Others
Pricing
Pricing table for a 8 node (1 core, 3.5gb) cluster:
| Short-term (100 hrs) / per month | Long-term (3yrs committed) / per month | |
|---|---|---|
| GKE | 40$ | 125$ |
| AKS | 60$ | 150$ |
| EKS | 50$+20$ (master) | 150$ + 144$ (master) |
https://blog.hasura.io/gke-vs-aks-vs-eks-411f080640dc
https://www.toptal.com/kubernetes/k8s-aws-vs-gcp-vs-azure-aks-eks-gke
Kaniko
Kaniko is an open source tool to build container images within Kubernetes
It can build an image using any standard Dockerfile
Rook
Rook is an open sourcecloud-native storage orchestratorfor Kubernetes, providing the platform, framework, and support for a diverse set of storage solutions to natively integrate with cloud-native environments.
Rook turns storage software into self-managing, self-scaling, and self-healing storage services. It does this by automating deployment, bootstrapping, configuration, provisioning, scaling, upgrading, migration, disaster recovery, monitoring, and resource management. Rook uses the facilities provided by the underlying cloud-native container management, scheduling and orchestration platform to perform its duties.
Ceph
Ceph is a distributed storage system that provides file, block and object storage and is deployed in large scale production clusters.
https://ceph.com/community/rook-automating-ceph-kubernetes
CloudEvents
CloudEvents is a specification for describing event data in common formats to provide interoperability across services, platforms and systems.
https://github.com/cloudevents/spec
Ship
Replicated Ship is a Kubernetes app deployment and automation tool that can:
- Track and automate the maintenance of 3rd-party applications whether packaged as Helm Charts, Kubernetes YAML manifests, or Knative apps.
- Quickly develop app kustomizations using Ship's easy-to-use import & migration tools.
- Enable application developers to package and deliver a canonical version of their application configuration while encouraging last-mile customizations through overlays instead of forking or upstream requests.
https://github.com/replicatedhq/ship
https://www.replicated.com/ship
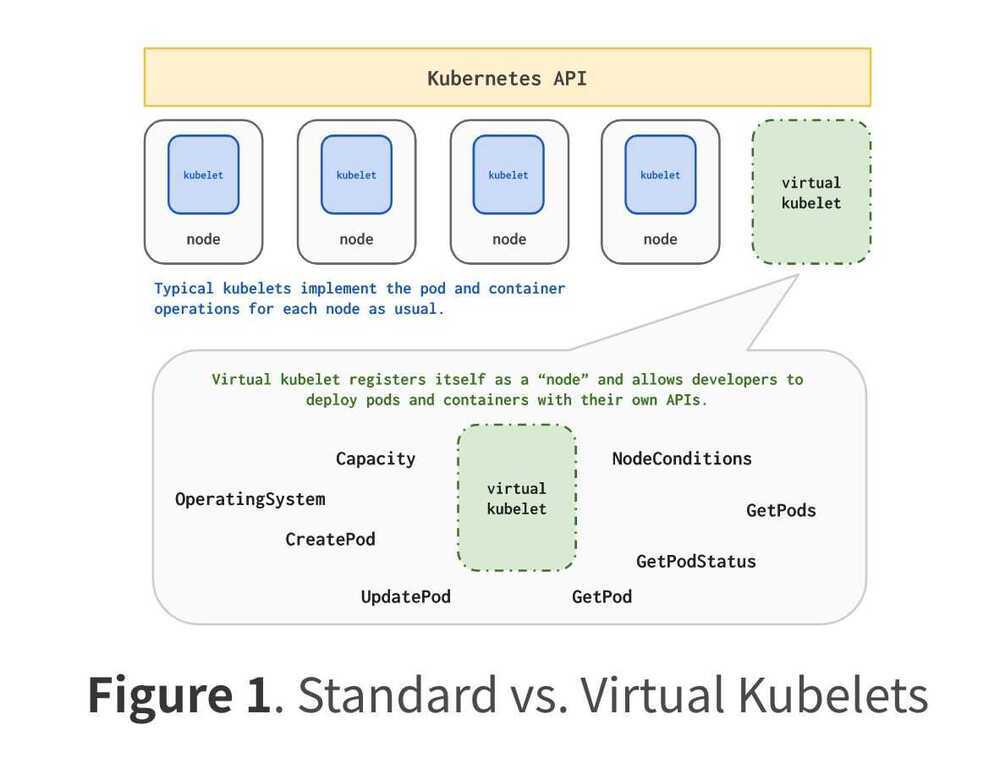
Virtual Kubelet
Kubelet is the name of the Kubernetes agent that runs on every node of our cluster. When a node boots up, Kubelet is started. It connects to the Kubernetes API server, and it says (more or less) "Hi there, my name isnode752. I have that many cores, that much RAM and disk space. Do you per chance have any pod that I should run?" and after that, it waits for the Kubernetes API server for instructions. The Kubernetes API server registers the node in etcd. From that point, the scheduler knows about the node, and will be able to assign pods to it. When a pod gets assigned to the node, the pod's manifest is pushed to the node, and the node runs it. Later on, the Kubelet will keep updating the API server with the node's status.
