Architecture
Data Platform as a Self-managed Service
Snowflake is a true self-managed service, meaning:
- There is no hardware (virtual or physical) to select, install, configure, or manage.
- There is virtually no software to install, configure, or manage.
- Ongoing maintenance, management, upgrades, and tuning are handled by Snowflake.
Snowflake runs completely on cloud infrastructure. All components of Snowflake’s service (other than optional command line clients, drivers, and connectors), run in public cloud infrastructures.
Snowflake uses virtual compute instances for its compute needs and a storage service for persistent storage of data. Snowflake cannot be run on private cloud infrastructures (on-premises or hosted).
Snowflake is not a packaged software offering that can be installed by a user. Snowflake manages all aspects of software installation and updates.
Snowflake Architecture
Snowflake’s architecture is a hybrid of traditional shared-disk and shared-nothing database architectures. Similar to shared-disk architectures, Snowflake uses a central data repository for persisted data that is accessible from all compute nodes in the platform. But similar to shared-nothing architectures, Snowflake processes queries using MPP (massively parallel processing) compute clusters where each node in the cluster stores a portion of the entire data set locally. This approach offers the data management simplicity of a shared-disk architecture, but with the performance and scale-out benefits of a shared-nothing architecture.
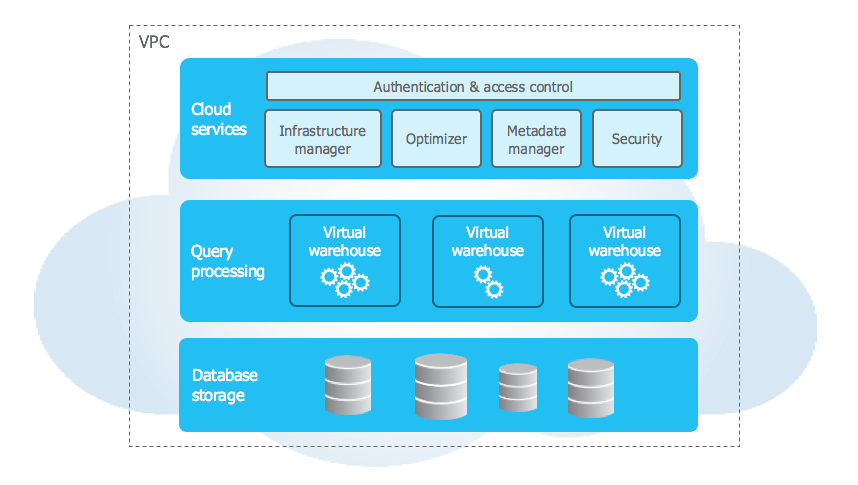
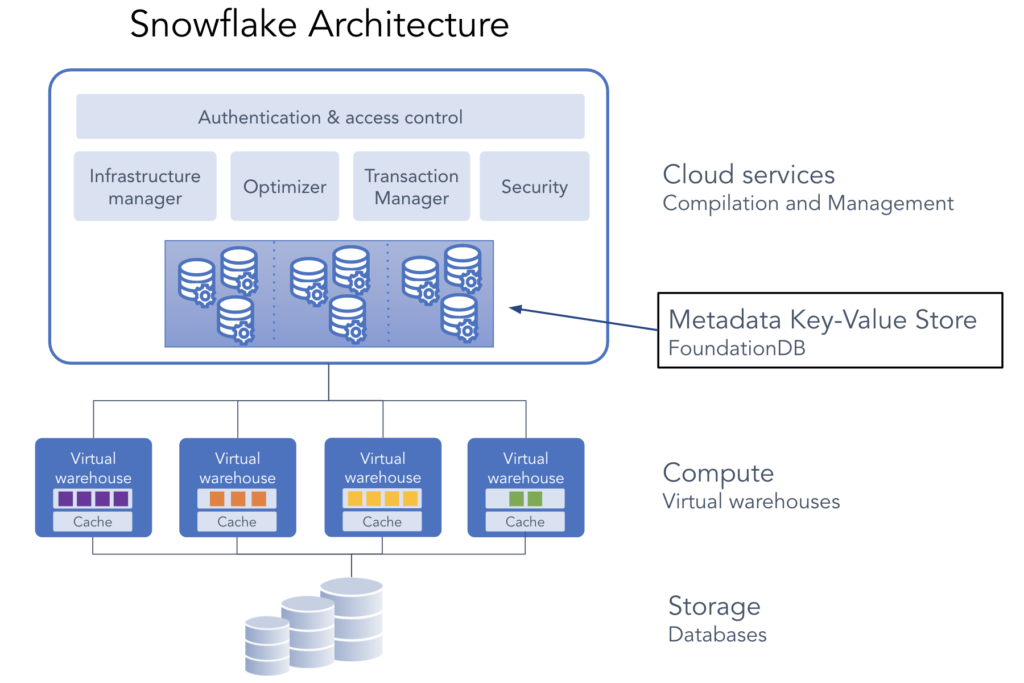
Snowflake’s unique architecture consists of three key layers:
Database Storage
When data is loaded into Snowflake, Snowflake reorganizes that data into its internal optimized, compressed, columnar format. Snowflake stores this optimized data in cloud storage.
Snowflake manages all aspects of how this data is stored - the organization, file size, structure, compression, metadata, statistics, and other aspects of data storage are handled by Snowflake. The data objects stored by Snowflake are not directly visible nor accessible by customers; they are only accessible through SQL query operations run using Snowflake.
Query Processing
Query execution is performed in the processing layer. Snowflake processes queries using “virtual warehouses”. Each virtual warehouse is an MPP compute cluster composed of multiple compute nodes allocated by Snowflake from a cloud provider.
