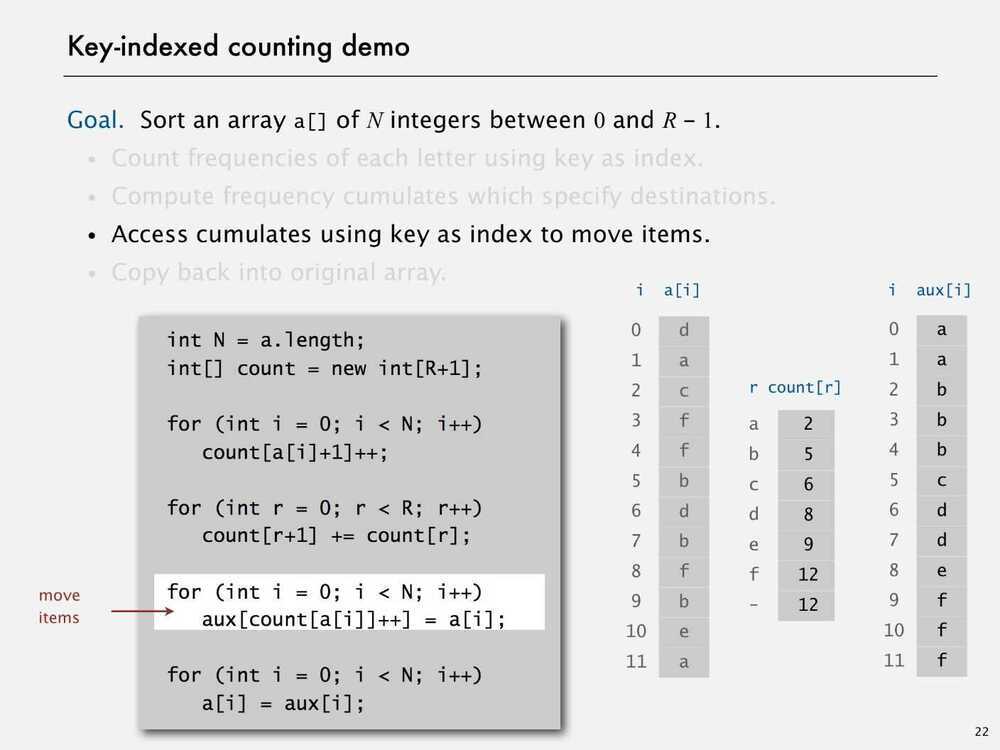
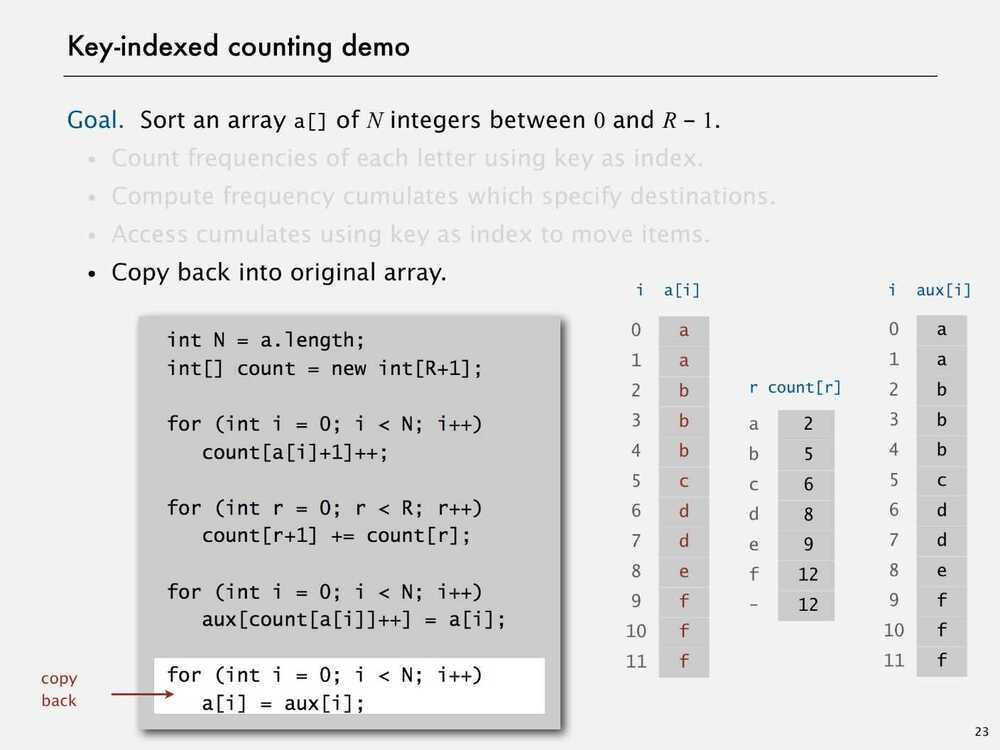
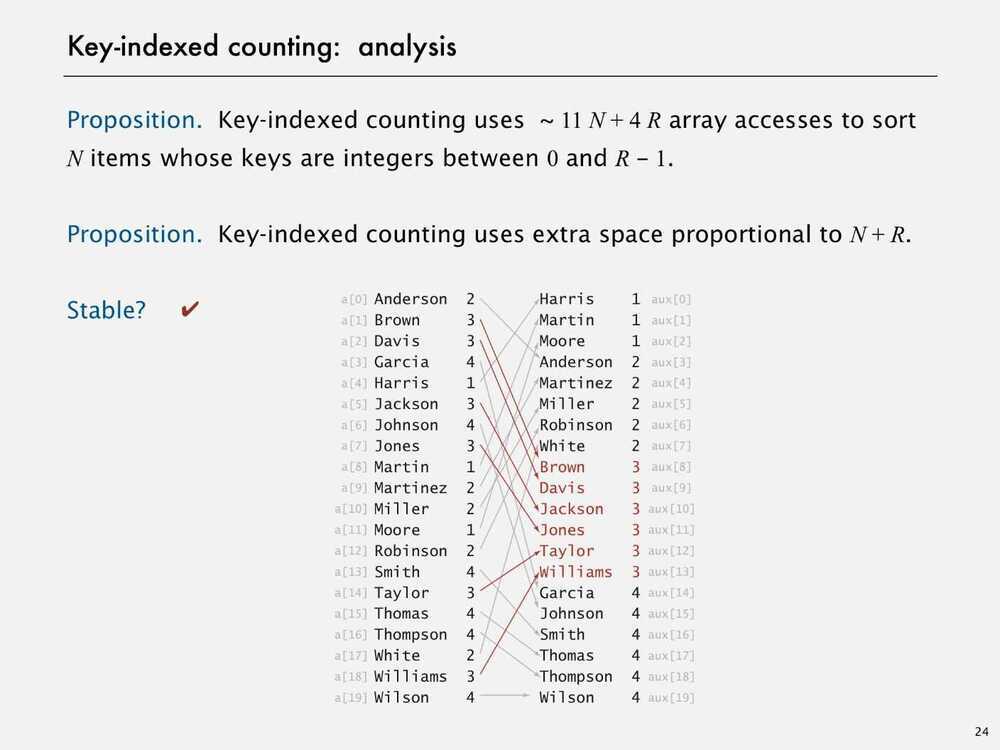
Key-indexed Counting
Proporties
- Linear time algorithm for sorting
- Stable
