Intro
A vector database is a specialized DBMS that stores vector embeddings utilizing innovative techniques for storage, indexing, and query processing. They offer data management capabilities, such as CRUD and language bindings to widely used data science languages such as Python, SQL, Java, and Tensorflow. Additionally, they deliver advanced features such as high-speed ingestion, sharding, and replication.
Vector databases are designed to handle critical query and algorithmic styles seen in similarity search, anomaly search, observability, fraud detection, and IoT sensor analytics. Such emerging styles are the outcome of digital transformation and the rise of generative AI.
A Vector Database is a specialized database designed to store, index, and search high-dimensional vectors—numerical representations of data like text, images, audio, or code.
These vectors are typically produced by AI models and encode the semantic meaning of content.
Traditional databases (SQL, NoSQL) work well with exact values, strings, or simple filters. But they fail when you want to do semantic similarity search—e.g., finding:
- "Articles similar to this one"
- "Products like this"
A Vector DB lets you find "closest meaning" instead of exact keyword matches by using Approximate Nearest Neighbor (ANN) search algorithms.
A Comprehensive Guide to Vector Databases - KDB.AI
A Fun & Absurd Introduction to Vector Databases • Alexander Chatzizacharias • GOTO 2024 - YouTube
Databases
- pinecone
- LanceDB
- Epsilla
- Welcome | Weaviate - Vector Database
- PostgresML: Leveraging Postgres as a Vector Database for AI
- Learn Vector Database in 10 Mins - Hottest AI Apps DB!
- What Are Vector Databases? | MongoDB
- Chroma - the AI-native open-source embedding database
- GitHub - milvus-io/milvus: A cloud-native vector database, storage for next generation AI applications
- Qdrant - Vector Database - Qdrant
- GitHub - kuzudb/kuzu: Embedded property graph database built for speed. Vector search and full-text search built in. Implements Cypher.
Working
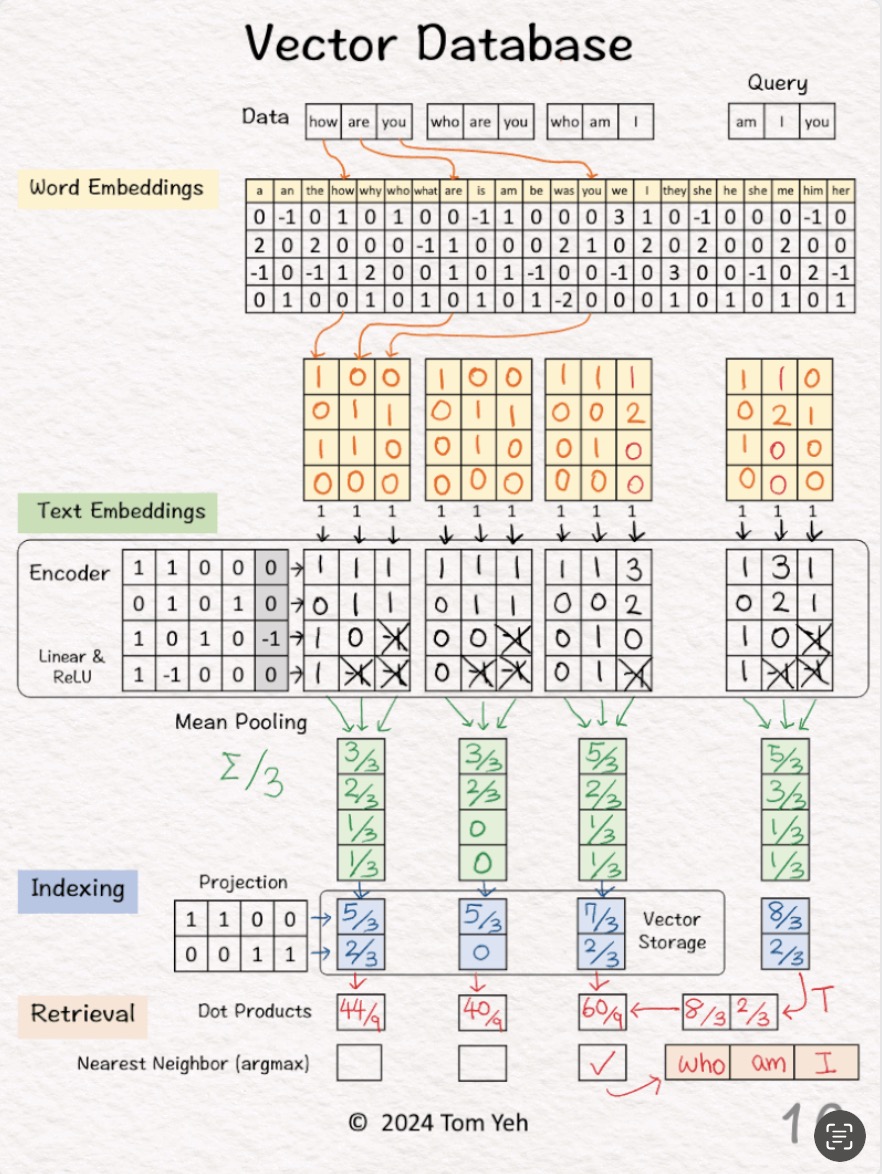
Links
- Key considerations when choosing a database for your generative AI applications | AWS Database Blog
- InterviewReady | System Design Course | Gaurav Sen

- Graph Database - https://lnkd.in/dRGBGSxe
- Vector Database - https://lnkd.in/d93DKJqg
- Inverted Index - https://lnkd.in/dmwVF2BD
- Sharding - https://lnkd.in/d8Tyu9FW
- Multi-tenancy - https://lnkd.in/dCianKsc
- Relational Database - https://lnkd.in/d3Jhq7xn