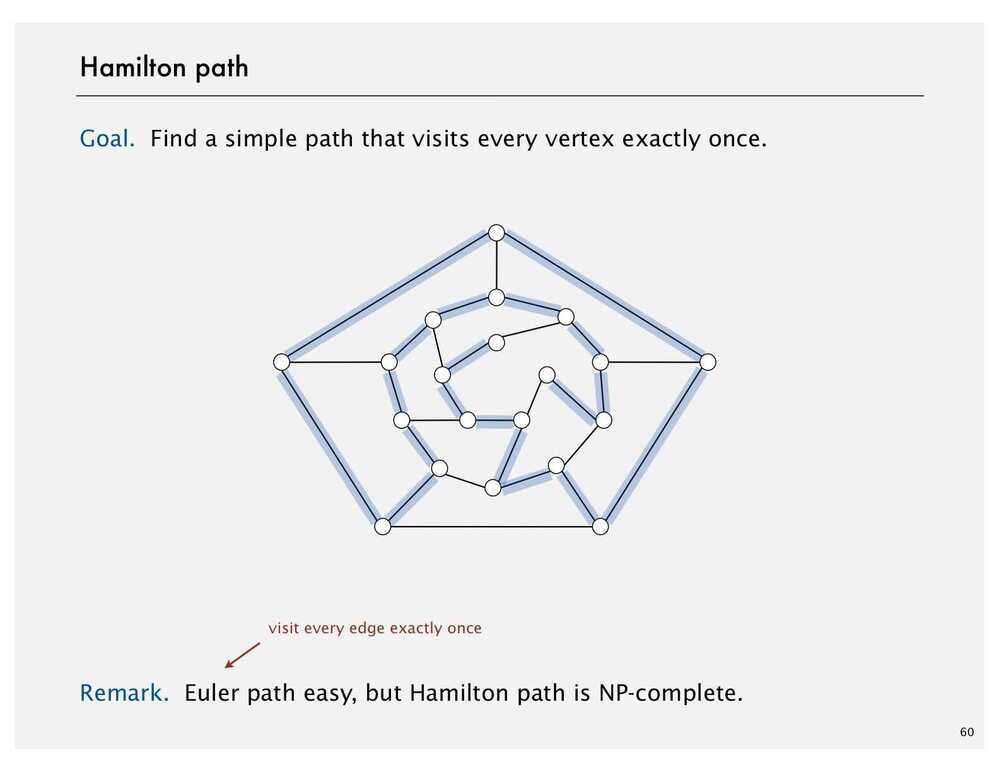
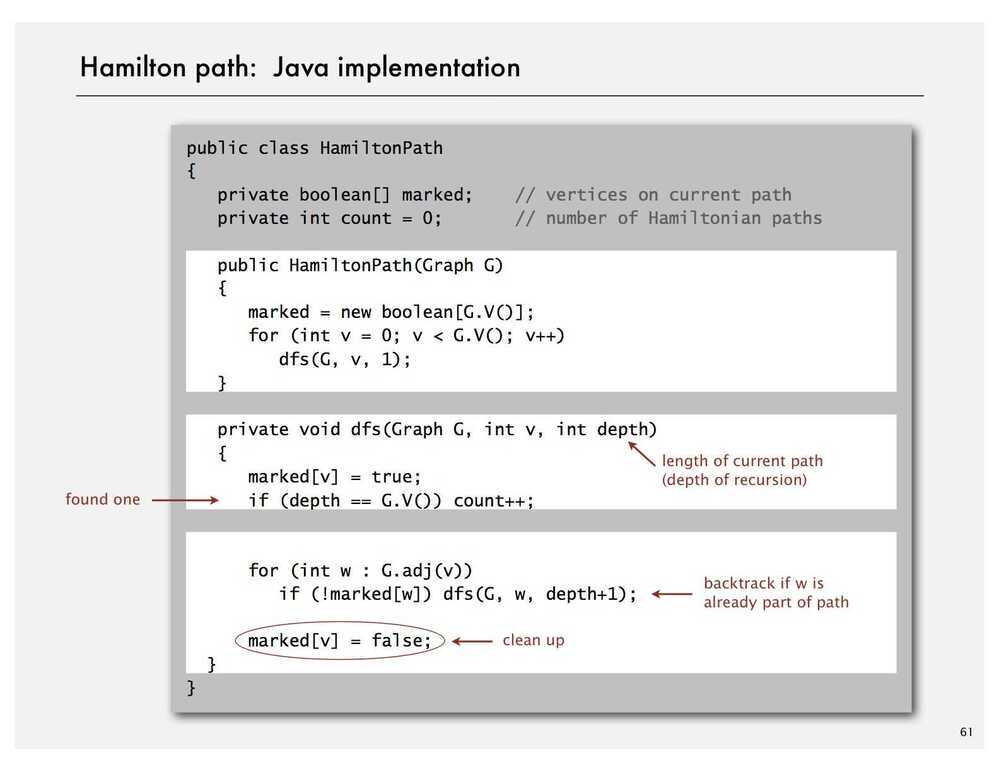
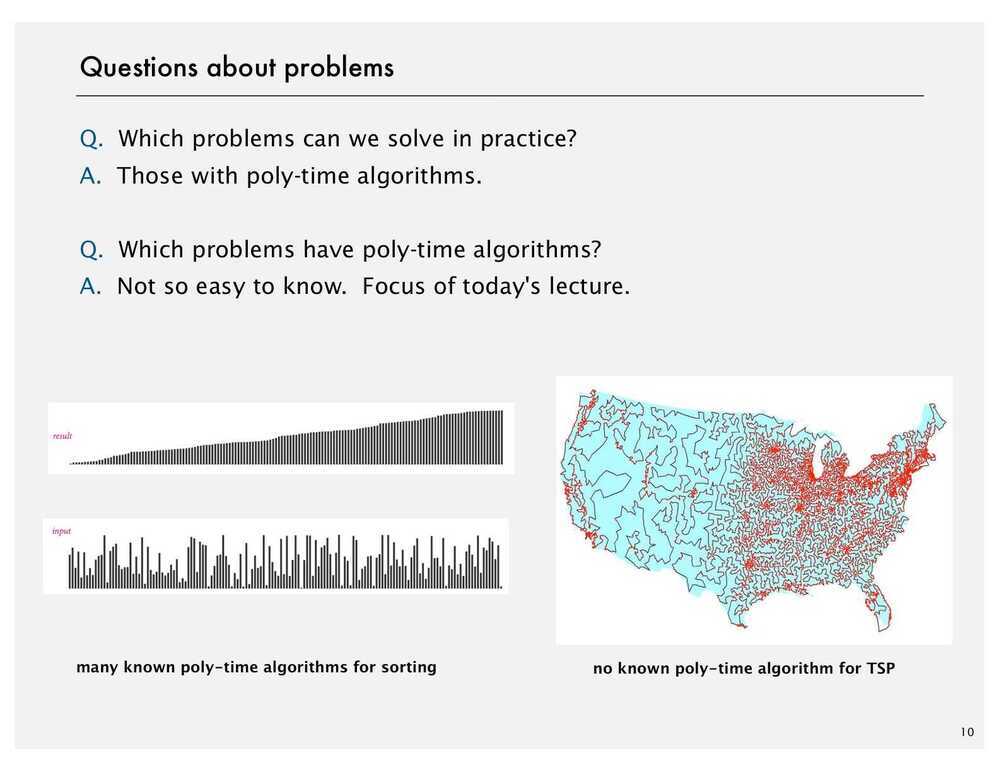
Intractability
Is there a universal problem-solving model to which all problems that we would like to solve reduce and for which we know an efficient algorithm? You may be surprised to learn that we do not know the answer to this question. In this lecture we introduce the complexity classes P, NP, and NP-complete, pose the famous P = NP question, and consider implications in the context of algorithms that we have treated in this course.

