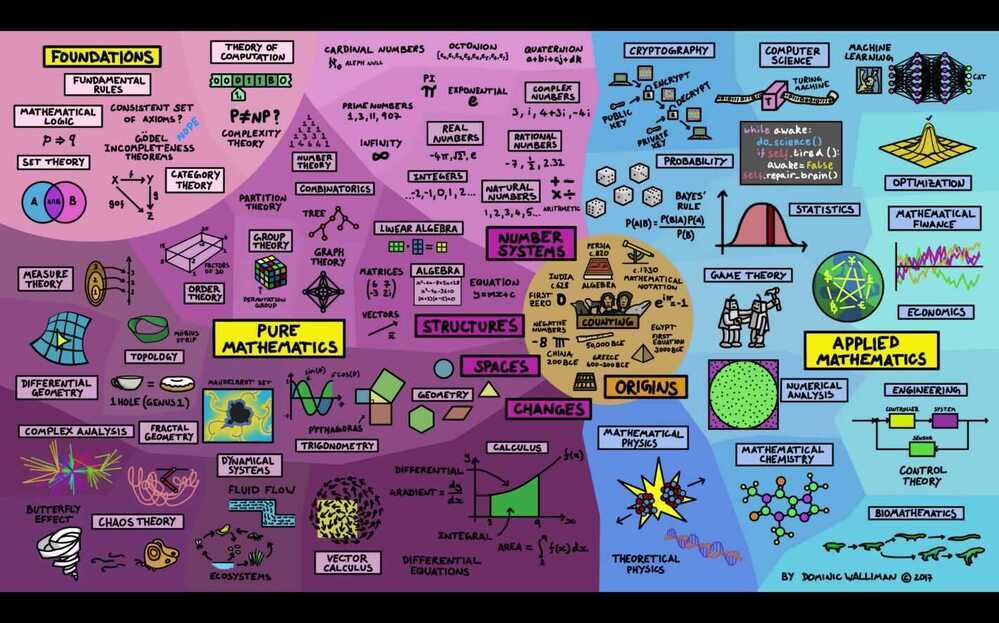
Mathematics
- Mahematics General
- Geometry
- Algebra
- Linear Algebra
- Statistics
- Probability
- Combinatorics
- Calculus
- Aptitude
Outline
Foundation which underlies mathematic logic and the rest of mathematics. It tries to formalize valid reasoning. It attempts to define what constitutes a proof.- Intuitionistic logic
Study of algebraic structures, which are sets and operations defined on these sets satisfying certain axioms.- Associative algebra
- Category theory
- Differential algebra
- Field theory
- Group theory
- Homological algebra
- K-theory
- Lattice theory(Order theory)
- Lie algebra
- Linear algebra(Vector space)
- Multilinear algebra
- Non-associative algebra
- Representation theory
- Ring theory
- Universal algebra- Analysis
Calculus and Analysis - Studies the computation of limits, derivatives, and integrals of functions of real numbers, and in particular studies instantaneous rates of change.- Complex analysis
- Functional analysis
- Harmonic analysis
- Non-standard analysis
- Ordinary differential equations
- p-adic analysis
- Partial differential equations
- Real analysis
Probability theory is the formalization and study of the mathematics of uncertain events or knowledge. The related field of mathematical statistics develops statistical theory with mathematics.Statistics, the science concerned with collecting and analyzing data,- Ergodic theory
Study of spatial figures like circles and cubes.
