Sharding / Replication
Sharding
Sharding is a method for distributing data across multiple machines.
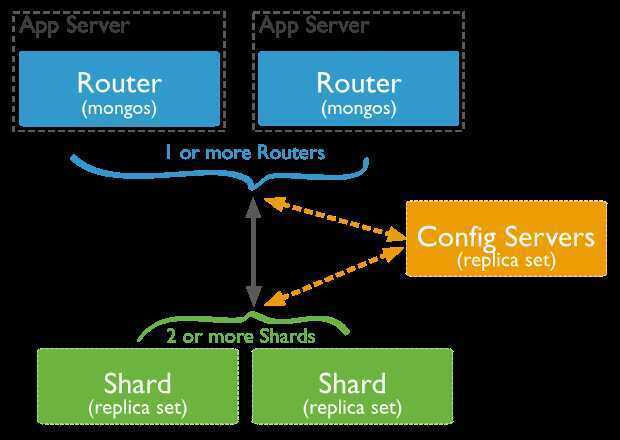
Sharded Cluster
A MongoDB sharded cluster consists of the following components:
- shard: Each shard contains a subset of the sharded data. Each shard can be deployed as a replica set.
- mongos: The
mongosacts as a query router, providing an interface between client applications and the sharded cluster. Starting in MongoDB 4.4,mongoscan support hedged reads to minimize latencies. - config servers: Config servers store metadata and configuration settings for the cluster.
Hedged Reads
Starting in version 4.4, mongos instances can hedge reads that use non-primary read preferences. With hedged reads, the mongos instances route read operations to two replica set members per each queried shard and return results from the first respondent per shard. The additional read sent to hedge the read operation uses the maxTimeMS value of maxTimeMSForHedgedReads.
Shard Key / Chunks / Balancer
- MongoDB shards data at the collection level, distributing the collection data across the shards in the cluster.
- MongoDB uses the shard key to distribute the collection's documents across shards. The shard key consists of a field or multiple fields in the documents.
- MongoDB partitions sharded data into chunks. Each chunk has an inclusive lower and exclusive upper range based on the shard key.
- In an attempt to achieve an even distribution of data across all shards in the cluster, a balancer runs in the background to migrate ranges across the shards.
- You must connect to a mongos router to interact with any collection in the sharded cluster. This includes sharded and unsharded collections. Clients should never connect to a single shard in order to perform read or write operations.
Sharding Strategy
- Hashed Sharding involves computing a hash of the shard key field's value. Each chunk is then assigned a range based on the hashed shard key values.
- Ranged sharding involves dividing data into ranges based on the shard key values. Each chunk is then assigned a range based on the shard key values.
Replication
MongoDB achieves replication by the use of replica set. A replica set is a group of mongod instances that host the same data set. In a replica, one node is primary node that receives all write operations. All other instances, such as secondaries, apply operations from the primary so that they have the same data set. Replica set can have only one primary node.
rs.status()
db.setProfilingLevel()
Troubleshoot Replica Sets - MongoDB Manual
Sharding vs Replicasets
Replica sets focus on high availability and fault tolerance by replicating data across multiple nodes, while sharding aims at horizontal scaling by distributing data across multiple shards to handle larger datasets and higher workloads. Combining replica sets within shards in a sharded cluster allows for a comprehensive solution that addresses both availability and scalability requirements.
Can replica set members handle read queries in mongodb?
Replica set members in MongoDB can handle read queries. MongoDB allows for different read preferences, which determine from which members of a replica set clients can read data. The primary and secondary members of a replica set can be involved in handling read operations. Here are the key points:
Primary Node
- The primary node in a MongoDB replica set is the node that receives all write operations. It is also the default node for read operations.
- All write operations, as well as the default read operations, are directed to the primary node.
- The primary node is the most up-to-date member in terms of data because it receives all writes first.
Secondary Nodes
- Secondary nodes in a replica set contain copies of the data from the primary node, and they replicate data asynchronously.
- Clients can direct read operations to secondary nodes by specifying a read preference other than the default "primary" preference.
- Read preferences include options like "primaryPreferred," "secondary," "secondaryPreferred," and others. These preferences allow you to control from which members clients read data.
Read Preferences
- The choice of read preference depends on the application's requirements for consistency, availability, and latency.
- For example, if read consistency is crucial, you might direct all reads to the primary node using the "primary" read preference. If you can tolerate reading potentially stale data, you can distribute read operations across secondary nodes using preferences like "secondary" or "secondaryPreferred."
MongoDB - Replication and Sharding - GeeksforGeeks
Data Distribution: Sharding and Partitioning in MongoDB | by Dayanand Thombare | Medium