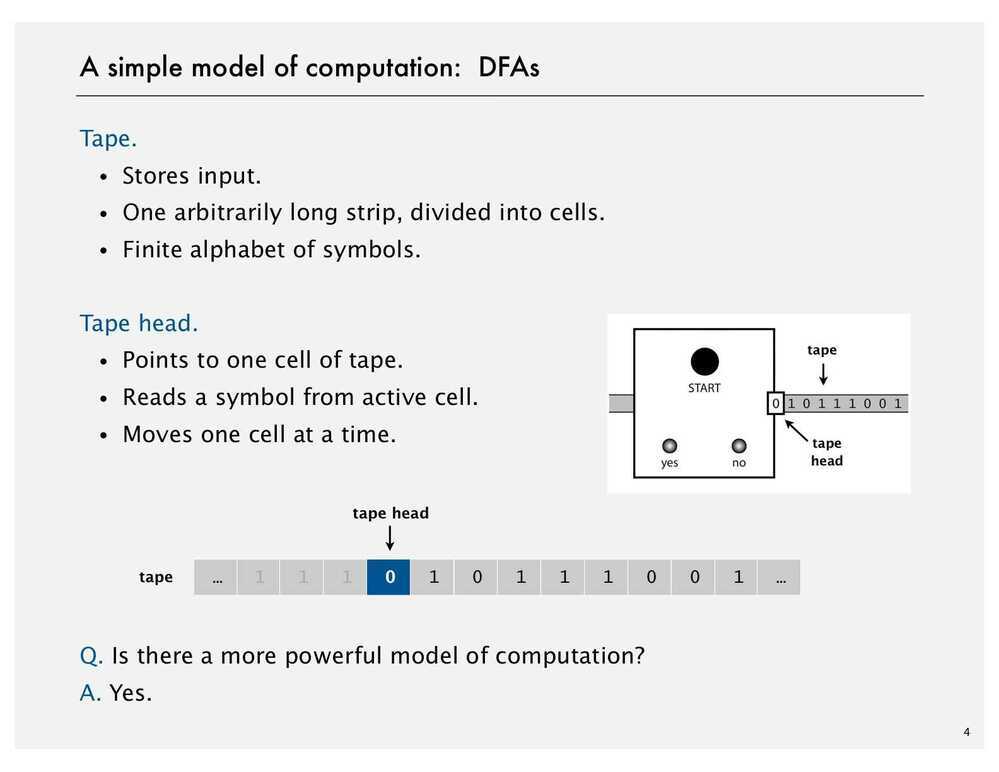
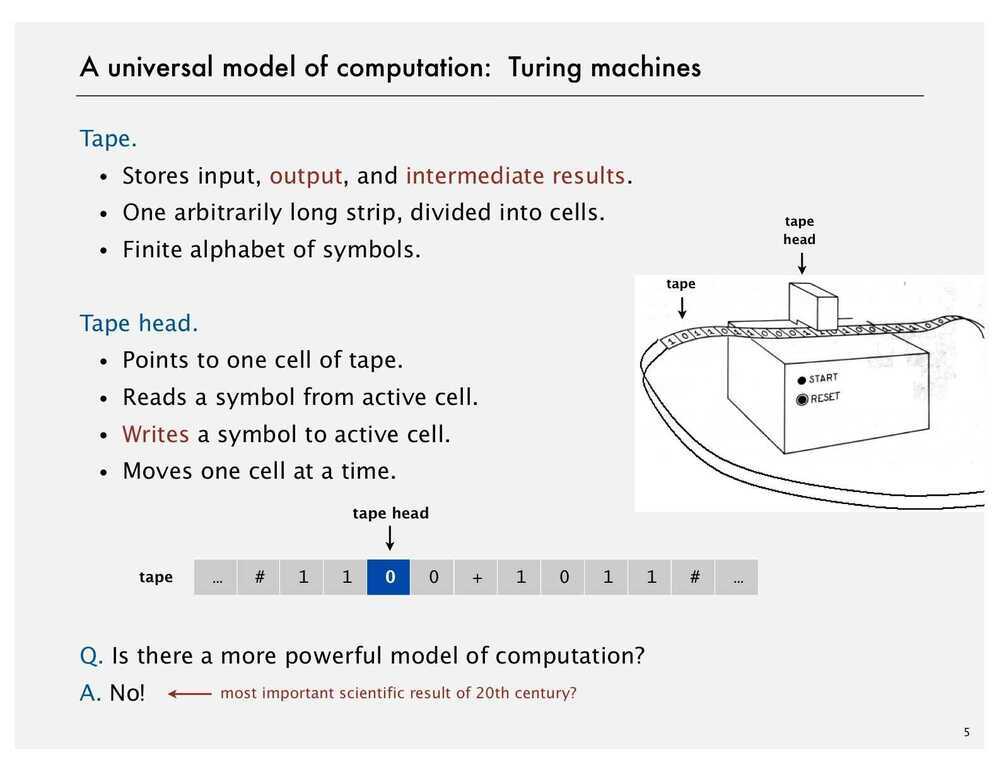
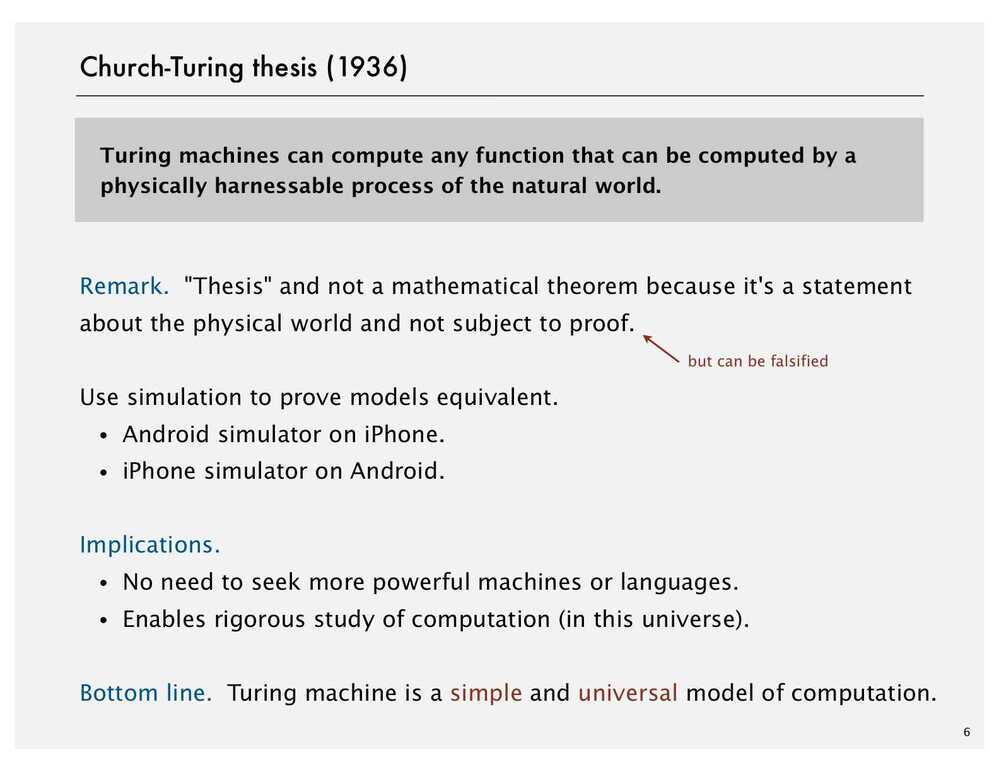
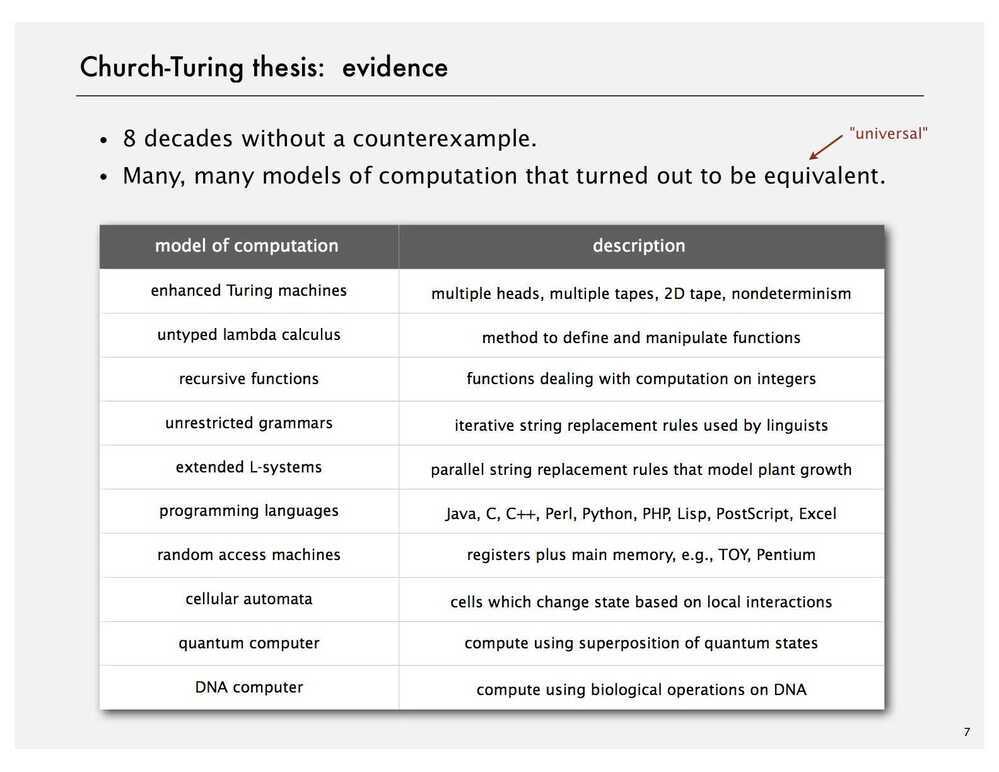
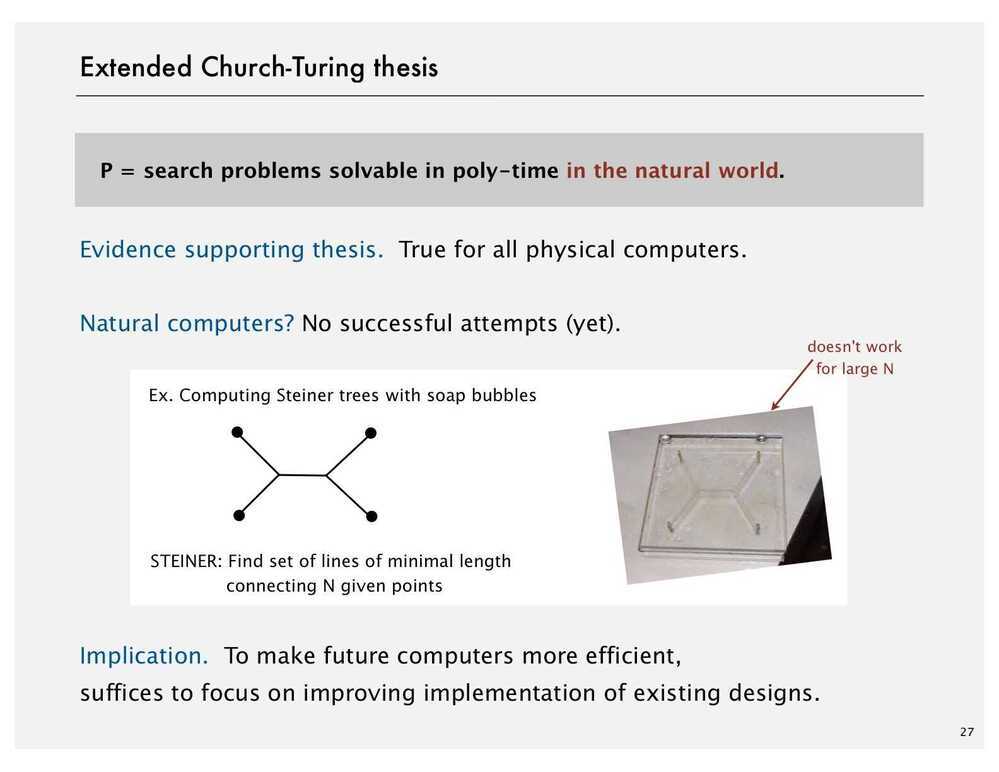
Church-Turing Thesis (Computability Thesis)
Church-Turing Thesis is a hypothesis about the nature of computable functions. It states that a function on the natural numbers is computable by a human being following an algorithm, ignoring resource limitation, if and only if it is computable by a Turing machine