Each virtual warehouse is an independent compute cluster that does not share compute resources with other virtual warehouses. As a result, each virtual warehouse has no impact on the performance of other virtual warehouses.
A virtual warehouse is essentially a set of resources (compute clusters) that are used to process queries. It can be scaled up or down based on the workload requirements. The concept of virtual warehouses contributes to workload isolation by allowing different workloads or user groups to have dedicated resources for their queries, preventing resource contention. It also aids optimization as you can allocate the appropriate amount of resources to meet the performance needs of specific tasks.
Cloud Services
The cloud services layer is a collection of services that coordinate activities across Snowflake. These services tie together all of the different components of Snowflake in order to process user requests, from login to query dispatch. The cloud services layer also runs on compute instances provisioned by Snowflake from the cloud provider.
Services managed in this layer include:
- Authentication
- Infrastructure management
- Metadata management
- Query parsing and optimization
- Access control
Metadata Layer
Snowflake efficiently manages metadata storage. Metadata, which includes information about tables, columns, and other database objects, is stored separately from the user data. This separation allows Snowflake to optimize metadata storage independently. All this metadata is stored in FoundationDB and is deployed when snowflake is provisioned
Multi-cluster, and how it is implemented in Snowflake for scalability?
In Snowflake, multi-cluster refers to the ability to have multiple virtual warehouses (compute clusters) that can be independently scaled up or down. Each virtual warehouse operates independently but can access the same underlying data stored in Snowflake's storage layer. This parallel processing capability allows for scalable and efficient query performance.
Snowflake Caching
1. Metadata Cache
- Object Definition
- Statistics
2. Result Cache
- Exact results from exact queries
- Last 24hrs
- Underlying data cannot have changed
- Functions like current time causes expiration
- User can be different but role must be same
3. Warehouse Cache
- Sometime called "Local", or "SSD", or "Data Cache"
- Contain Raw data from the table, not aggregated
- When warehouse is suspended, data is dropped/purged
- Can use partial data and go deeper for remaining
4. Centralized Storage
- Long term storage, database and tables, remote
Links
Key Concepts & Architecture | Snowflake Documentation