Key-Indexed Counting
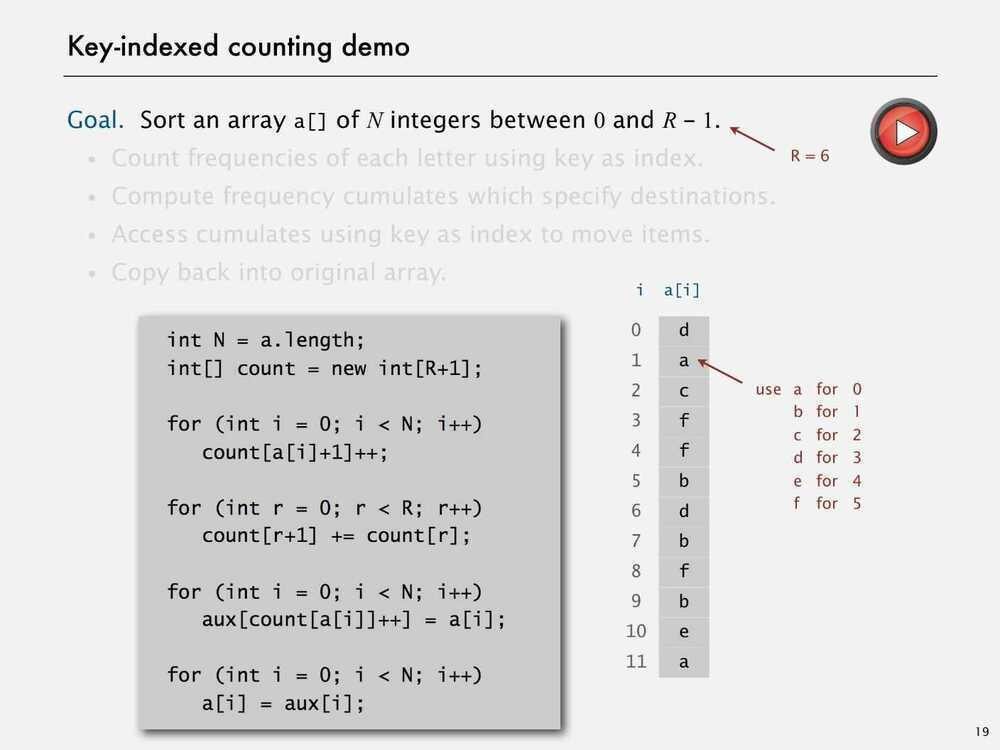
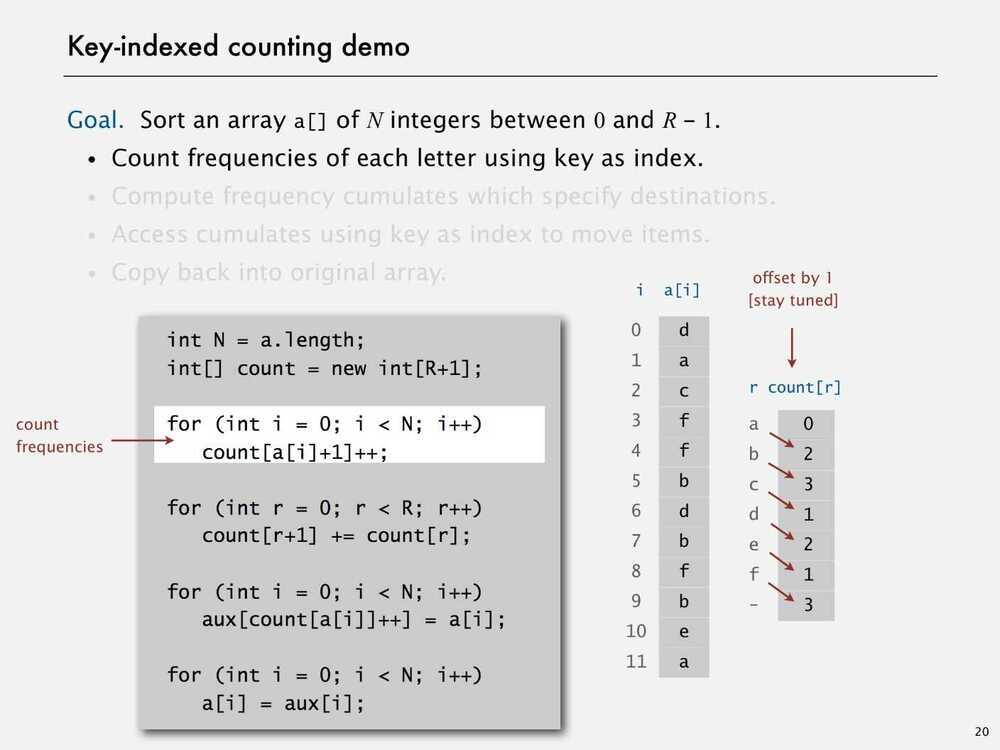
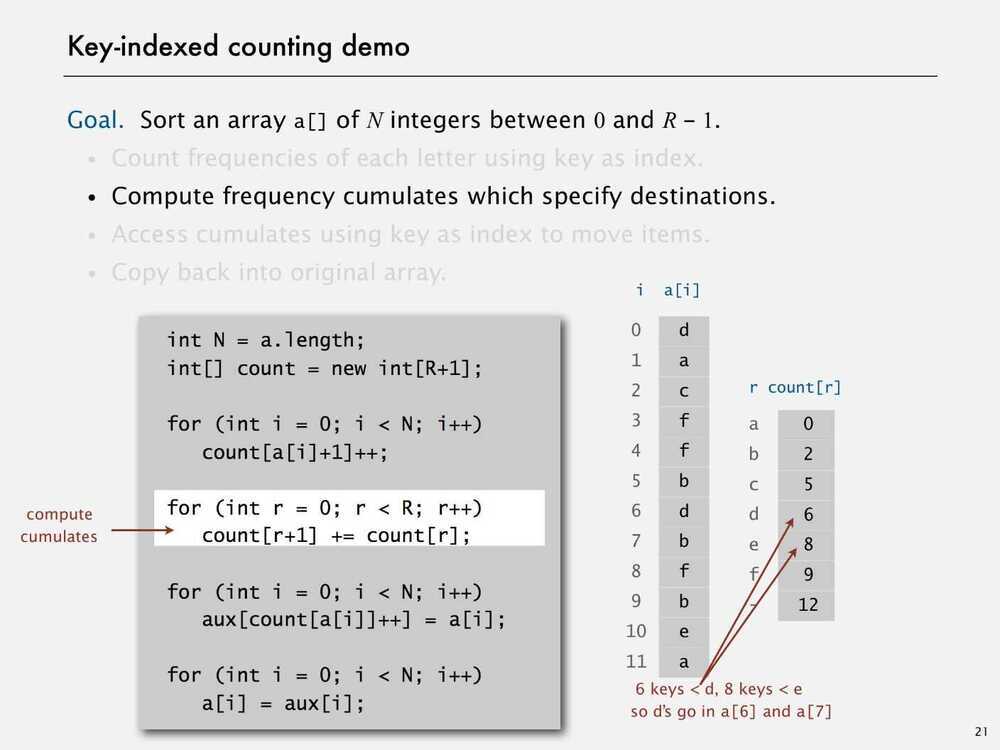
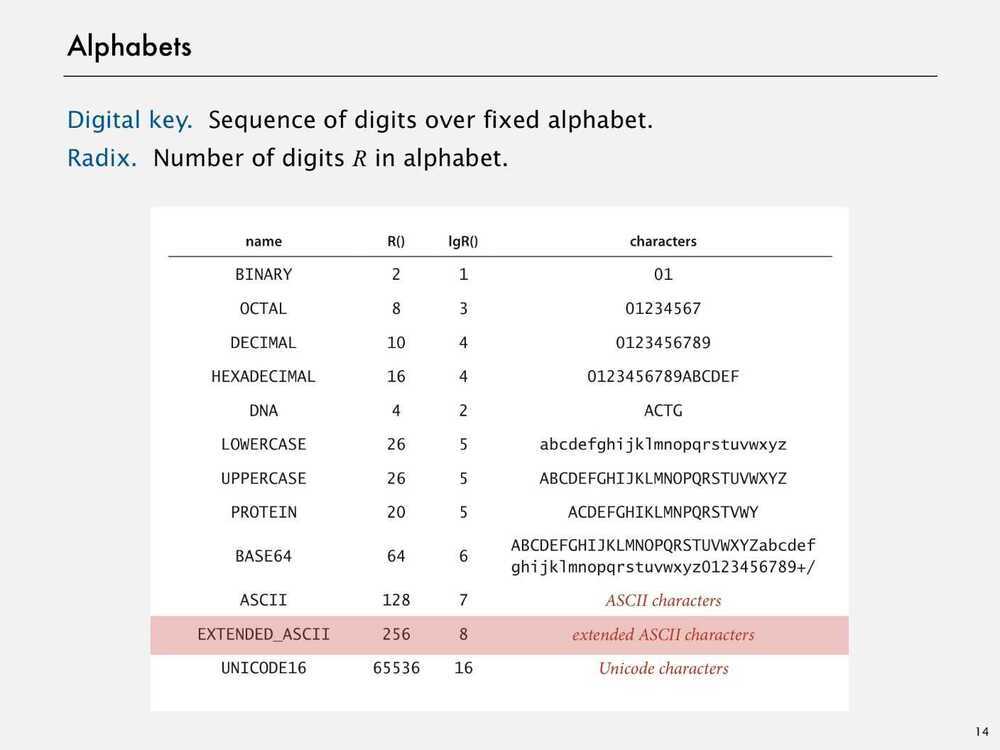
Assumption - Keys are integers between 0 and R-1
Implication - Can use key as an array index
Applications
- Sort string by first letter.
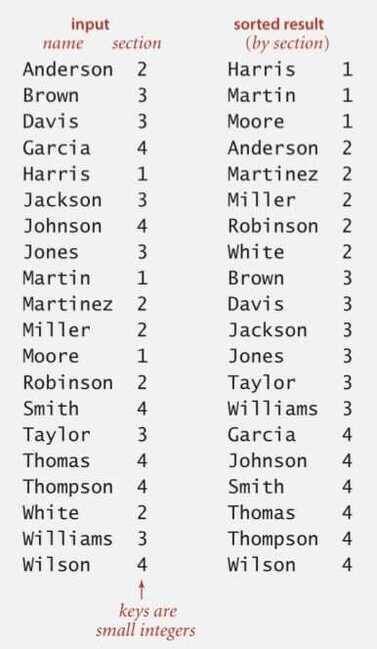
- Sort class roster by section.
- Sort phone numbers by area code.
- Subroutine in a sorting algorithm.
Remarks - Keys may have associated data => can't just count up number of keys of each value (because we have to transfer the data as well)