Virtual Kubeletis a program that uses the same API as Kubelet. It connects to the API server, introduces itself, and announces that it can run pods. Except, when it is assigned a pod, instead of creating containers (with Docker, CRI-O, containerd, or what have you), Virtual Kubelet will defer that work to a provider like Fargate or ACI.
So Virtual Kubelet looks like a regular cluster node (it shows up in the output ofkubectl get nodes) except that it doesn't correspond to an actual node. Anything scheduled on Virtual Kubelet will run on its configured provider.
https://jpetazzo.github.io/2019/02/13/running-kubernetes-without-nodes-with-kiyot
Virtual Kubelet is an open source Kubernetes kubelet implementation that masquerades as a kubelet for the purposes of connecting Kubernetes to other APIs. This allows the nodes to be backed by other services like ACI, AWS Fargate, IoT Edge etc. The primary scenario for VK is enabling the extension of the Kubernetes API into serverless container platforms like ACI and Fargate, though we are open to others. However, it should be noted that VK is explicitly not intended to be an alternative to Kubernetes federation.
Virtual Kubelet features a pluggable architecture and direct use of Kubernetes primitives, making it much easier to build on.
https://github.com/virtual-kubelet/virtual-kubelet
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/aks/virtual-kubelet#installation
Others - Kiyot
https://static.elotl.co/docs/latest/kiyot/kiyot.html
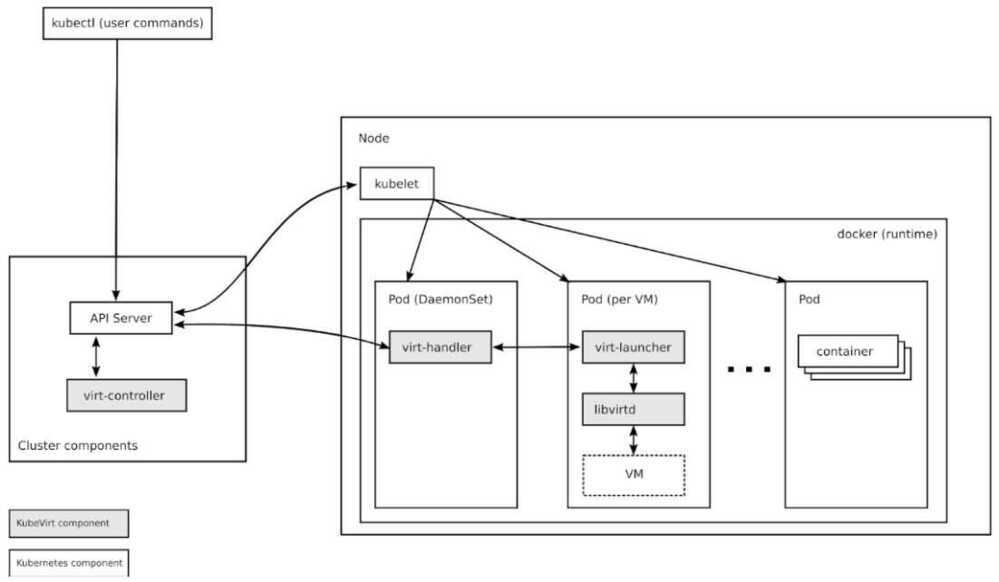
KubeVirt
KubeVirt technology addresses the needs of development teams that have adopted or want to adopt Kubernetes but possess existing Virtual Machine-based workloads that cannot be easily containerized. More specifically, the technology provides a unified development platform where developers can build, modify, and deploy applications residing in both Application Containers as well as Virtual Machines in a common, shared environment.