Intractable - hard to control or deal with (difficult or stubborn)

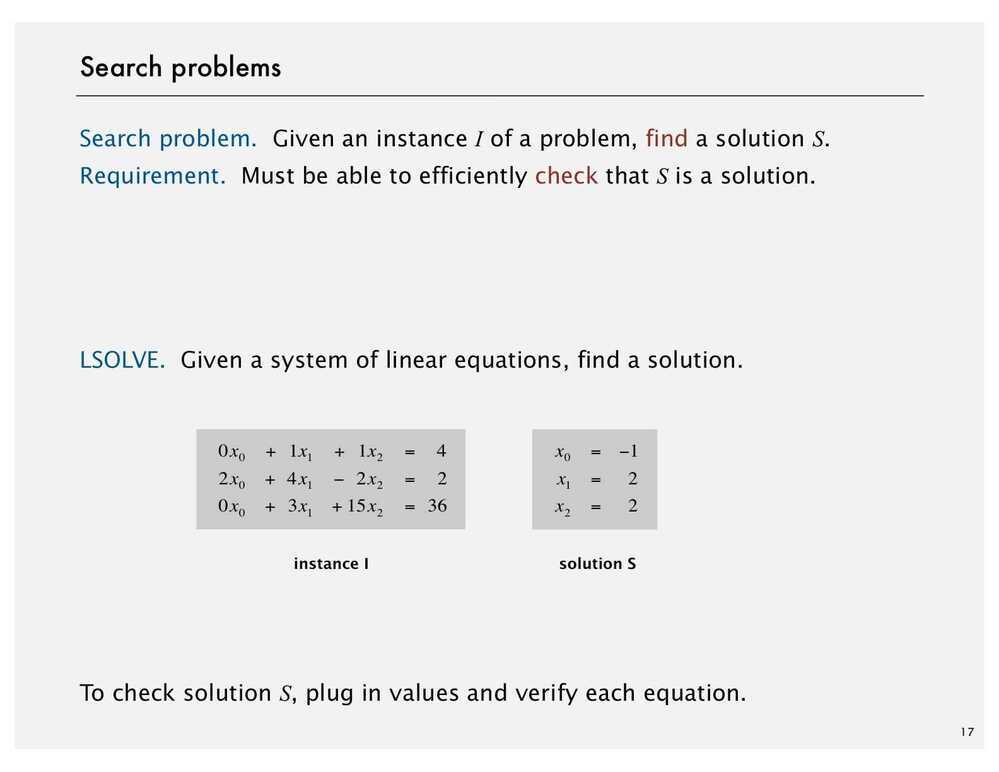
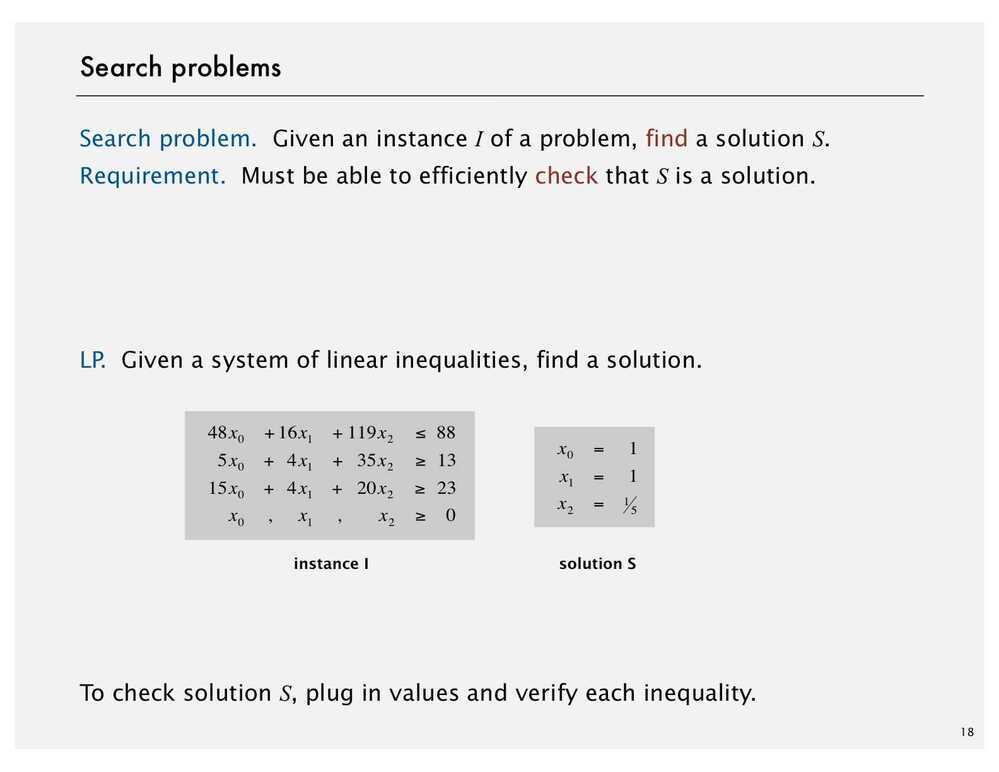
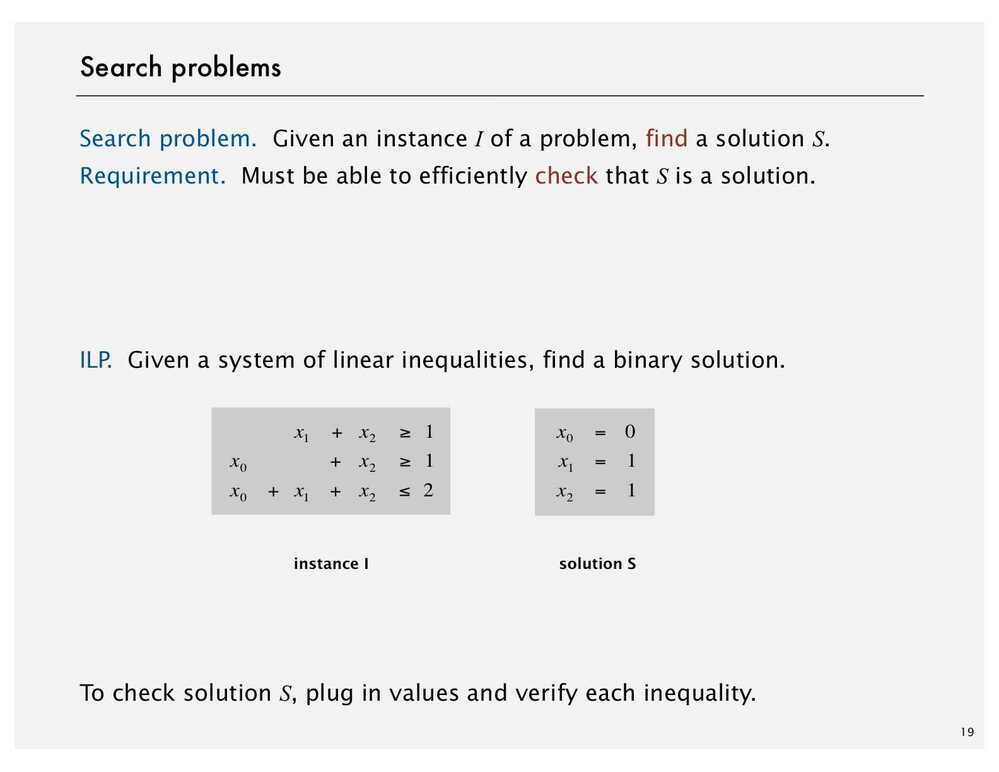
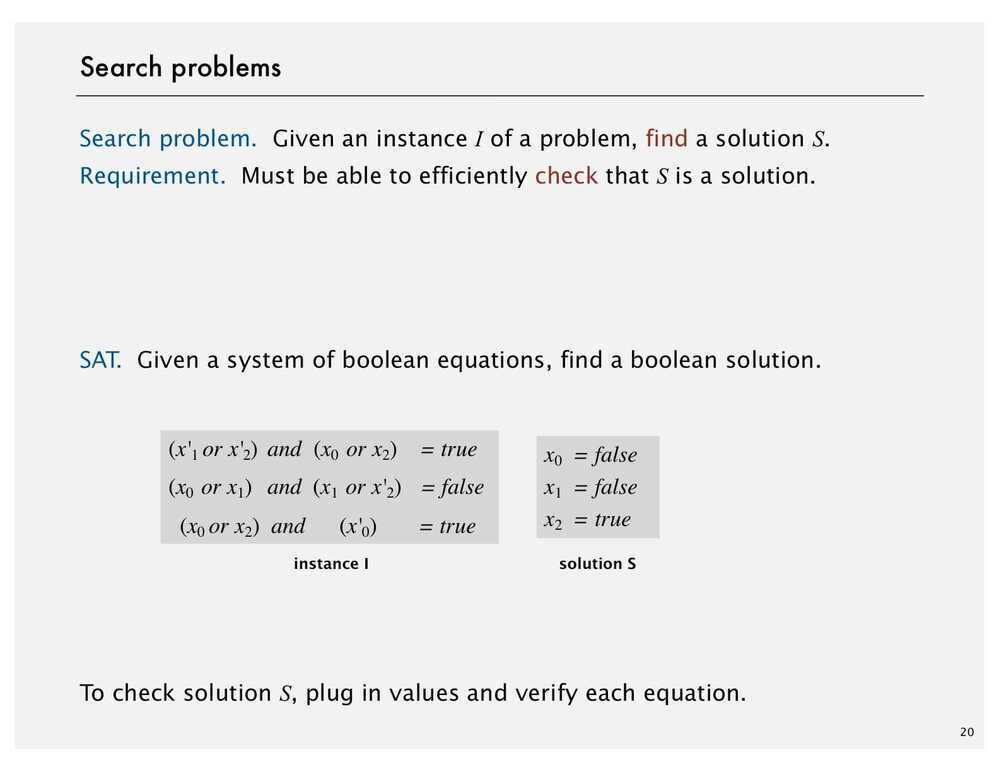
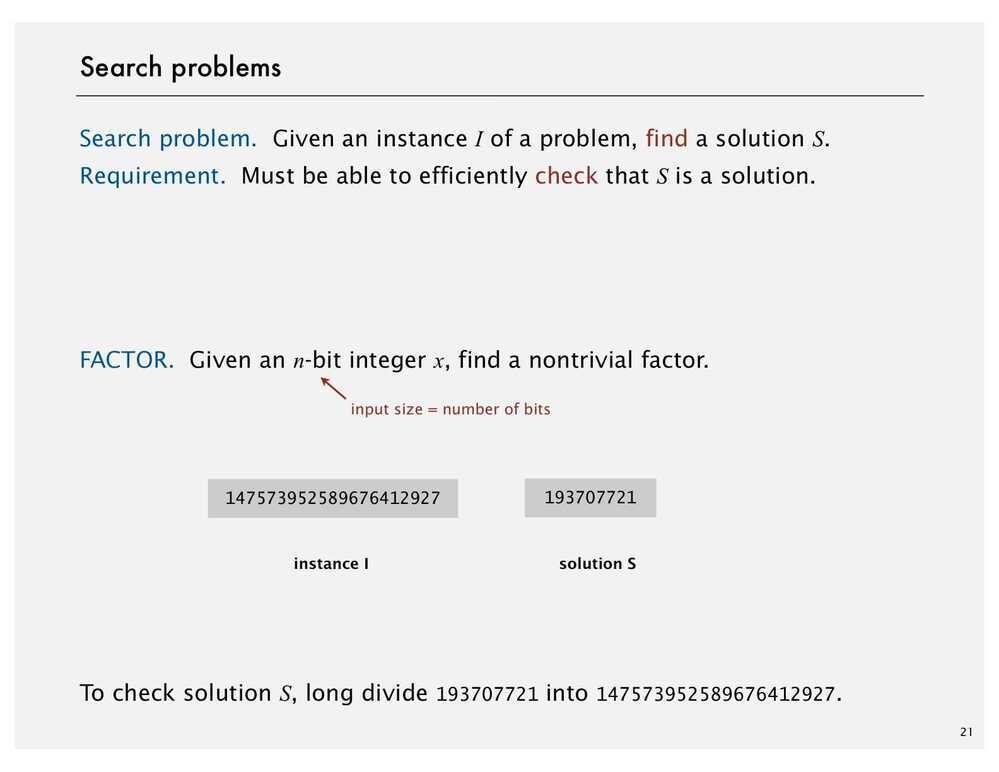
Search Problems
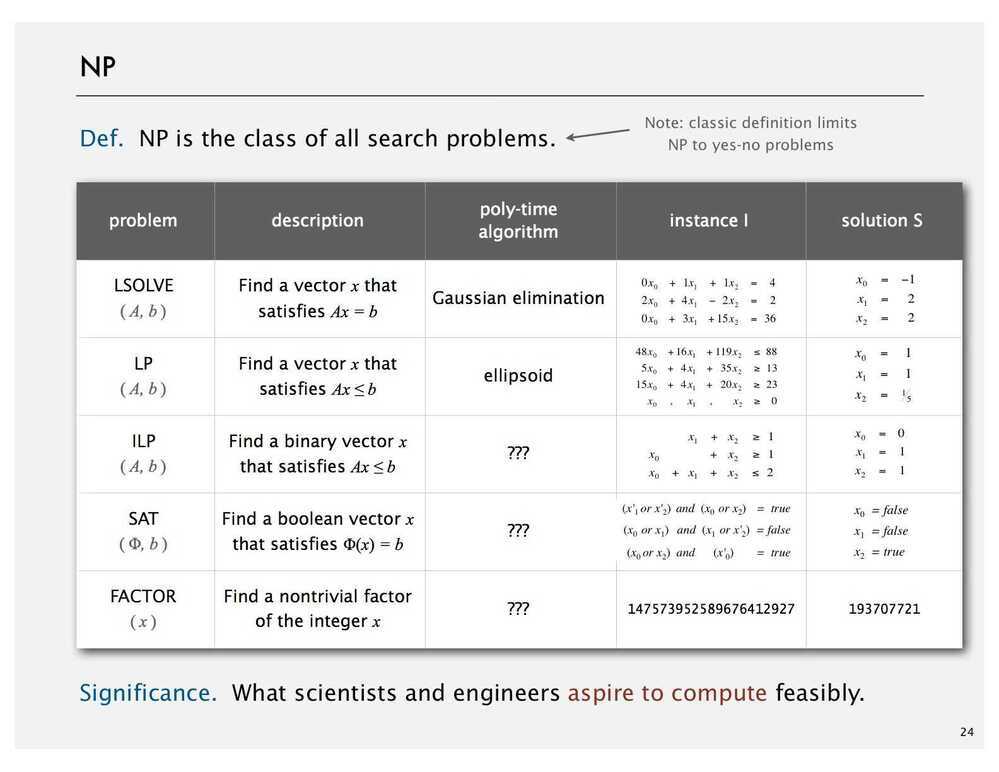
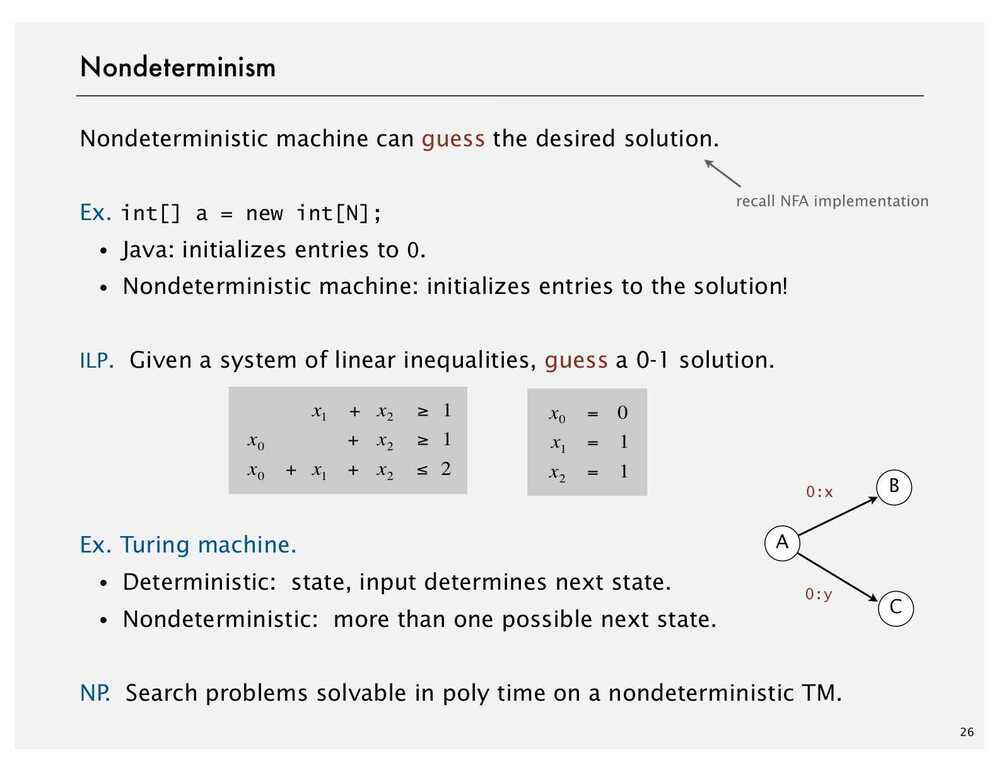
ILP - Integer Linear Programming
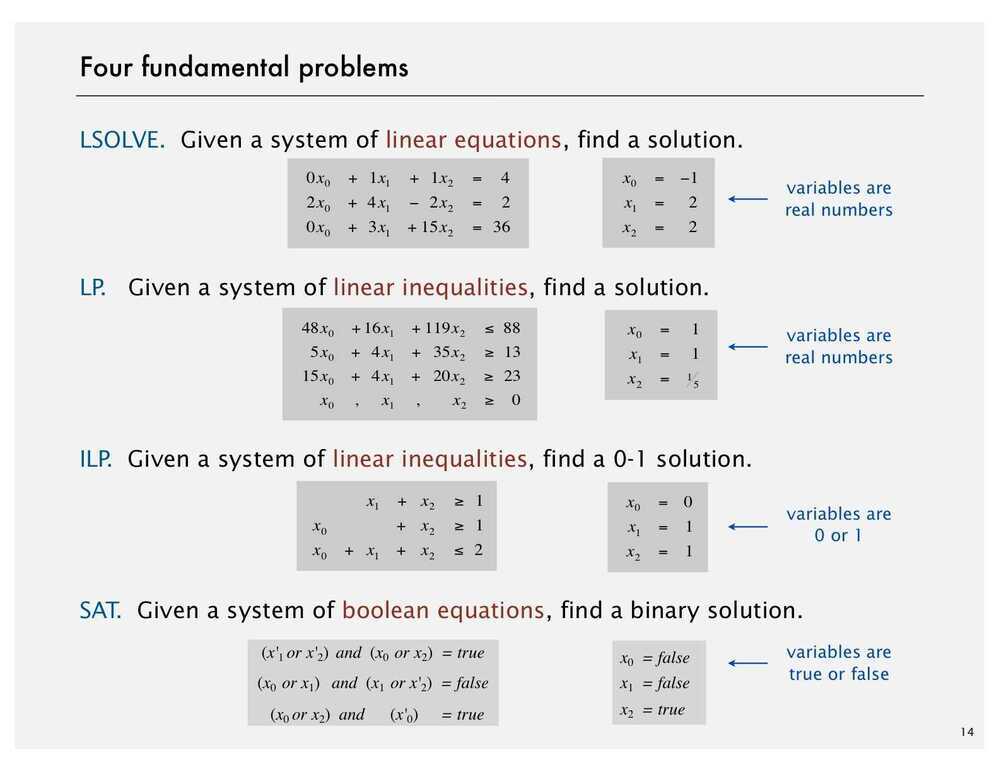
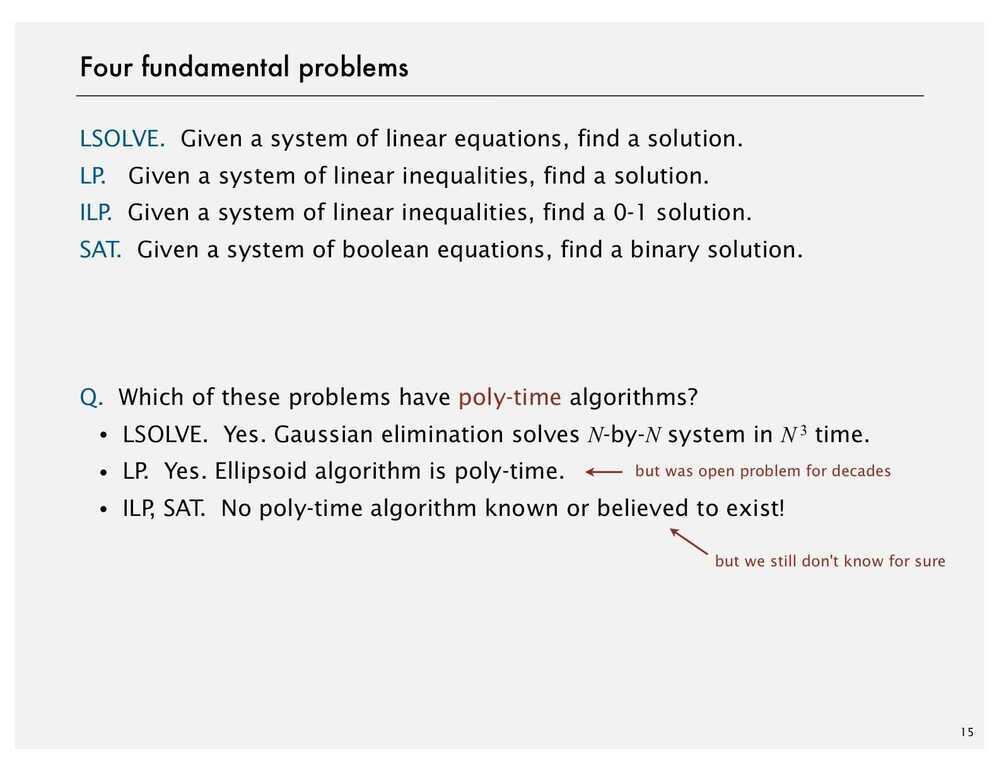
