OpenWhisk functions directly from Kong.
- WebSockets: Communicate to your upstream services via WebSockets.
- OAuth2.0: Easily add OAuth2.0 authentication to your APIs.
- Logging: Log requests and responses to your system over HTTP, TCP, UDP, or to disk.
- Security: ACL, Bot detection, whitelist/blacklist IPs, etc...
- Syslog: Logging to System log.
- SSL: Setup a Specific SSL Certificate for an underlying service or API.
- Monitoring: Live monitoring provides key load and performance server metrics.
- Forward Proxy: Make Kong connect to intermediary transparent HTTP proxies.
- Authentications: HMAC, JWT, Basic, and more.
- Rate-limiting: Block and throttle requests based on many variables.
- Transformations: Add, remove, or manipulate HTTP requests and responses.
- Caching: Cache and serve responses at the proxy layer.
- CLI: Control your Kong cluster from the command line.
- REST API: Kong can be operated with its RESTful API for maximum flexibility.
- Geo-Replicated: Configs are always up-to-date across different regions.
- Failure Detection & Recovery: Kong is unaffected if one of your Cassandra nodes goes down.
- Clustering: All Kong nodes auto-join the cluster keeping their config updated across nodes.
- Scalability: Distributed by nature, Kong scales horizontally by simply adding nodes.
- Performance: Kong handles load with ease by scaling and using NGINX at the core.
- Plugins: Extendable architecture for adding functionality to Kong and APIs.
Kong DB Less Declarative Config
https://docs.konghq.com/1.3.x/db-less-and-declarative-config
Kong Helm Charts
helm install --name kg \
--set=admin.type=ClusterIP,proxy.type=LoadBalancer,proxy.loadBalancerIP=104.211.225.153 \
--namespace kong \
stable/kong
helm upgrade --set=admin.useTLS=true --namespace kong kg stable/kong
helm delete --purge kg
helm status kg
export POD_NAME=$(kubectl get pods --namespace kong -l "release=kg, app=kong" -o jsonpath="{.items[0].metadata.name}")
kubectl port-forward --namespace kong $POD_NAME 8444:8444
# Notes
1. Kong Admin can be accessed inside the cluster using:
DNS=kg-kong-admin.kong.svc.cluster.local
PORT=8444
To connect from outside the K8s cluster:
HOST=127.0.0.1
# Execute the following commands to route the connection to Admin SSL port:
export POD_NAME=$(kubectl get pods --namespace kong -l "release=kg, app=kong" -o jsonpath="{.items[0].metadata.name}")
kubectl port-forward --namespace kong $POD_NAME 8444:8444
2. Kong Proxy can be accessed inside the cluster using:
DNS=kg-kong-proxy.kong.svc.cluster.localPORT=443To connect from outside the K8s cluster:
HOST=$(kubectl get svc --namespace kong kg-kong-proxy -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress.ip}')
PORT=$(kubectl get svc --namespace kong kg-kong-proxy -o jsonpath='{.spec.ports[0].nodePort}')
https://github.com/helm/charts/tree/master/stable/kong
Commands
docker network create kong-net
docker run --name kong-database \
--network=kong-net \
-p 5432:5432 \
-e POSTGRES_USER=kong \
-e POSTGRES_DB=kong \
postgres:11.2
docker run --rm \
--network=kong-net \
-e KONG_DATABASE=postgres \
-e KONG_PG_HOST=kong-database \
kong:latest kong migrations bootstrap
docker run --name kong \
--network=kong-net \
-e KONG_DATABASE=postgres \
-e KONG_PG_HOST=kong-database \
-e KONG_PROXY_ACCESS_LOG=/dev/stdout \
-e KONG_ADMIN_ACCESS_LOG=/dev/stdout \
-e KONG_PROXY_ERROR_LOG=/dev/stderr \
-e KONG_ADMIN_ERROR_LOG=/dev/stderr \
-e "KONG_ADMIN_LISTEN=0.0.0.0:8001, 0.0.0.0:8444 ssl" \
-p 8000:8000 \
-p 8443:8443 \
-p 8001:8001 \
-p 8444:8444 \
kong:latest
docker run -p 1337:1337 \
--network=kong-net \
--name konga \
-v /Users/kongadata:/app/kongadata \
-e NODE_ENV=production \
pantsel/konga
curl -X POST \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"name":"JohnDoe","username":"jdoe"}' \
http://localhost:8000/fake-api/users
http://localhost:8000/fake-api/users
Konga
More than just another GUI to Kong Admin API
https://github.com/pantsel/konga
Getting Started
Get started with Konnect - Kong Konnect | Kong Docs
Installation using Konnect
brew tap kong/deck
brew install deck
export DECK_KONNECT_CONTROL_PLANE_NAME='serverless-default'
export DECK_KONNECT_TOKEN='kpat_eIfenaD74twNK4GTWCmAACVV0Dh69DML9fjDNU9YbXxAOrH9G'