Benefits are broad and significant. Teams with a reliance on existing virtual machine-based workloads are empowered to rapidly containerize applications. With virtualized workloads placed directly in development workflows, teams can decompose them over time while still leveraging remaining virtualized components as is comfortably desired.
Kubernetes migrations & Disaster Management
https://github.com/kubemove/kubemove
https://github.com/heptio/velero
https://heptio.github.io/velero/master/migration-case.html
https://akomljen.com/kubernetes-backup-and-restore-with-velero
ExternalDNS
ExternalDNS synchronizes exposed Kubernetes Services and Ingresses with DNS providers.
Inspired by Kubernetes DNS, Kubernetes' cluster-internal DNS server, ExternalDNS makes Kubernetes resources discoverable via public DNS servers. Like KubeDNS, it retrieves a list of resources (Services, Ingresses, etc.) from the Kubernetes API to determine a desired list of DNS records.UnlikeKubeDNS, however, it's not a DNS server itself, but merely configures other DNS providers accordingly - e.g.AWS Route 53 or Google Cloud DNS.
In a broader sense, ExternalDNS allows you to control DNS records dynamically via Kubernetes resources in a DNS provider-agnostic way.
https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/external-dns
Brigade: Event-based Scripting for Kubernetes
Script simple and complex workflows using JavaScript. Chain together containers, running them in parallel or serially. Fire scripts based on times, GitHub events, Docker pushes, or any other trigger. Brigade is the tool for creating pipelines for Kubernetes.
Bitnami Kubernetes Production Runtime (BKPR)
Bitnami Kubernetes Production Runtime (BKPR) is a curated collection of the services needed to deploy on top of your Kubernetes cluster to enable logging, monitoring, certificate management, automatic discovery of Kubernetes resources via public DNS servers, and other common infrastructure needs. The services are ready-to-run and pre-integrated with each other, so they work out of the box.
BKPR is open source under the Apache 2 License and is available for Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) and Amazon Elastic Container Service for Kubernetes (EKS) clusters.
Monitoring
- Prometheus
- Grafana
- Alertmanager
Monitoring in the Kubernetes Era | Datadog
Logging
- Elasticsearch
- Kibana
- Fluentd
Ingress
- nginx-ingress
- ExternalDNS
- cert-manager
- OAuth2 Proxy
Forge
Forge is an open source tool that lets you deploy source straight into Kubernetes, whether it's for development, testing, or production. Forge supports dependency management, fast parallel builds, and more. Forge is self-contained, and designed to run anywhere from your laptop to your CI system.
https://github.com/datawire/forge
Sonobuoy
Sonobuoy is a diagnostic tool that makes it easier to understand the state of a Kubernetes cluster by running a set of plugins (including Kubernetes conformance tests) in an accessible and non-destructive manner. It is a customizable, extendable, and cluster-agnostic way to generate clear, informative reports about your cluster.
Cluster operators
- Is my cluster in a good state?
- Why is my cluster misbehaving?
Service providers
- Does my service work in this cluster?
- Does cluster with my service still pass conformance?
https://github.com/vmware-tanzu/sonobuoy
Others
- https://medium.com/free-code-camp/how-to-set-up-a-serious-kubernetes-terminal-dd07cab51cd4
- https://www.weave.works/blog/application-checklist-kubernetes
- https://www.weave.works/blog/production-ready-checklist-kubernetes
- https://www.stackrox.com/post/2019/09/12-kubernetes-configuration-best-practices
- API Versions - https://matthewpalmer.net/kubernetes-app-developer/articles/kubernetes-apiversion-definition-guide.html
- Using private container registry - https://container-solutions.com/using-google-container-registry-with-kubernetes
- Centralized monitoring on Kubernetes - https://github.com/coreos/prometheus-operator/tree/master/contrib/kube-prometheus
- Questions - https://ymmt2005.hatenablog.com/entry/k8s-things
- Stakater · GitHub