Aninteger programmingproblem is a mathematical optimization or feasibility program in which some or all of the variables are restricted to be integers. In many settings the term refers tointeger linear programming(ILP), in which the objective function and the constraints (other than the integer constraints) are linear.
Integer programming is NP-complete. In particular, the special case of 0-1 integer linear programming, in which unknowns are binary, and only the restrictions must be satisfied, is one of Karp's 21 NP-complete problems.
If some decision variables are not discrete the problem is known as amixed-integer programmingproblem.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Integer_programming
https://www.toptal.com/algorithms/mixed-integer-programming

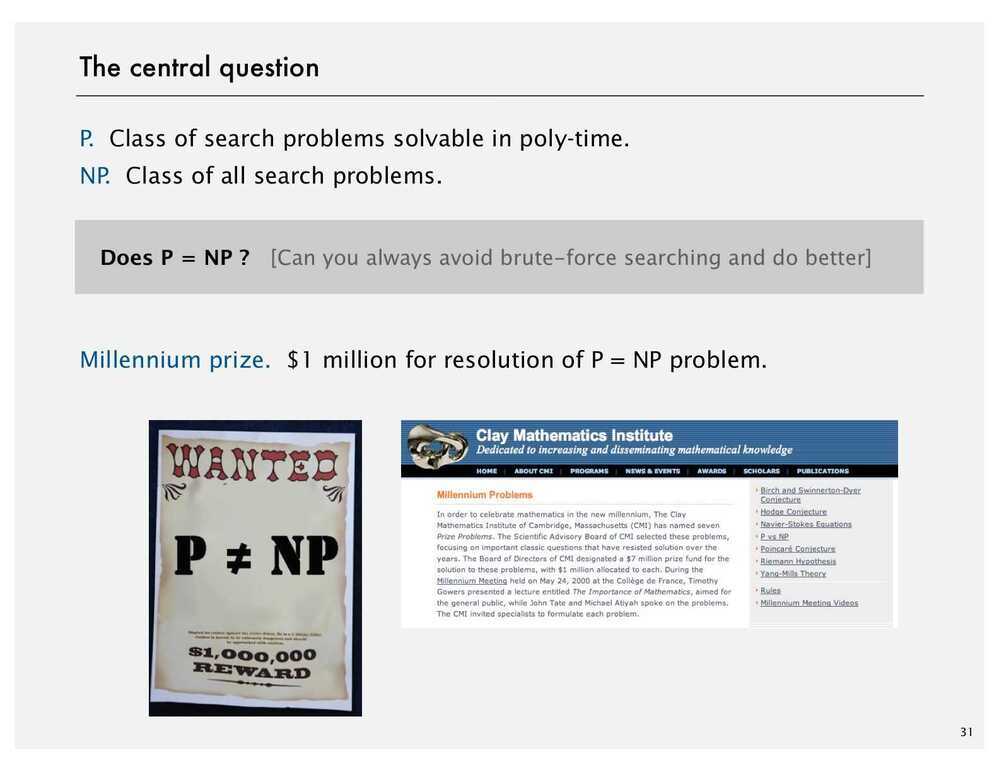
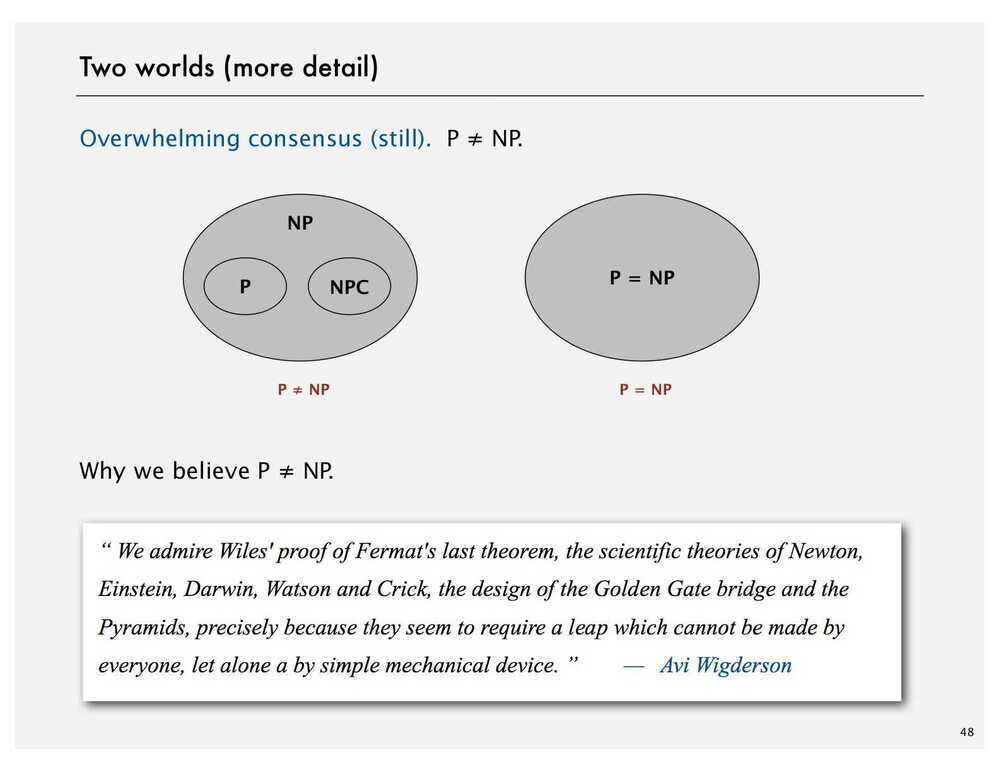
P vs NP
NP - Non Deterministic Polynomial Time (The complexity class NPcontains all of the problems inP - it is often incorrectly ascribed to mean "not polynomial time.")