deck gateway ping
Config
# Welcome to Konnect!
# In this quickstart, you'll set up a sample API and test key Kong Gateway
# features, including authentication and rate-limiting. Using decK, you'll
# sync the configuration in this file to a Serverless Gateway, giving you
# hands-on experience with managing Gateway setups as code.
# Once you're comfortable, you can define your own API in a decK configuration
# or sync this configuration to a Gateway running in another environment.
_format_version: "3.0"
# A service is Kong Gateway's entity that describes an API or microservice.
services:
- host: api.kong-air.com
name: Kong-Air-Flights-API
path: /flights
port: 443
protocol: https
# A route defines the rules for how incoming requests are matched
# by Kong Gateway and sent to the appropriate backend service.
routes:
- name: deck-demo-route
methods:
- GET
- OPTIONS
paths:
- /first-route
protocols:
- http
# A plugin adds functionality to Kong Gateway, enabling features like
# authentication, rate limiting, logging, and more.
plugins:
# The key-auth plugin secures your service by requiring consumers to
# provide an API key for access.
- name: key-auth
config:
key_names:
- apikey
hide_credentials: false
# In order to be able to access your authenticated API, we need to define a consumer and credentials.
consumers:
- username: demo_user
keyauth_credentials:
- key: hello_world
Sync & Test
deck gateway sync ./demo_deck_config.yaml
# test
curl https://kong-578a9e8f3ausw9mj7.kongcloud.dev/first-route -H "apikey: hello_world"
Components
Kong Konnect Demo: Revolutionize Your API Management with a Unified Cloud-Native Platform - YouTube
- Gateway Manager
- Mesh Manager
- API Products
- Dev Portal
- Analytics
- Service Hub
Kong Entities
- Services: A service is an entity representing an external upstream API or microservice. For example, a data transformation microservice, a billing API, and so on.
- Routes: Routes determine how (and if) requests are sent to their services after they reach the gateway. Where a service represents the backend API, a route defines what is exposed to clients. A single service can have many routes. Once a route is matched, the gateway proxies the request to its associated service.
- Consumers: Consumer objects represent users of a service, and are most often used for authentication. They provide a way to divide access to your services, and make it easy to revoke that access without disturbing a service’s function.
- Load balancers: Load balancing is a method of distributing API request traffic across multiple upstream services. Load balancing improves overall system responsiveness and reduces failures by preventing overloading of individual resources.
- Upstream targets: Upstream refers to an API, application, or micro-service that Kong Gateway forwards requests to. In Kong Gateway, an upstream object represents a virtual hostname and can be used to health check, circuit break, and load balance incoming requests over multiple services.
Quiz
Question 1
What is a primary benefit of using Kong's plugin-driven architecture?
- It reduces the need for API versioning.
- It allows custom extensions in multiple programming languages.
- It eliminates the need for load balancing.
- It replaces the need for microservices.
Answer: 2. It allows custom extensions in multiple programming languages.
Question 2
Which of the following best describes Kong's role in a microservices architecture?
- It replaces microservices with a single monolithic application.
- It acts as an entry point for client requests, managing traffic to microservices.
- It serves as a database for microservices data.
- It directly processes client requests without routing them.
Answer: 2. It acts as an entry point for client requests, managing traffic to microservices.
Question 3
Which authentication methods are supported by Kong?
- Basic, JWT, HMAC, OAuth 2
- Basic, SSH, HMAC, LDAP
- OAuth 1, JWT, SAML, SSH
- OAuth 2, SSH, LDAP, SAML
Answer: 1. Basic, JWT, HMAC, OAuth 2
Question 4
What is Kong's "Admin API" primarily used for?
- Managing backend service configurations.
- Controlling consumer-level traffic directly.
- Configuring and managing Kong Gateway settings.
- Monitoring API health and performance metrics.
Answer: 3. Configuring and managing Kong Gateway settings.