Topology developed from geometry; it looks at those properties that do not change even when the figures are deformed by stretching and bending, like dimension- Affine geometry
- Algebraic geometry
- Algebraic topology
- Convex geometry
- Differential topology
- Discrete geometry
- Finite geometry
- Galois geometry
- General topology
- Geometric topology
- Integral geometry
- Noncommutative geometry
- Non-Euclidean geometry
- Projective geometry- Number theory
Studies natural, whole and prime numbers.- Algebraic number theory
- Analytic number theory
- Arithmetic combinatorics
- Geometric number theory Applied mathematics
- Approximation theory
- Combinatorics(outline)
Study of discrete (and usually finite) objects
- Enumerative combinatorics
Counting the objects satisfying certain criteria
- Combinatorial designs and matroid theory
Deciding when the criteria can be met, and constructing and analyzing objects meeting the criteria
- External combinatorics and combinatorial optimization
Finding "largest", "smallest", or "optimal" objects
- Algebraic combinatorics
Finding algebraic structures these objects may have- Coding theory- Cryptography
A differential equation is an equation involving an unknown function and its derivatives- Chaos theory
Game theory is a branch of mathematics that uses models to study interactions with formalized incentive structures ("games").- Graph theory
Operations research is the study and use of mathematical models, statistics and algorithms to aid in decision-making, typically with the goal of improving or optimizing performance of real-world systems.- Assignment problem
- Decision analysis
- Dynamic programming
- Inventory theory
- Linear programming
- Mathematical optimization
- Optimal maintenance
- Real options analysis
- Scheduling
- Stochastic processes
- Systems analysis- Statistics(outline)
- Theory of computation
Study of algorithms and data structures- Computational complexity theory- Information theory and signal processing
Quantification of information (fundamental limits on compressing and reliably communicating data)
Processing signals (filtering, storage and reconstruction, separation of information from noise, compression, and feature extraction)
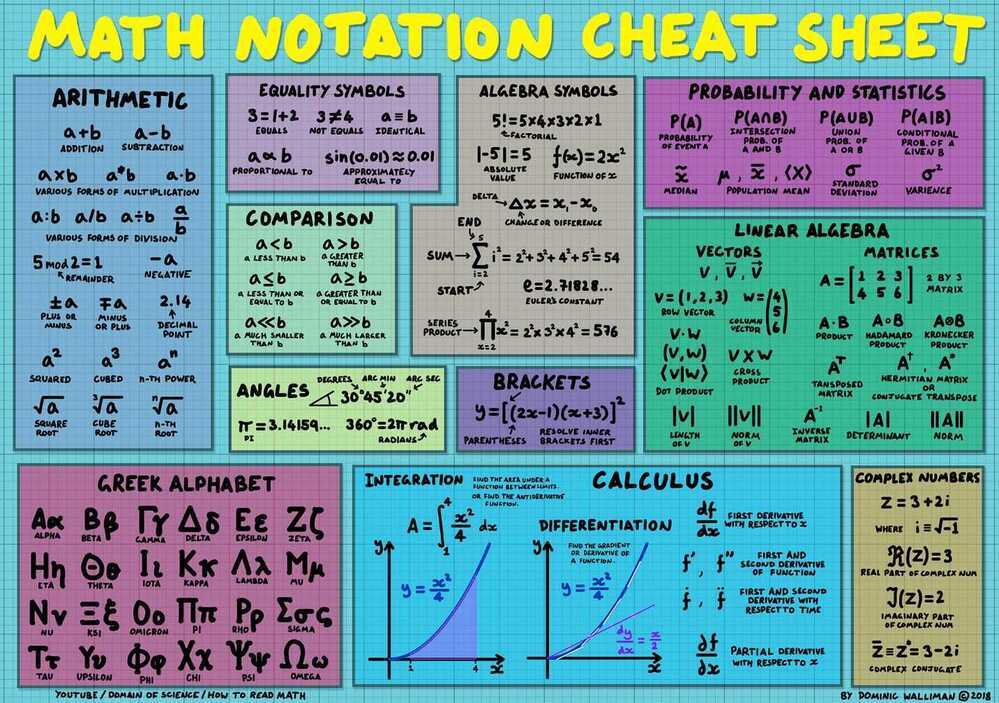
References
A few of the best math explainers from this summer
How a Computer Broke a 50-Year Math Record - YouTube
The hidden networks of everything | Albert-László Barabási - YouTube
How can maths help us make better predictions? - with Kit Yates - YouTube