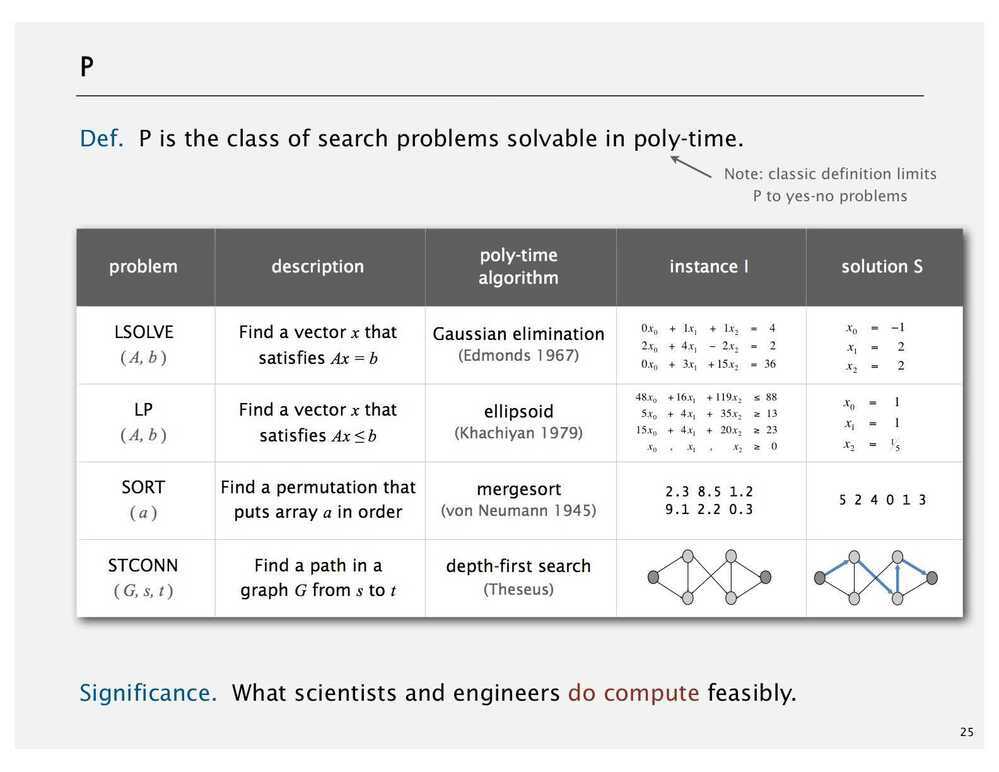



Classifying Problems
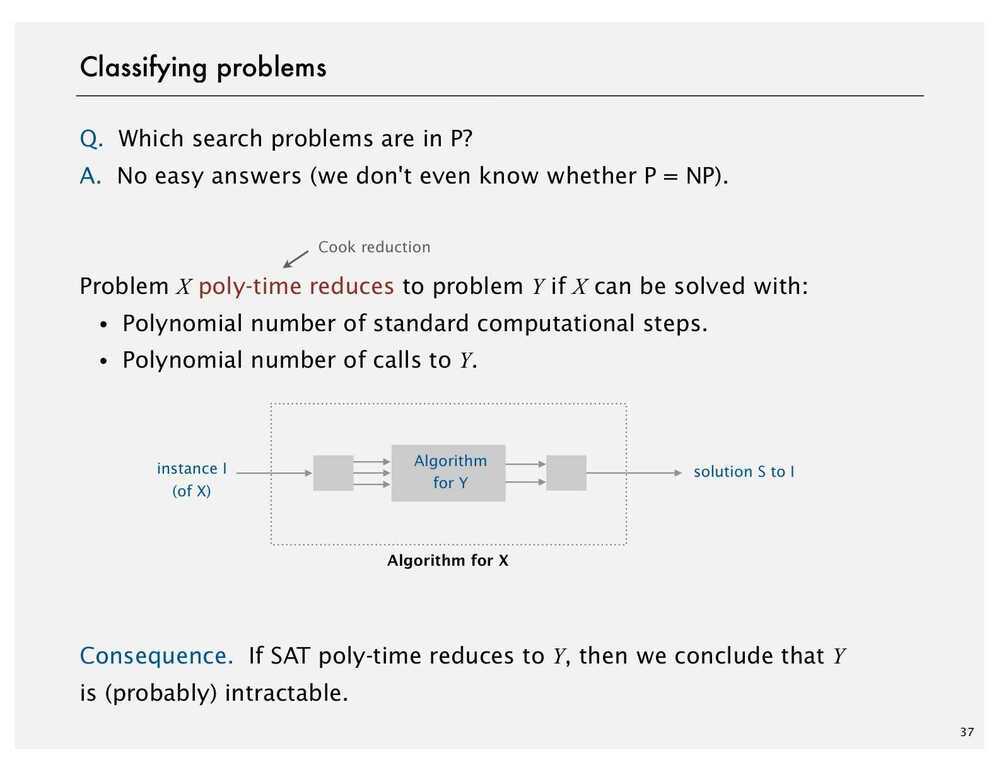
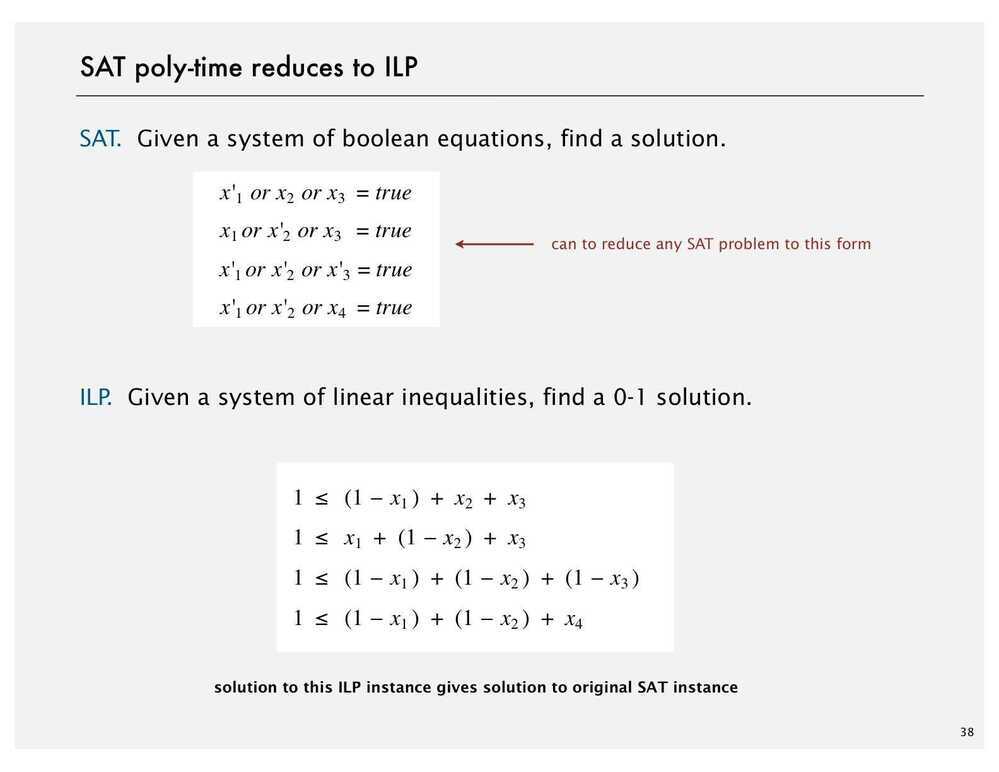
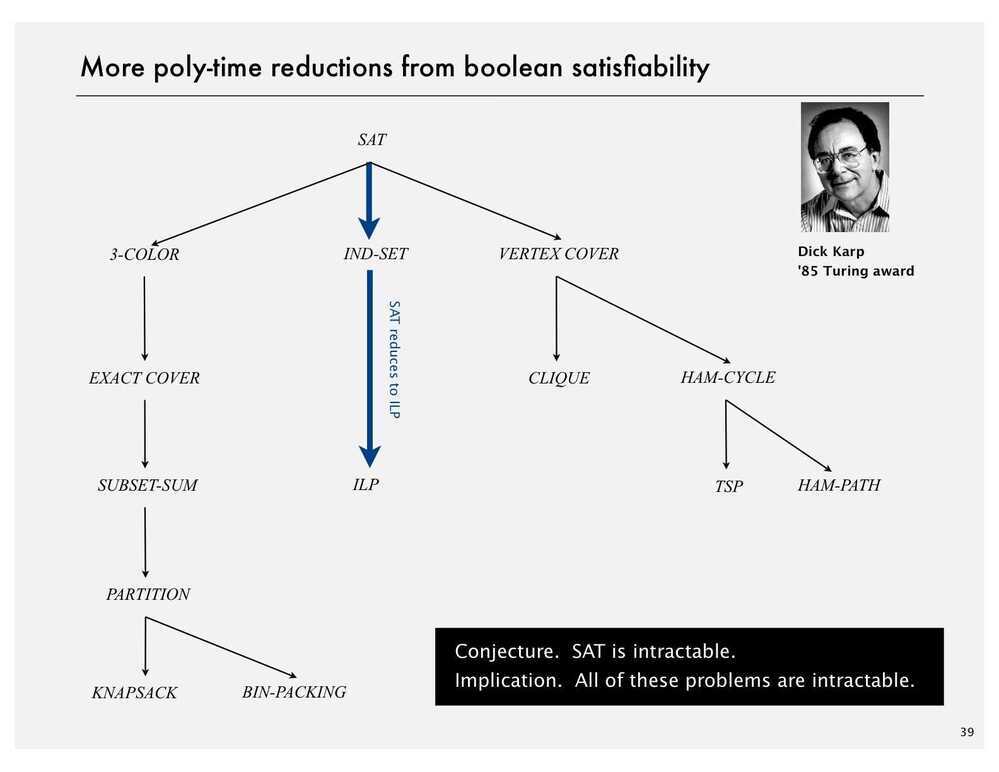

https://sahandsaba.com/understanding-sat-by-implementing-a-simple-sat-solver-in-python.html
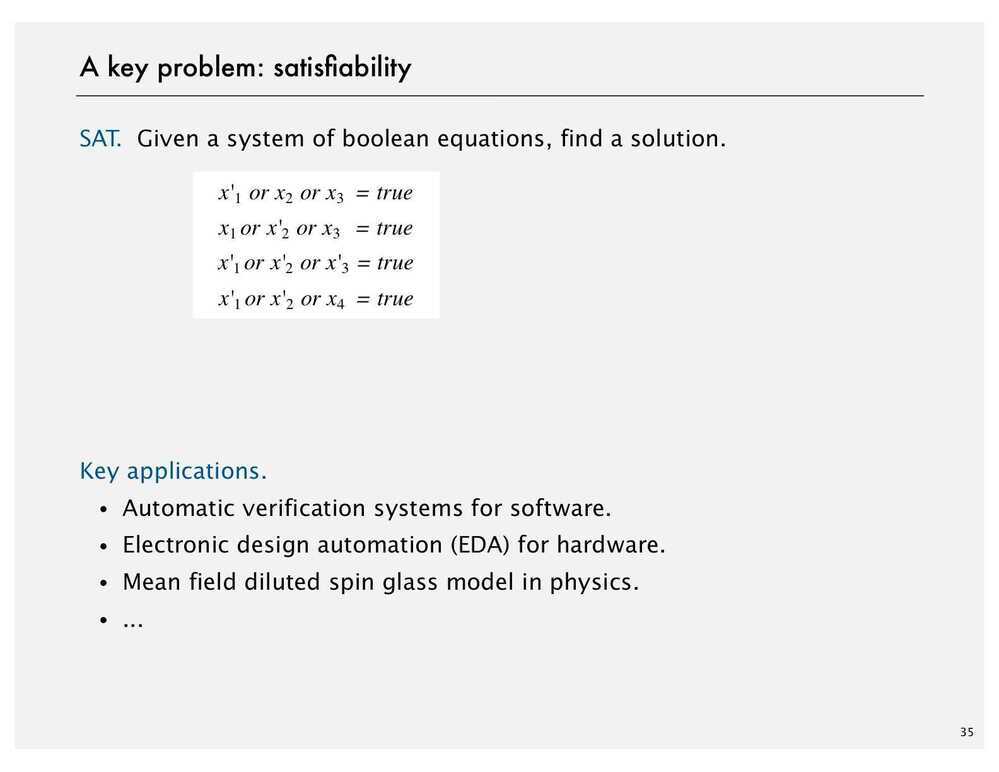
NP-completeness
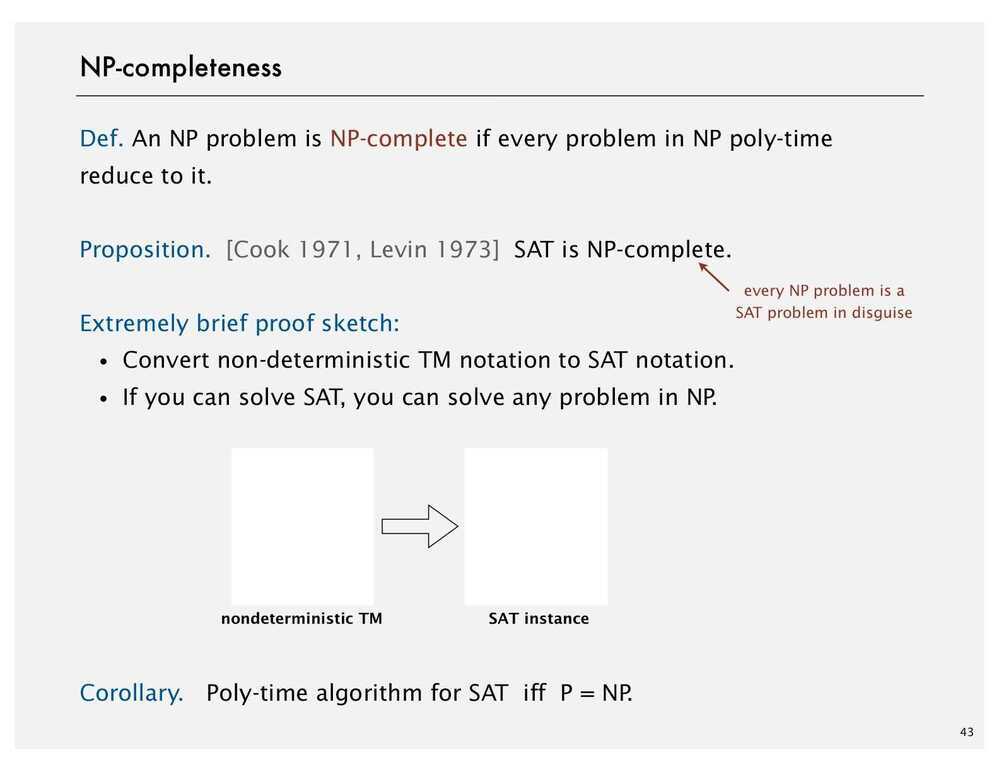
Cook - Levin Theorem
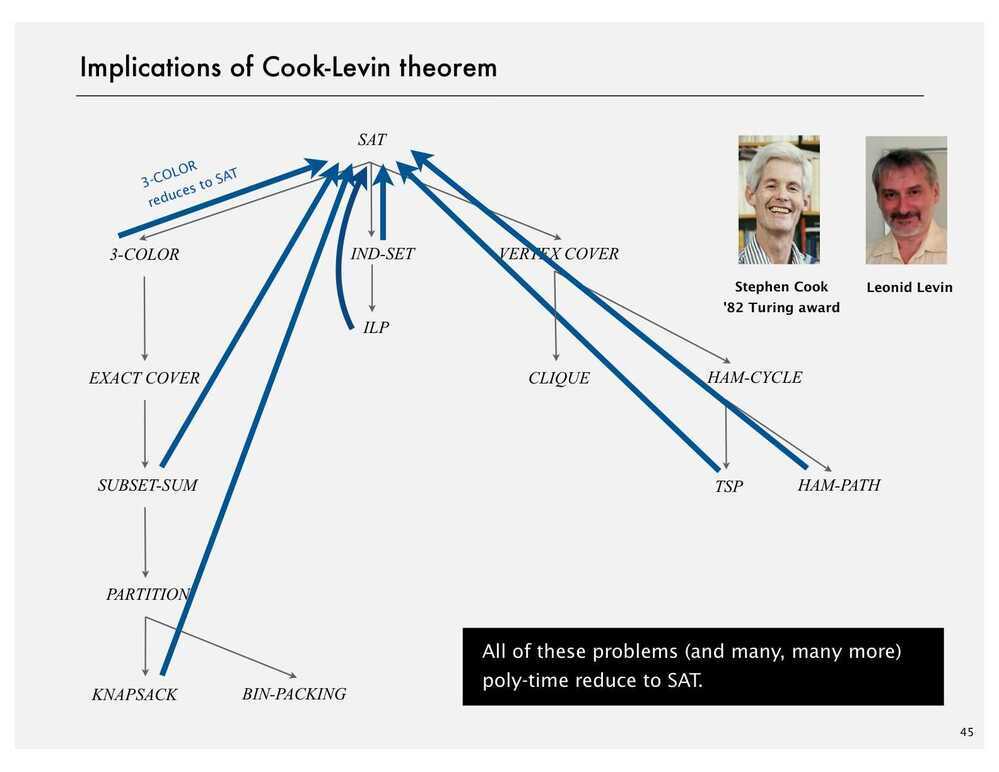
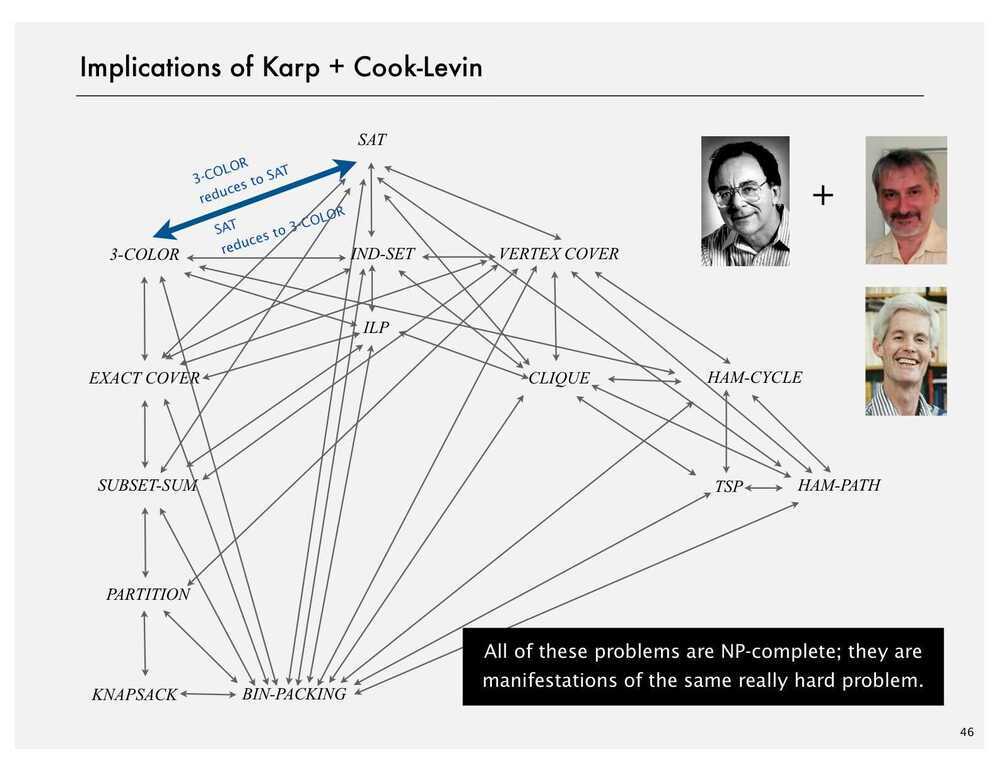
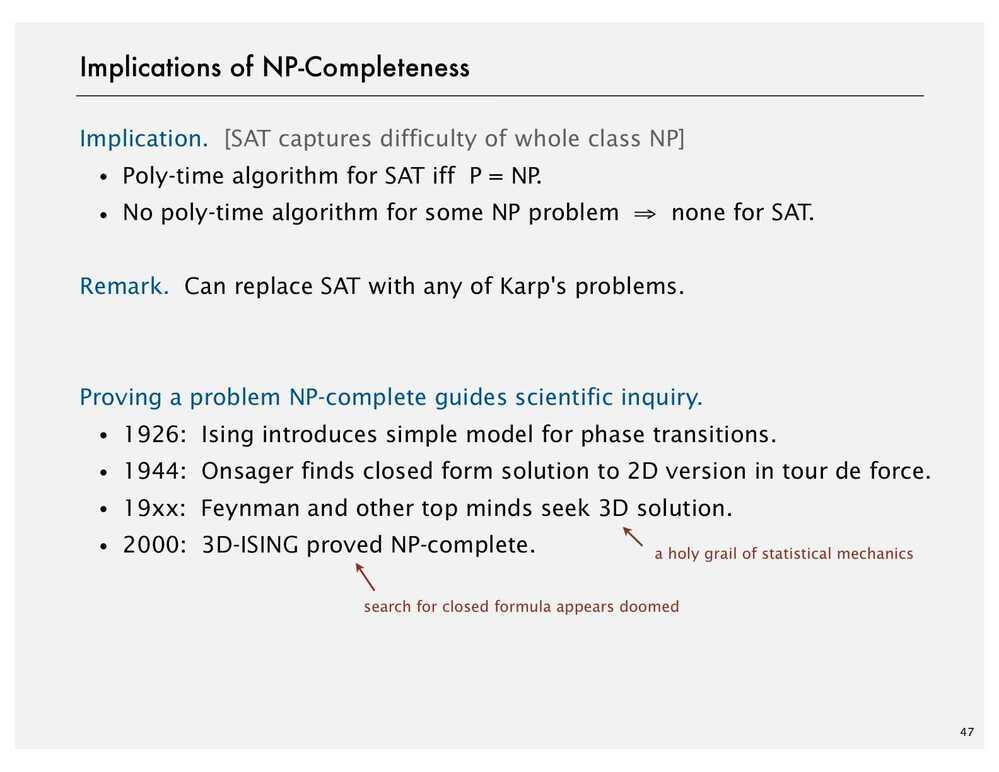
In computational complexity theory, theCook--Levin theorem, also known as Cook's theorem, states that the Boolean satisfiability problem is NP-complete. That is, any problem in NP can be reduced in polynomial time by a deterministic Turing machine to the problem of determining whether a Boolean formula is satisfiable.
An important consequence of this theorem is that if there exists a deterministic polynomial time algorithm for solving Boolean satisfiability, then every NP problem can be solved by a deterministic polynomial time algorithm.

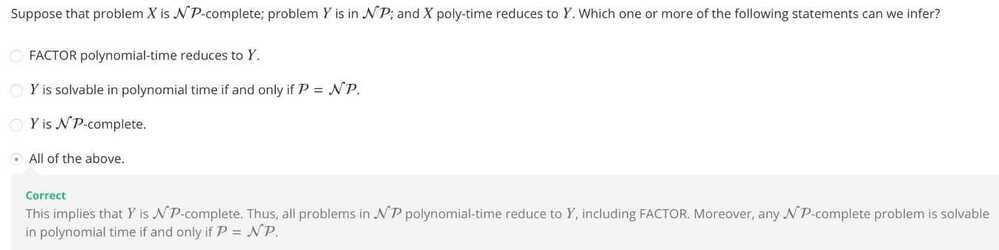
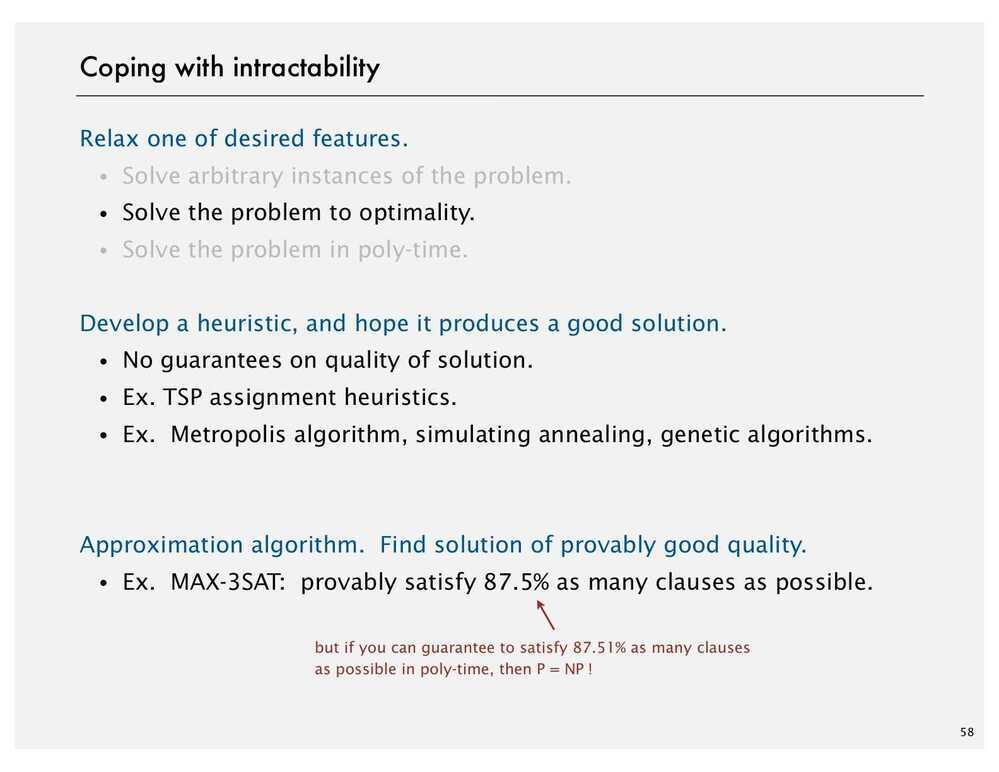
Coping with intractability